TO FIND
THE INDUCTANCE
OF
RF COILS
1.
Connect
a
low value
capacitor
across the unknown inductor;
for example
100
pF.
2. Use
the Dip Meter in the
injection
mode.
3. By trial and
error, find
a coil that will dip on
the resonant frequency of
the parallel
circuit. Record
the
frequency.
4. Compute the
inductance
of the coil with the following
formula:
1
39.48
xfxC
1
nH
=
10"
6
henries
1 mH
=
1fJ
3
henries
TO FIND THE INDUCTANCE
OF TOROID COILS
The previous
steps cannot
be applied
to toroid coils because they have
self-shielding properties.
However,
these coil values may
be
determined
in the
following manner:
1 .
Use the Dip Meter in the injection mode.
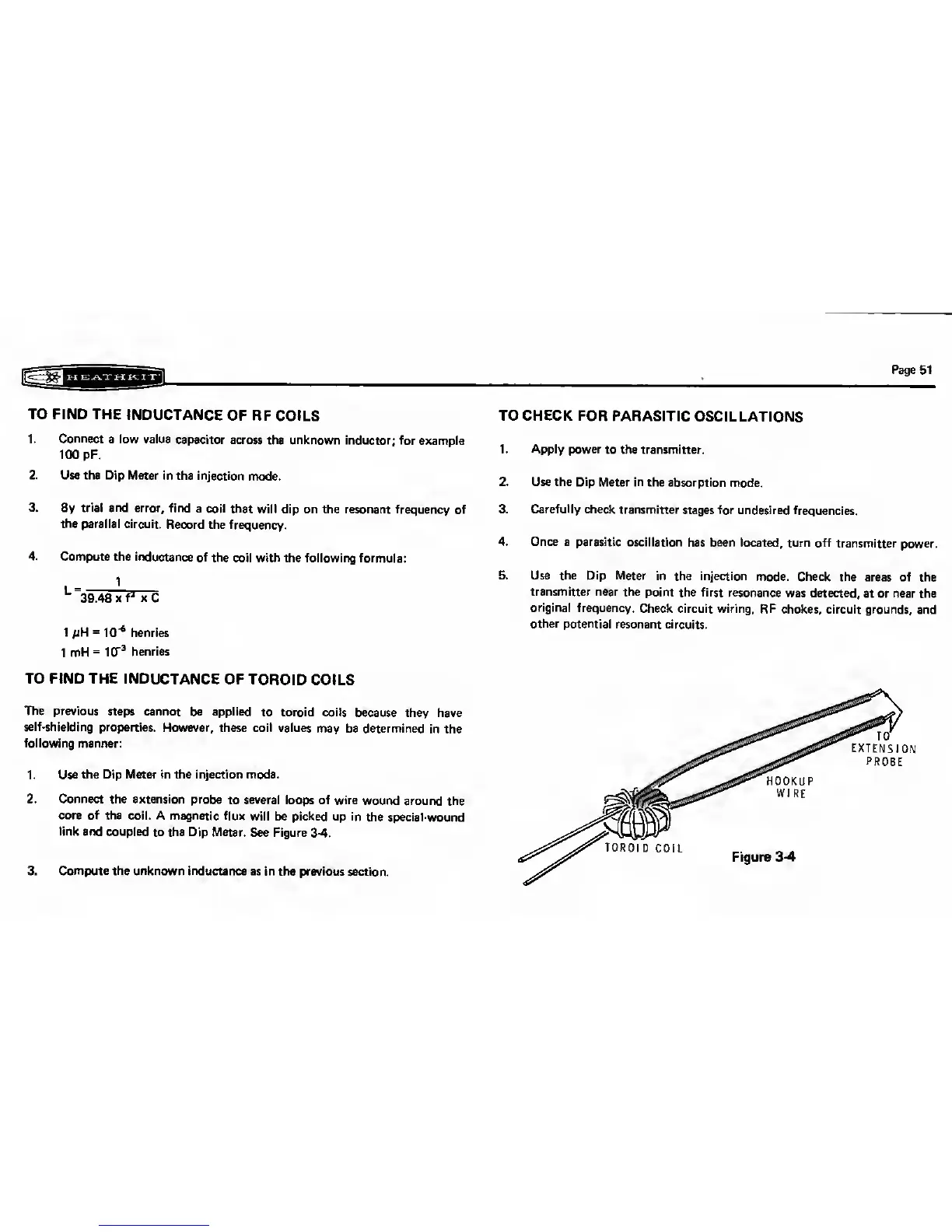
2. Connect
the extension probe
to several loops of
wire wound around
the
core
of
the coil. A
magnetic flux will
be picked up in the
special-wound
link and
coupled
to
the
Dip Meter. See Figure
3-4.
3. Compute the unknown inductance
as in the previous
section.
TO
CHECK FOR PARASITIC
OSCILLATIONS
1.
Apply
power to the transmitter.
2. Use the Dip Meter in
the absorption mode.
3.
Carefully
check transmitter
stages for
undesired frequencies.
4.
Once
a parasitic oscillation
has been located,
turn off transmitter
power.
5. Use the Dip Meter in
the injection mode.
Check the areas of
the
transmitter near
the point
the
first
resonance
was detected, at or near the
original frequency.
Check circuit wiring,
RF chokes,
circuit grounds, and
other potential resonant
circuits.

 Loading...
Loading...