3-49
IT EN
648870 IT-EN-PL (04/05/2015)
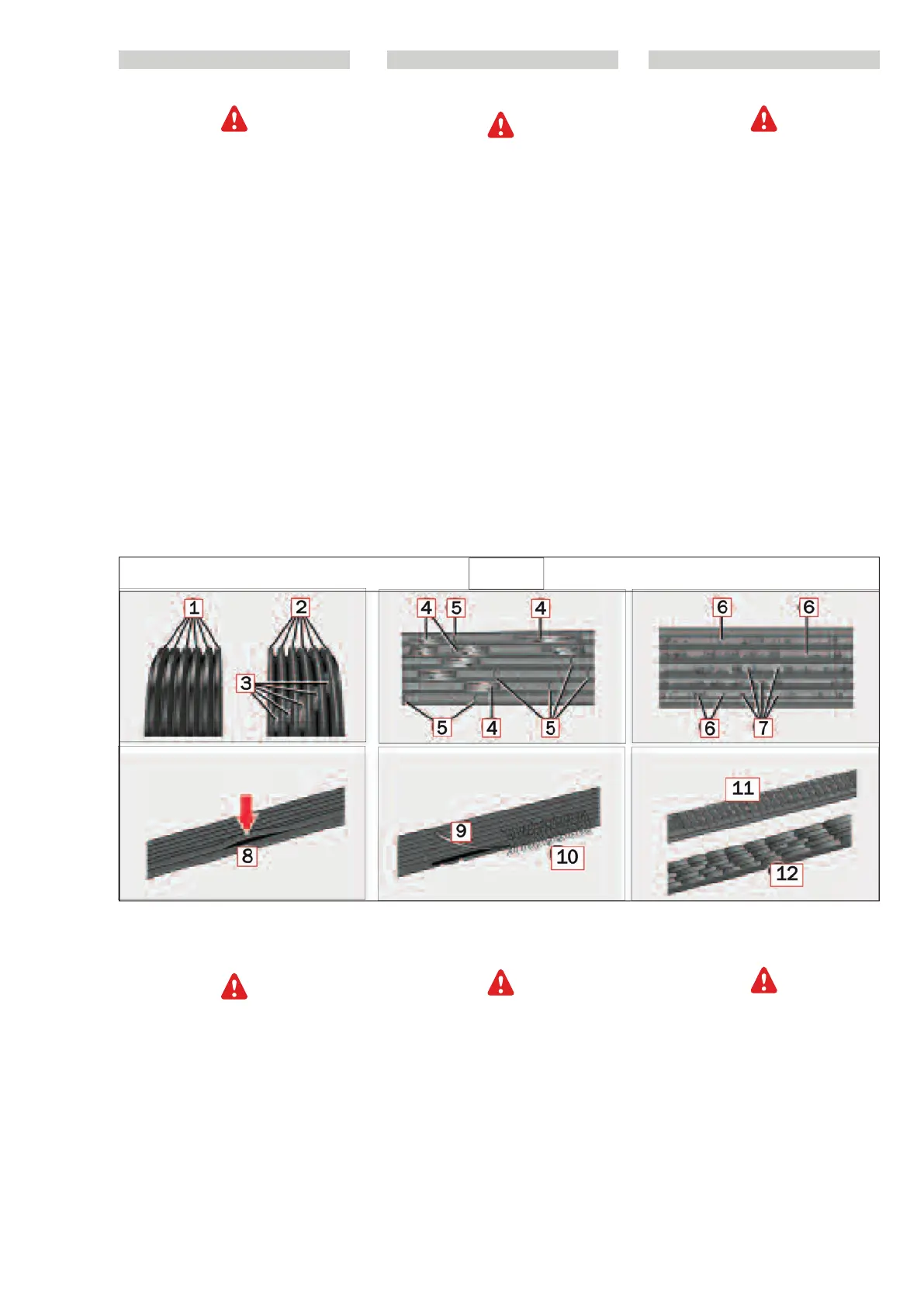
Patterns of damage
Replace the poly-V-belts if one of the
following damage patterns occurs on the
poly-V-belt. (D5/2.1)
1 – New belt (for comparison; ribbed fan
belt)
2 – Wear on the sides: wedge-shaped
ribbing
3 - Structure visible at the bottom of
theribbing
4 – Broken ribbing
5 – Transverse fissures in various ribs
6 – Rubber nodules at the bottom of the-
belt
7 – Dirt or rubble deposits
8 – Ribbing detached from the bottom of
the belt
9 – Strands of the structure torn on the
sides
10 – Outer strands of the structure frayed
11 – Transverse fissures on the dorsal side
12 – Transverse fissures in various ribs
Replacing the poly-V-belt
The tensioning device is spring-tensioned.
