Page 9 of 47
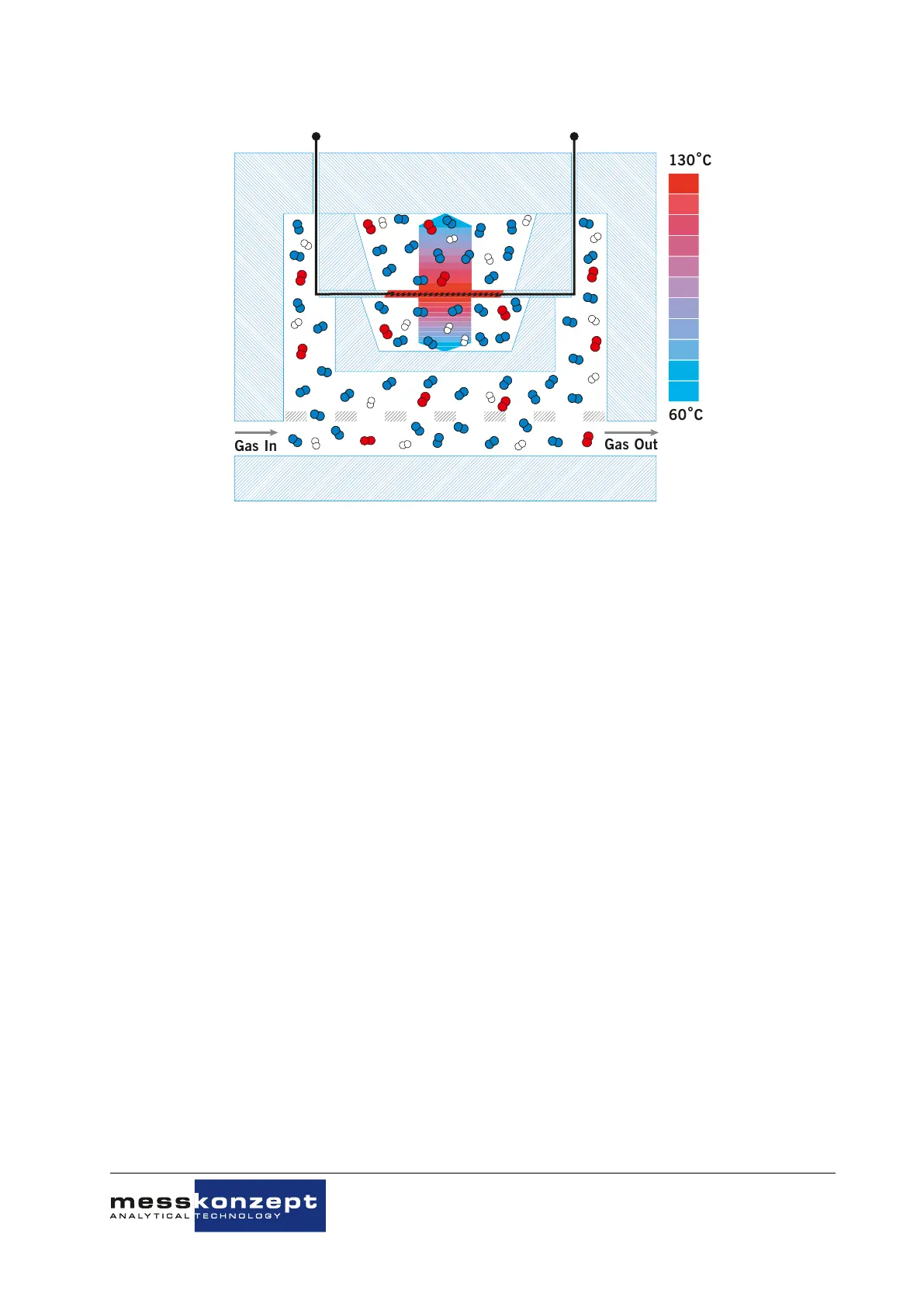
Figure 2.1: Schematic drawing of thermal conductivity measurement. The sensor is comprised in the
stainless-steel block which is kept at a constant temperature.
The FTC320 contains a thermal conductivity sensor that analyzes the quantitative composition of gas
mixtures. The measurement is based on the heat transfer between a heat source and a heat sink.
The measuring gas is led through a stainless-steel block that is kept at a constant temperature of
63
◦
C (for most applications). The block temperature is stabilized using a control loop - it serves as
a heat sink of constant temperature. A micro mechanically manufactured membrane with a thin-film
resistor serves as a heat source. A control loop stabilizes the membrane temperature at 135
◦
C (for
most applications).
Above and below the membrane two small cavities are etched into the silicon. These cavities are filled
with measuring gas by diffusion. The surfaces opposite the membrane are thermally connected with
the heat sink. Through maintaining a constant temperature gradient between the two opposite surfaces,
the heat flow is dependent on the gas mixture’s thermal conductivity alone. Hence the voltage needed
to keep the membrane temperature constant is a reliable measure for the thermal conductivity of the
mixture and can be used further to determine the gas mixture’s composition.
File name:
FTC320 Operating Manual_1.09KD201009MPO5V04.pdf
 Loading...
Loading...