Section 12: Calculating with Matrices 169
6. Press ´ > 2 to transform A
P
into Ã.
7. Designate the result matrix; it must not be the same as the matrix
representing A.
8. Press ÷; this calculates X
P
. The values of these matrix elements
are placed in the result matrix, and the descriptor of the result
matrix is placed in the X-register.
9. If you want the solution in the form X
C
, press | c.
Note that you don’t transform B
P
into B.
You can derive the complex elements of the solution X by recalling the
elements of X
P
or X
C
and combining them according to the conventions
described earlier.
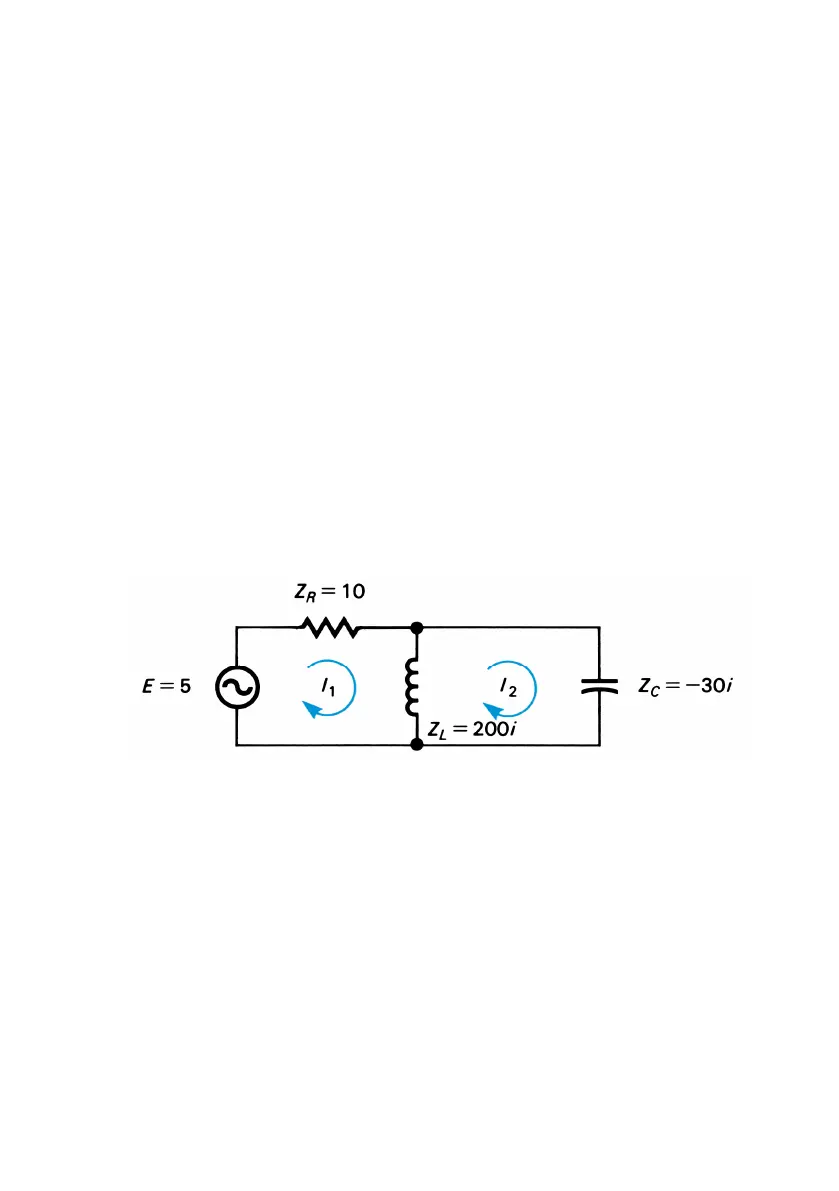
Example: Engineering student A. C. Dimmer wants to analyze the
electrical circuit shown below. The impedances of the components are
indicated in complex form. Determine the complex representation of the
currents I
1
and I
2
.
This system can be represented by the complex matrix equation
10+200i −200i
−200i 200−30i
I
1
I
2
=
5
0
 Loading...
Loading...