When it is loosened or tightened, there is
a risk of injury from crushing or entrap-
ment in pretensioned parts.
- Always carry out work on the tensioning
device with extreme care.
- Make sure that the tool is handled cor-
rectly.
D5/2.1
Configurazioni dei danni
Sostituire le cinghie trapezoidali se uno
dei seguenti tipi di danno si verifica sulla-
cinghia trapezoidale. (D5 / 2.1)
1 - Cinghia nuova (per confronto; nervatu-
re trapezoidali)
2 - Usura sui fianchi: nervature cuneiformi
3 - Struttura visibile sul fondo della ner-
vatura
4 - Rotture della nervatura
5 - Fessurazioni trasversali in diverse ner-
vature
6 - Noduli in gomma sul fondo della cing-
hia
7 - Depositi di sporco o pietrisco
8 - Nervature staccate dal fondo della
cinghia
9 - Fili della struttura strappati lateralmente
10 - Fili esterni della struttura sfrangiati
11 - Fessurazioni trasversali sul dorso
12 - Fessurazioni trasversali in diverse
nervature
Sostituzione della cinghia trapezoidale
a nervature
Il dispositivo tendicinghia è dotato di
un sistema di tensionamento a molla.
Rilasciando il dispositivo o mettendolo
in tensione sussiste il pericolo di lesioni
qualora le mani o le dita rimangano
schiacciate o incastrate tra gli elementi
precaricati.
-Si raccomanda di eseguire gli interventi
sul dispositivo tendicinghia con partico-
lare cautela.
-Prestare la massima attenzione al corret-
to utilizzo dell’attrezzo.
PL
Przykłady uszkodzenia
Jeżeli jedno z niżej wymienionych uszkod-
zeń pojawi się na pasku klinowym, należy
go wymienić. (D5 / 2.1)
1 - Pasek nowy (do porównania żebra tra-
pezowe)
2 - Zużycie na bokach: żebra trapezowe
3 - Widoczna struktura dna żeber
4 - Uszkodzenie żeber
5 - Poprzeczne pęknięcia na różnych
żebrach
6 - Gumowe kulki na dnie pasa
7 - Osady z brudu lub kamienia
8 - Żebra odłączone od dolnej warstwy
pasa
9 - Oderwane włókna na boku
10 - Wystrzępione włókna zewnętrzne
11 - Poprzeczne pęknięcia na grzbiecie
12 - Poprzeczne pęknięcia na różnych
żebrach
Wymiana paska klinowego, użebrowa-
nego
Urządzenie napinające pasek z napinac-
zem sprężynowym. Przy zwalnianiu lub
naprężaniu urządzenia istnieje ryzyko
obrażeń, jeżeli dłonie lub palce zostałyby
zaciśnięte lub „uwięzione” między wstęp-
nie obciążonymi elementami.
- Zaleca się zachować maksymalną
ostrożność podczas prac z urządzeniem
napinającym pasek.
- Zwracać uwagę na prawidłową obsługę
przyrządu.
648870 IT-EN-PL (04/05/2015)
 Loading...
Loading...









