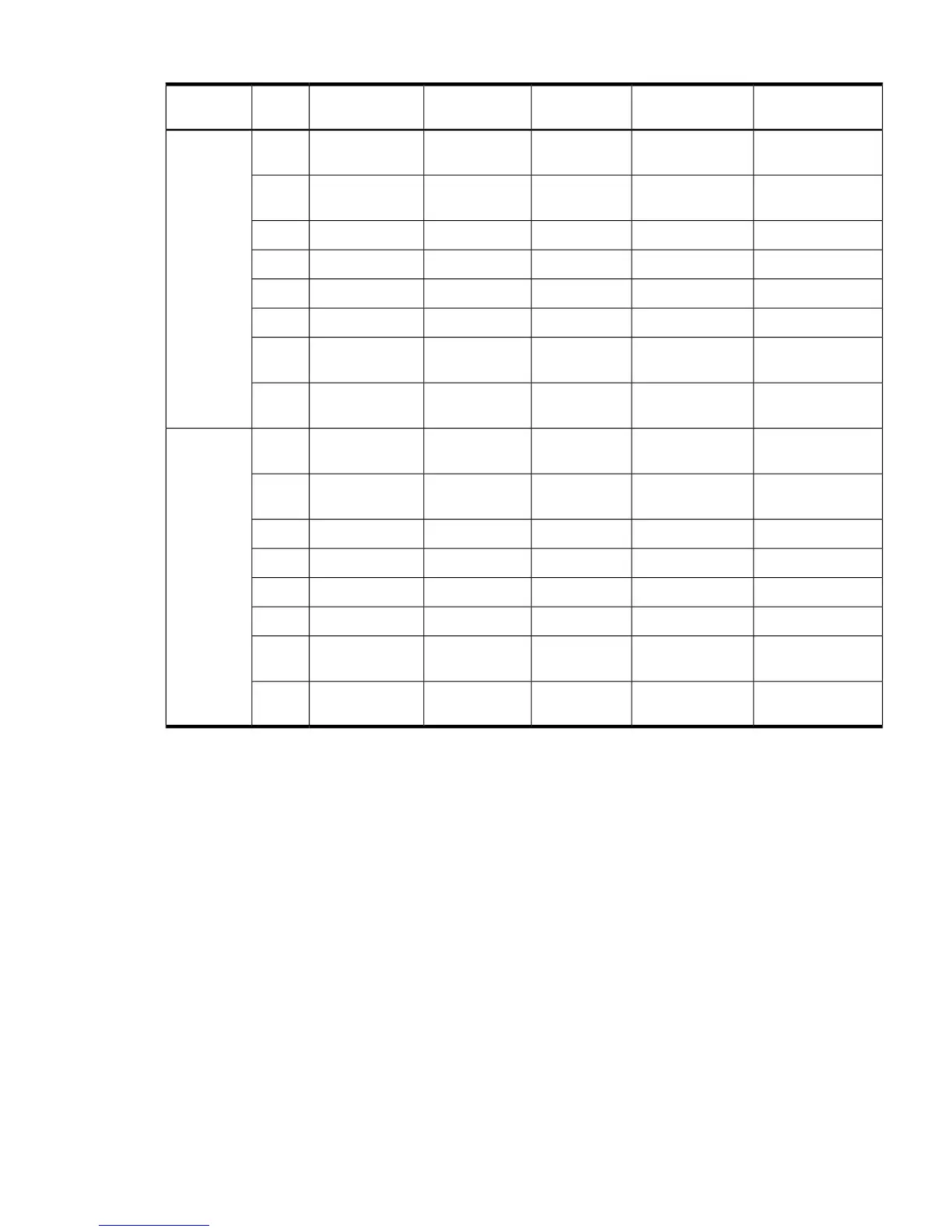
Table 1-5 PCI-X Slot Types
PCI Mode SupportedSupported CardsRopesMaximum Peak
Bandwidth
Maximum MHzSlot
1
I/O Partition
PCI or PCI-X Mode
1
3.3 V001533 MB/s13380
PCI or PCI-X Mode
1
3.3 V002/0031.06 GB/s1337
PCI-X Mode 23.3 V or 1.5 V004/0052.13 GB/s2666
PCI-X Mode 23.3 V or 1.5 V006/0072.13 GB/s2665
PCI-X Mode 23.3 V or 1.5 V014/0152.13 GB/s2664
PCI-X Mode 23.3 V or 1.5 V012/0132.13 GB/s2663
PCI or PCI-X Mode
1
3.3 V010/0111.06 GB/s1332
PCI or PCI-X Mode
1
3.3 V008/0091.06 GB/s1331
PCI or PCI-X Mode
1
3.3 V001533 MB/s13381
PCI or PCI-X Mode
1
3.3 V002/0031.06 GB/s1337
PCI-X Mode 23.3 V or 1.5 V004/0052.13 GB/s2666
PCI-X Mode 23.3 V or 1.5 V006/0072.13 GB/s2665
PCI-X Mode 23.3 V or 1.5 V014/0152.13 GB/s2664
PCI-X Mode 23.3 V or 1.5 V012/0152.13 GB/s2663
PCI or PCI-X Mode
1
3.3 V010/0111.06 GB/s1332
PCI or PCI-X Mode
1
3.3 V008/0091.06 GB/s1331
1 Each slot will auto select the proper speed for the card installed up to the maximum speed for the slot. Placing high
speed cards into slow speed slots will cause the card to be driven at the slow speed.
PCI-X/PCIe Backplane
The 16–slot (8 PCI and PCI-X; 8 PCI-Express) mixed PCI-X/PCI-Express (“PCI-X/PCIe”) I/O
backplane was introduced for the Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® processor 9100 Series release and
is heavily leveraged from the PCI-X backplane design. Only the differences will be descibed
here.See “I/O Subsystem” (page 22) for common content between the two boards.
The PCI-Express I/O backplane comprises two logically independent I/O circuits (partitions) on
one physical board.
• The I/O chip in cell location zero (0) and its associated four PCI-X ASICs, four PCIe ASICs,
and their respective PCI/PCI-X/PCIe slots form PCI-Express I/O partition 0 plus core I/O.
• The I/O chip in cell location one (1) and its associated four PCI-X ASICs, four PCIe ASICs,
and their respective PCI/PCI-X/PCIe slots form PCI-Express I/O partition 1 plus core I/O.
Each PCI/PCI-X slot has a host-to-PCI bridge associated with it, and each PCIe slot has a
host-to-PCIe bridge associated with it. A dual slot hot swap controller chip and related logic is
also associated with each pair of PCI or PCIe slots. The I/O chip on either cell location 0 or 1 is a
primary I/O system interface. Upstream, the I/O chips communicate directly with the cell controller
ASIC on the host cell board via a high bandwidth logical connection known as the HSS link.When
installed in the SEU chassis within a fully configured system, the ASIC on cell location 0 connects
Detailed Server Description 25

 Loading...
Loading...