Appendix C: Differences with FX2N-1PG
Appendix C-3 Differences in Operation
133
FX3U-1PG User's Manual
11
Troubleshooting
A
Version
Information
B
Example
Connection
C
Differeces with
FX
2N
-1PG
Appendix C-3-2 Differences in individual operation modes
Differences in individual operation modes of FX3U-1PG and FX2N-1PG are shown in the following table.
JOG operation
DOG type mechanical zero return operation
Interrupt 1-speed positioning operation
Change point FX3U-1PG FX2N-1PG Replacement point
Inching travel amount
The FX3U-1PG outputs pulses
corresponding to 1 user unit.
However, the FX3U-1PG outputs 1
pulse even if the value "Position data
multiplier x Pulse rate" is smaller than
the feed rate in the machine system
setting or combined system setting
and the pulse number required for the
travel in 1 user unit is less than 1
pulse.
The FX2N-1PG outputs 1 pulse.
Confirm that no problem is expected
in the system when the travel amount
generated by 1 inching operation is
large if the pulse number
corresponding to 1 user unit is larger
than 1 pulse.
Change the sequence program as
needed.
Change point FX3U-1PG FX2N-1PG Replacement point
DOG search operation when
the forward limit/reverse limit
is ON
The motor starts the DOG search
operation even when the direction of
the forward limit or reverse limit in the
ON status is the same as the zero
return direction.
The motor does not perform the
operation when the direction of the
forward pulse stop (forward limit) or
reverse pulse stop (reverse limit) in the
ON status is the same as the zero
return direction.
Confirm that no problem is expected
in the system when an error occurs at
the forward limit or reverse limit, the
zero return operation is executed
from the corresponding limit position,
and the motor reverses the operation
direction.
Change the sequence program as
needed.
Operation when the DOG
cannot be detected
The motor stops at the forward limit (or
reverse limit) and the forward limit/
reverse limit error occurs if the DOG
cannot be detected while the motor
starts the zero return operation,
reverses the operation direction at the
reverse limit (or forward limit) and then
reaches the forward limit (or reverse
limit).
The motor stops at the forward limit (or
reverse limit) but no error occurs if the
DOG cannot be detected while the
motor starts the zero return operation,
reverses the operation direction at the
reverse limit (or forward limit) and then
reaches the forward limit (or reverse
limit).
Confirm that no problem is expected
in the system when an error occurs at
the forward limit or reverse limit, the
zero return operation is executed
from the corresponding limit position,
and the motor reverses the operation
direction.
Change the sequence program as
needed.
Change point FX3U-1PG FX2N-1PG Replacement point
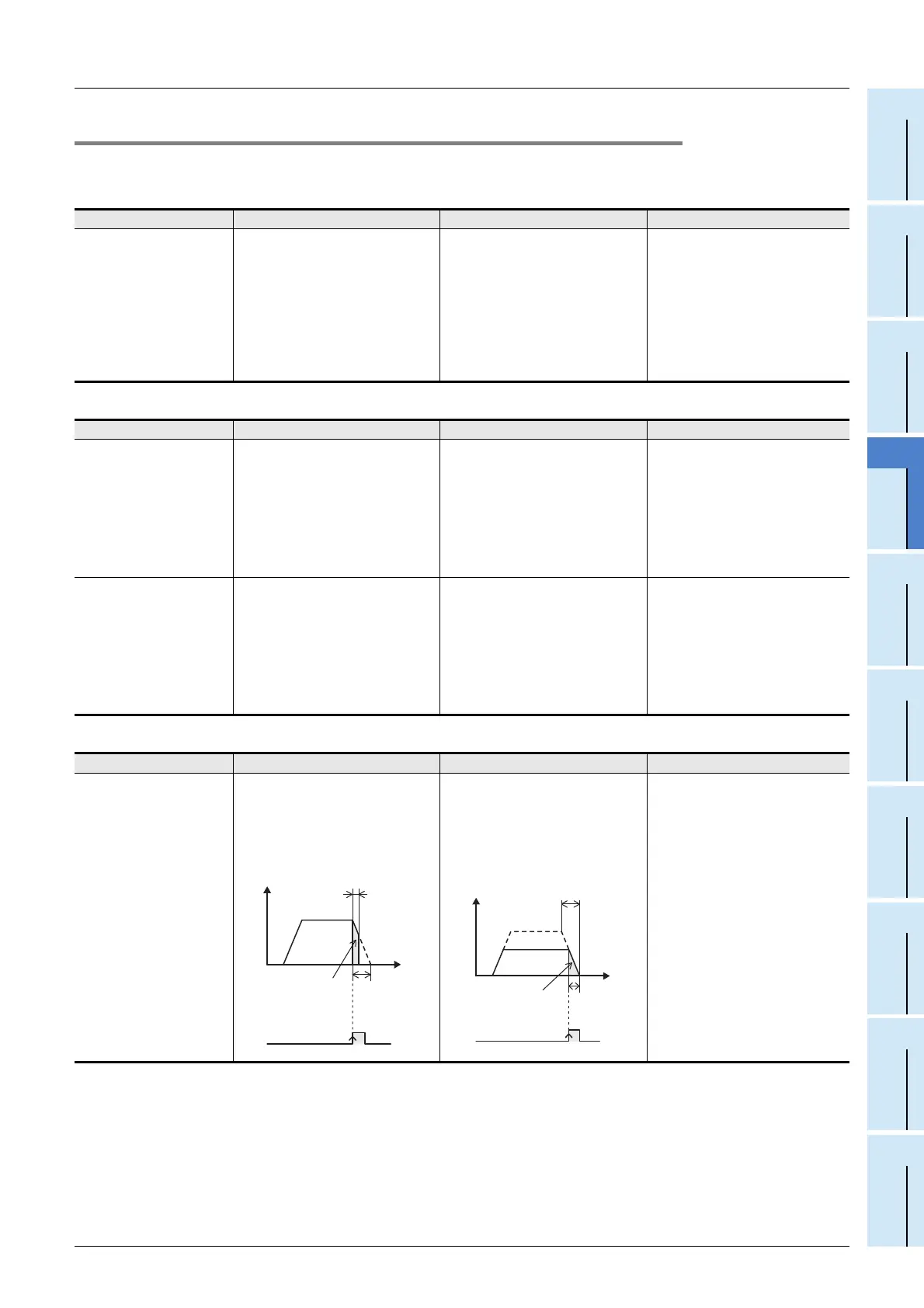
Operation when the travel
amount is small
(When the time required to
perform deceleration from
the operation speed I is
longer than the travel time)
The motor decelerates when the
interrupt input is detected, and stops at
the target address I.
The motor does not accelerate until
the operation speed I is reached, and
performs acceleration only until it
reaches a speed so as to achieve
"Travel amount during deceleration =
Target address I".
Confirm that no problem is expected
in the system when the operation
speed is different or when the travel
amount is small and the motor stops
immediately.
Change the sequence program as
needed so that the motor operation
using the FX
3U-1PG becomes the
same motor operation using the
FX2N-1PG by reducing the operation
speed I.
Speed
Time
Operation
speed I
Target address I
Travel time
Time required
for deceleration
DOG
OFF
ON
Speed
Time
Operation
speed I
Target address I
Travel time
Time required
for deceleration
DOG
OFF
ON

 Loading...
Loading...










