342 Keysight Signal Generators Programming Guide
Creating and Downloading User–Data Files
User File Data (Bit/Binary) Downloads (E4438C and E8267D)
and the hardware reads this data repeatedly. Firmware overwrites the volatile PRAM
memory to reflect the desired configuration only when the data source or TDMA format
changes.
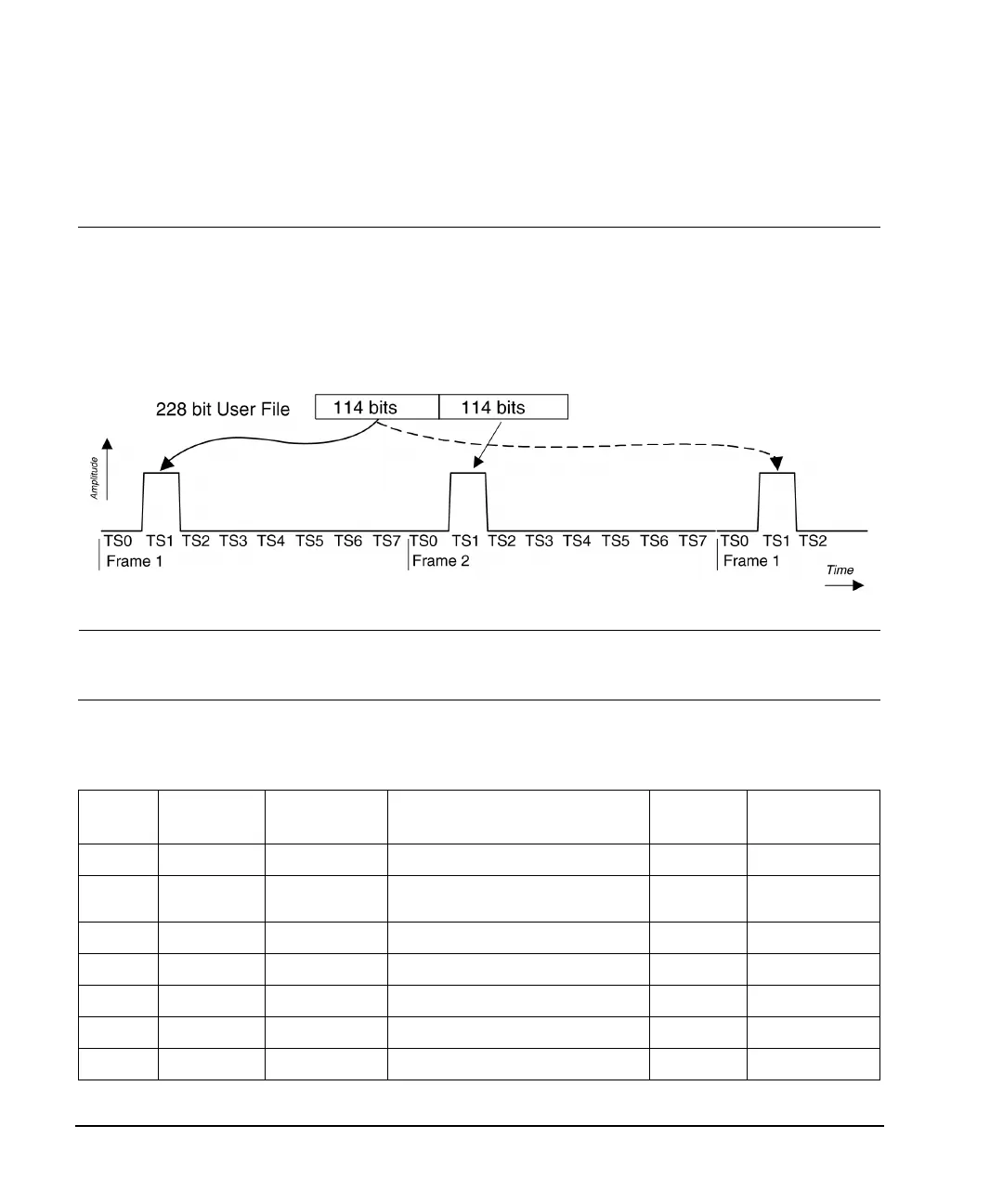
For example, transmitting a 228–bit user file for timeslot #1 (TS1) in a normal GSM transmission
creates two frames. Per the standard, a GSM normal channel is 156.25 bits long, with two 57–bit data
fields (114 user data bits total per timeslot), and 42 bits for control or signalling purposes.The user
file completely fills timeslot #1 for two consecutive frames, and then repeats. The seven remaining
timeslots in the GSM frame are off, as shown in Figure 6-2
Figure 6-2 Mapping User File Data to a Single Timeslot
NOTE Compliant with the GSM standard, which specifies 156.25–bit timeslots, the signal generator
uses 156–bit timeslots and adds an extra guard bit to every fourth timeslot.
For this protocol configuration, the signal generator’s firmware loads PRAM with the bits defined in
the following table. (These bits are part of the 32–bit word per frame bit.) The Pattern Reset bit, bit
7, is 0 for frame one and 1 for the last byte of frame two.
Frame Timeslot PRAM Word
Offset
Data Bits Burst Bits Pattern Reset Bit
1 0 0 - 155 0/1 (don’t care) 0 (off) 0 (off)
1 1 (on) 156 - 311 set by GSM standard (42 bits) & first
114 bits of user file
1 (on) 0
1 2 312 - 467 0/1 (don’t care) 0 0
1 3 468 - 624 0/1 (don’t care) 0 0
1 4 625 - 780 0/1 (don’t care) 0 0
1 5 781 - 936 0/1 (don’t care) 0 0
1 6 937 - 1092 0/1 (don’t care) 0 0

 Loading...
Loading...