RXF ROTARY SCREW COMPRESSOR UNITS
OPERATION
070.410-IOM (JAN 12)
Page 17
• Use the [ 0 ] key to change the Delta from 10 to 1, .10 or
.01% to tune the output to the objective of 4 or 20mA.
• Press [ 3 ] on the keypad to set the output to the high
end and repeat the process in the preceding steps to set
the output to 20mA.
• Power down the panel, remove the meter and reconnect
the control wires for the EZ-Cool
™
LIOC valve as they
were removed to terminals 1 & 2 of the P11A terminal
strip of analog board #1.
Description of Proportional Band and Gain setpoints:
• Proportional Band – This setpoint determines the size
of a region either above or below the Control Setpoint.
Within this region the Proportional component of the
PID Output value is the number between 0% and 100%
that directly corresponds to the difference between the
Control Input (Actual) and the Control Setpoint (Setpoint).
Outside of this region the Proportional component is
either 100% or 0%. If the PID Action is Forward, the
Proportional Band extends above the Control Setpoint. If
the PID Action is Reverse, the Proportional Band extends
below the Control Setpoint.
• Proportional Gain - This value is calculated from the
Proportional Band setpoint and is the same value that was
entered as a Proportional Gain setpoint in the Quantum.
The control setpoint will not be achieved with propor-
tional control only. Integral control is needed to further
correct the control input to achieve the setpoint.
• Integral Gain - This setpoint controls the inuence the
Integral component exerts on the PID Output value. The
Integral component works to push the Control Input
toward the Control Setpoint by tracking the difference
between the Control Input and the Control Setpoint over
time.
• Derivative Gain - This setpoint controls the inuence
the Derivative component exerts on the PID Output value.
The Derivative component reacts to rapid changes in the
value of the Control Input by predicting the direction the
Control Input is traveling and then turning it back toward
the Control Setpoint.
Example of Proportional Only Control:
Control Input: Discharge Temperature
Control Setpoint: 150°F
Dead Band: 0°F
Proportional Band: 25
Action: Forward
• Using the chart below, as long as the control input is 155°F
the output will be at 20% with proportional control only.
Integral control will increase the output in increments,
over time, to correct the control input to the setpoint.
Control Input Output %
150°F 0%
155°F 20%
160°F 40%
165°F 60%
170°F 80%
175°F 100%
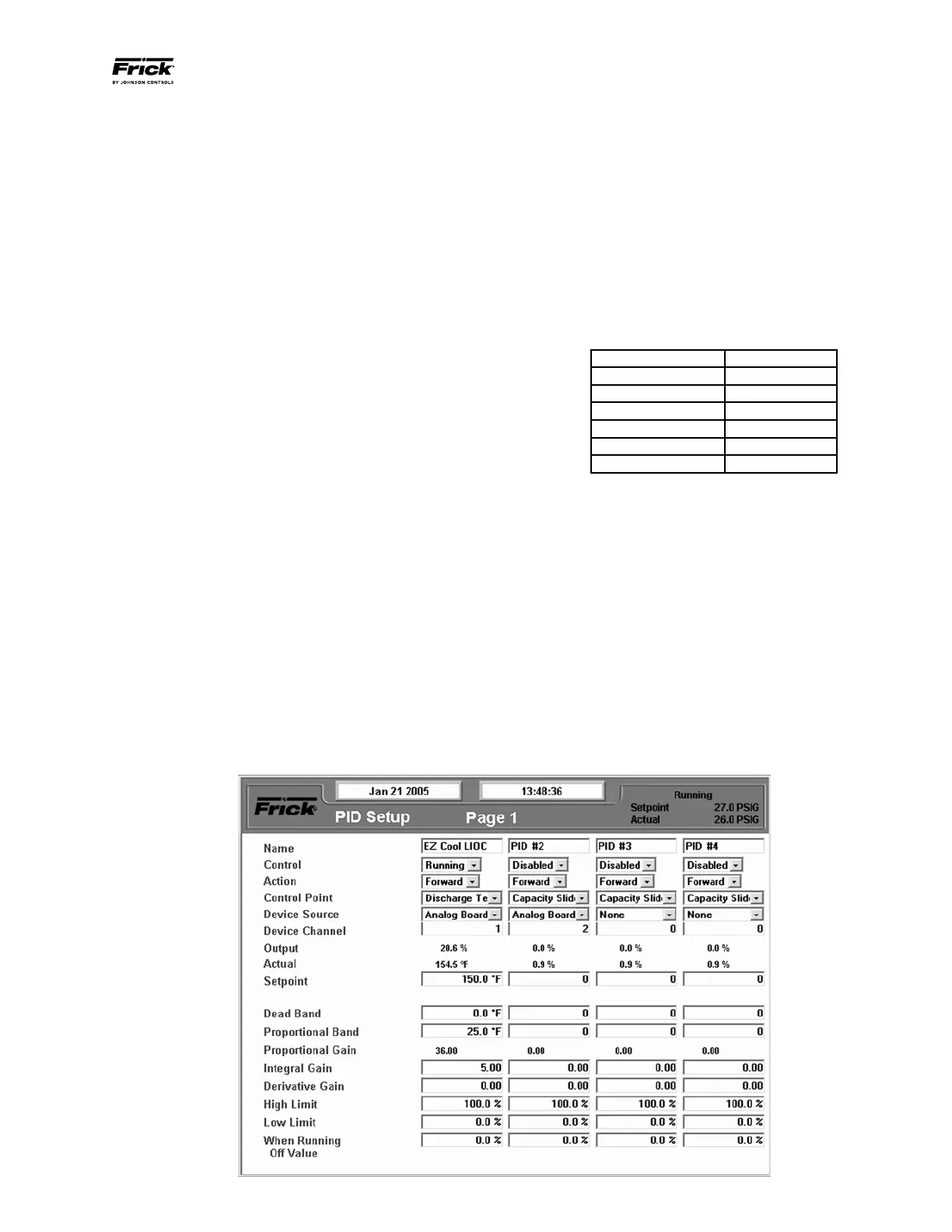
Based on these descriptions set PID #1 for EZ-Cool
™
LIOC
per Figure 22 as a starting point. Tuning of the output will be
required. There should be no need to use a derivative gain.
Notes:
1. Set the “Liquid Slugging” Alarm and Shutdown setpoints
to 90 to prevent nuisance shutdowns during the tuning
process. Be sure to return these setpoints to their original
values when nished.
2. While the discharge temperature will be the Control
Point, it reacts quickly to adjustments. Be sure to allow
an adjustment to the proportional band or integral gain
setpoints the opportunity to counter and correct the
control input (discharge temperature) before making
additional adjustments.
Figure 22

 Loading...
Loading...