XStream™OEMRFModule–ProductManualv5.x00[2006.02.24]
4.1. Addressing
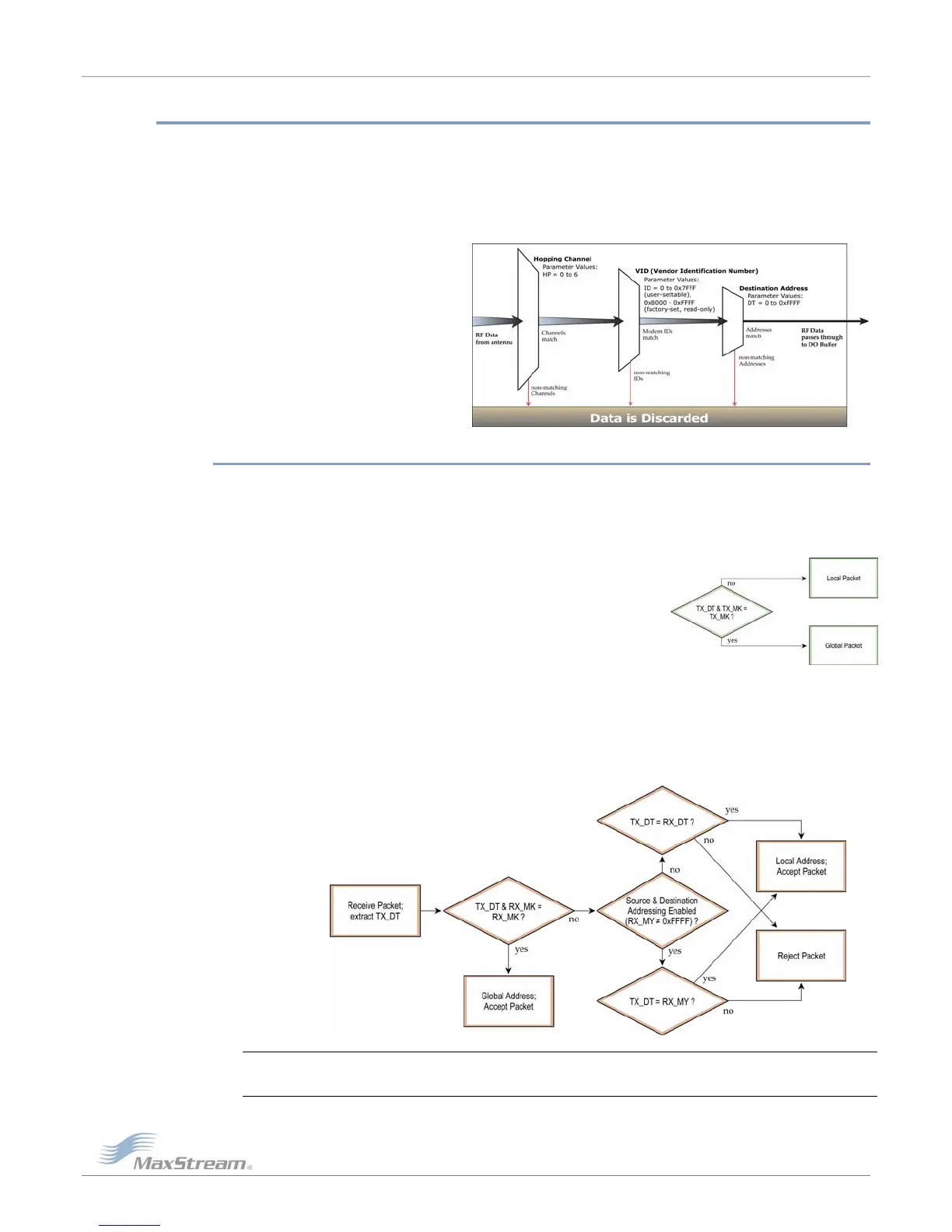
Each RF packet contains addressing information that is used to filter incoming RF data. Receiving
modules inspect the Hopping Channel (HP parameter), Vendor Identification Number (ID
parameter) and Destination Address (DT parameter) contained in each RF packet. Data that does
not pass through all three network security layers is discarded.
Figure4‐01. FiltrationlayerscontainedintheRFpacketheader
4.1.1. Address Recognition
Transmissions can be addressed to a specific module or group of modules using the DT
(Destination Address) and MK (Address Mask) parameters. The transmitting module dictates
whether the packet is intended for a specific module (local address) or multiple modules (global
address) by comparing the packet’s DT parameter to its own MK parameter.
Figure4‐02. LocalPacketsvs.GlobalPackets(TransmittingModule)
TX_DT=TransmitterDestinationAddress
TX_MK=TransmitterAddressMask
Note:WhenTX_DT=0xFFFF(default),RFpacketsareglobalandare
receivedbyallmoduleswithinrange.(ReceiversdonotsendACKs.)
A receiving module will only accept a packet if a packet is addressed to it (either as a global or
local packet). The RX module makes this determination by inspecting the destination address of
the RF packet and comparing it to its own address and mask. The Destination Address of the TX
module is logically “ANDed” with the Address Mask of the RX module.
Figure4‐03. AddressRecognition(ReceivingModule)
TX_DT=TransmitterDestinationAddress
RX_DT=ReceiverDestinationAddress
RX_MY=ReceiverSourceAddress
NOTE: For more information regarding addressing and masks, refer to Application Note ‘XST-
AN004b’. (Located on the MaxStream CD and on the web: www.maxstream.net)
©2006MaxStream,Inc.ConfidentialandProprietary 36
Downloaded from Elcodis.com electronic components distributor
 Loading...
Loading...