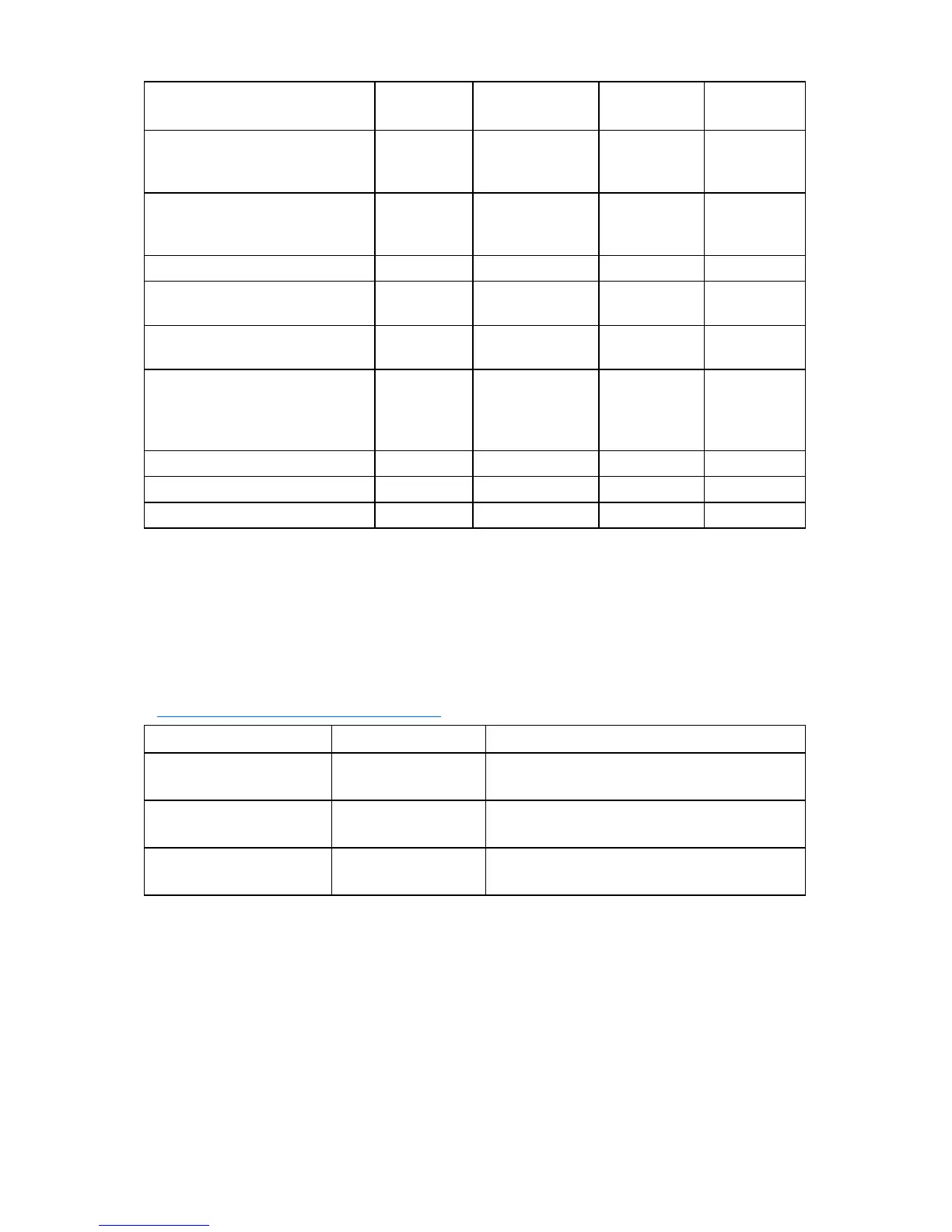
Drive arrays and fault-tolerance methods 103
Item RAID 0 RAID 1+0 RAID 5
RAID 6
(ADG)
Alternative name
Striping (no
fault
tolerance)
Mirroring
Distributed
Data
Guarding
Advanced
Data
Guarding
Formula for number of drives
usable for data (n = total number
of drives in array)
n n/2 n-1 n-2
Fraction of drive space usable* 100% 50% 67% to 93% 50% to 96%
Minimum number of physical
drives
1 2 3 4
Tolerates failure of one physical
drive
No Yes Yes Yes
Tolerates simultaneous failure of
more than one physical drive
No
Only if no two
failed drives are
in the same
mirrored pair
No Yes
Read performance High High High High
Write performance High Medium Low Low
Relative cost Low High Medium Medium
*Values for the fraction of drive space usable are calculated with these assumptions: (1) all physical drives in the
array have the same capacity; (2) online spares are not used; (3) no more than 14 physical drives are used per array
for RAID 5; and (4) no more than 56 drives are used with RAID 6 (ADG).
Selecting a RAID method
Some controllers do not support RAID 50, RAID 6, or RAID 60. To determine the RAID capabilities of your
controller, see the model-specific information for your controller on the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/products/smartarray
).
Most important criterion Also important Suggested RAID level
Fault tolerance Cost effectiveness
I/O performance
RAID 6
RAID 1+0, RAID 50, RAID 60
Cost effectiveness Fault tolerance
I/O performance
RAID 6
RAID 5 (RAID 0 if fault tolerance is not required)
I/O performance Cost effectiveness
Fault tolerance
RAID 5 (RAID 0 if fault tolerance is not required)
RAID 1+0, RAID 50, RAID 60
Alternative fault-tolerance methods
Your operating system may also support software-based RAID or controller duplexing.
• Software-based RAID resembles hardware-based RAID, except that the operating system works with
logical drives as if they were physical drives. To protect against data loss caused by physical drive
failure, each logical drive must be in a different array from the others.

 Loading...
Loading...