101
Section 9
Subroutines
When the same set of instructions needs to be used at more than one
point in a program, memory space can be conserved by storing those
instructions as a single subroutine.
The Mechanics
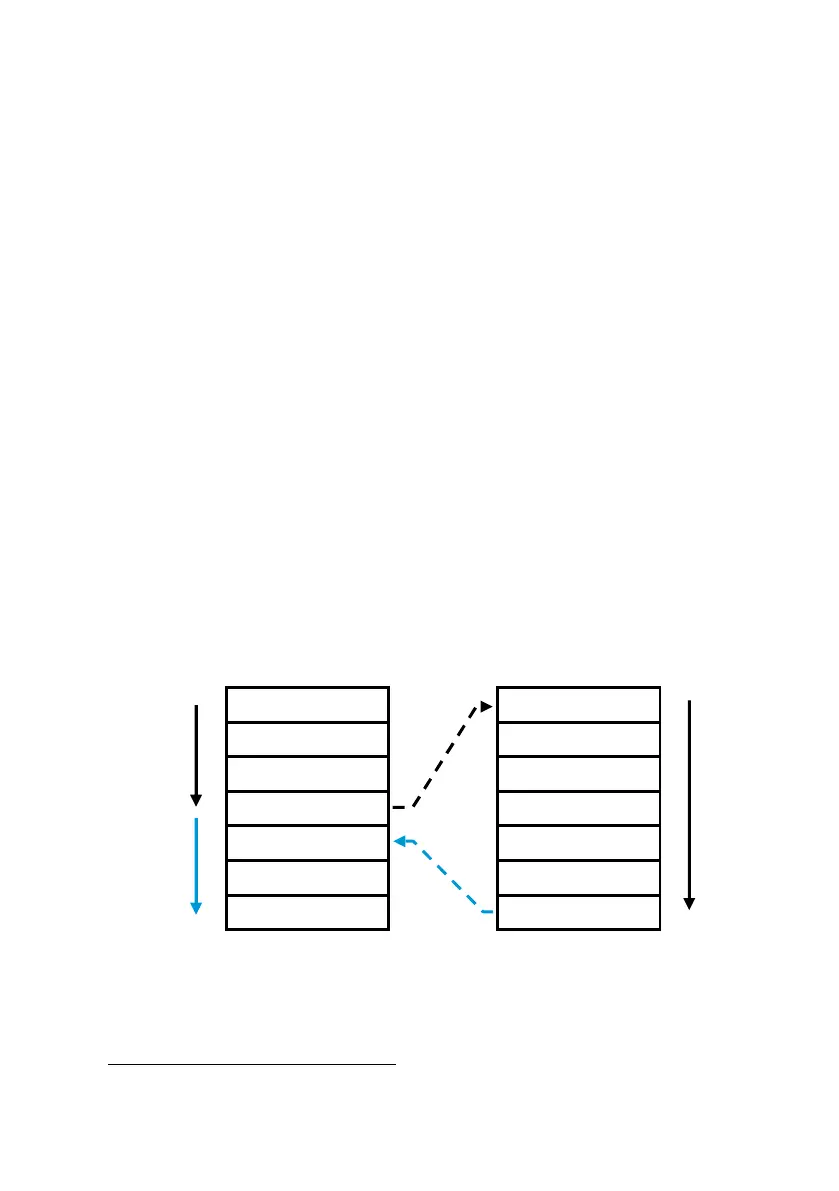
Go To Subroutine and Return
The G (go to subroutine) instruction is executed in the same way as
the t
branch, with one major difference: it establishes a pending
return condition. G label, like t label,
*
transfers program
execution to the line with the corresponding label (A to E, 0 to 9, or
.0 to .9). However, execution then continues until the first subsequent
n instruction is encountered—at which point execution transfers
back to the instruction immediately following the last G instruction,
and continues on from there.
Subroutine Execution
´ b A
´ b . 1
G . 1
| n
| n
END
RETURN
Execution transfers to line 000
and halts.
Execution transfers back to
original routine after G . 1.
*
A G or t instruction followed by a letter label is an abbreviated key sequence
(no ´ necessary). Abbreviated key sequences are explained on page 78.

 Loading...
Loading...