228
Configuring MPLS L3VPN
This chapter describes only MPLS L3VPN related information. For information about basic MPLS
configuration, see "Configuring basic MPLS." F
or information about BGP, see Layer 3—IP Routing
Configuration Guide.
The term "router" in this chapter represents both routers and Layer 3 switches.
MPLS L3VPN overview
MPLS L3VPN is a PE-based L3VPN technology. It uses BGP to advertise VPN routes and uses MPLS to
forward VPN packets over service provider backbones.
MPLS L3VPN provides flexible networking modes, excellent scalability, and convenient support for MPLS
QoS and MPLS TE.
MPLS L3VPN comprises the following types of devices:
• Customer edge device—A CE resides on a customer network and has one or more interfaces
directly connected to service provider networks. It can be a router, a switch, or a host. It can neither
"sense" the presence of any VPN nor does it need to support MPLS.
• Provider edge device—A PE resides at the edge of a service provider network and connects one or
more CEs. On an MPLS network, all VPN services are processed on the PEs.
• Provider device—A P device is a core device on a service provider network. It is not directly
connected to any CE. It has only basic MPLS forwarding capability.
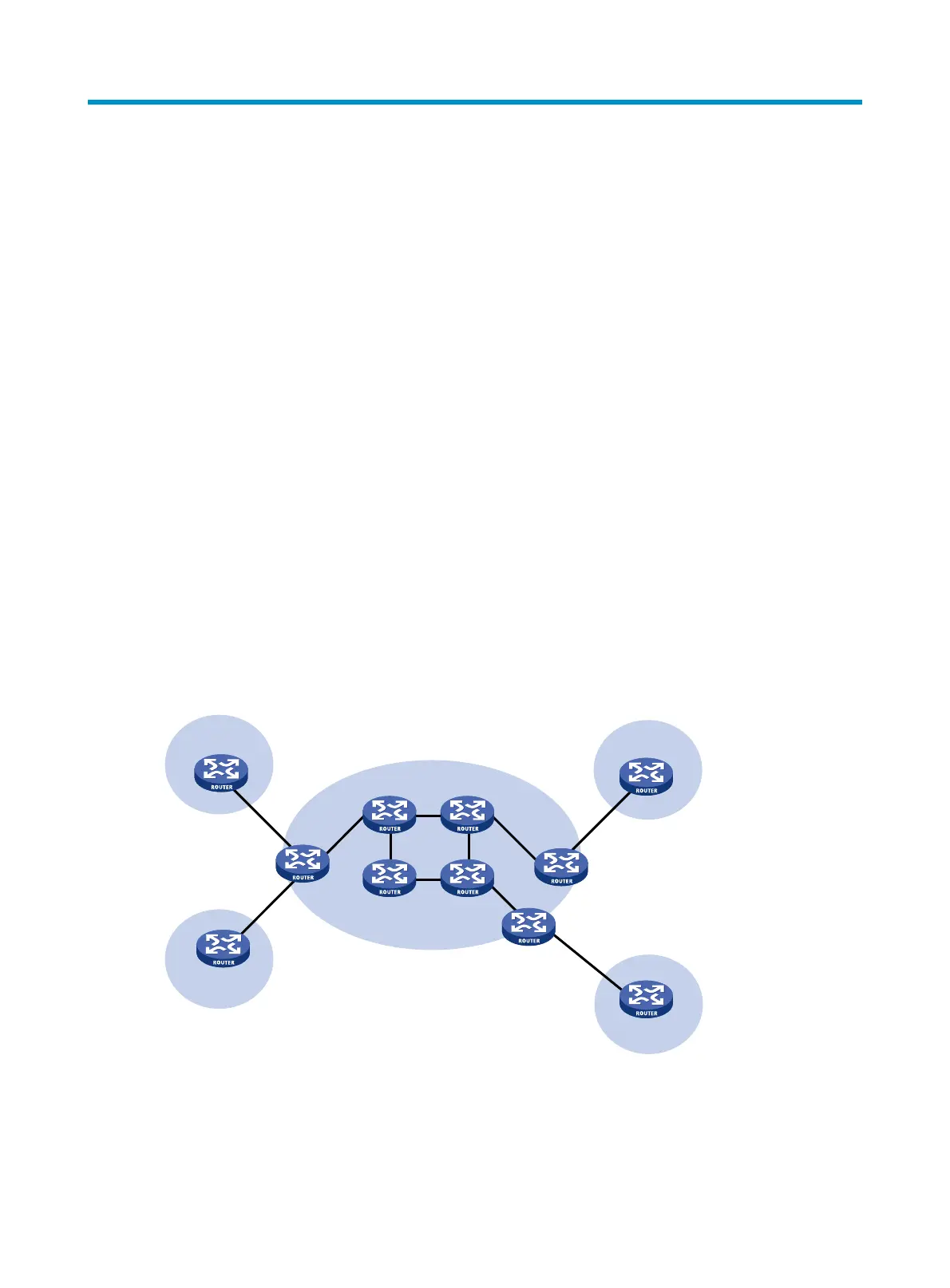
Figure 13 Network diagram for MPLS L3VPN model
CEs and PEs mark the boundary between the service providers and the customers.
After a CE establishes an adjacency with a directly connected PE, it advertises its VPN routes to the PE
and learns remote VPN routes from the PE. A CE and a PE can use BGP, an IGP, or static routing to
exchange routing information.
VPN 1
CE
Site 1
VPN 2
CE
CE
CE
Site 3
VPN 2
PE
VPN 1
Site 2
Site 4
PE
PE
PP
P
P

 Loading...
Loading...