6 - 83 6 - 83
MELSEC-Q/QnA
6 BASIC INSTRUCTIONS
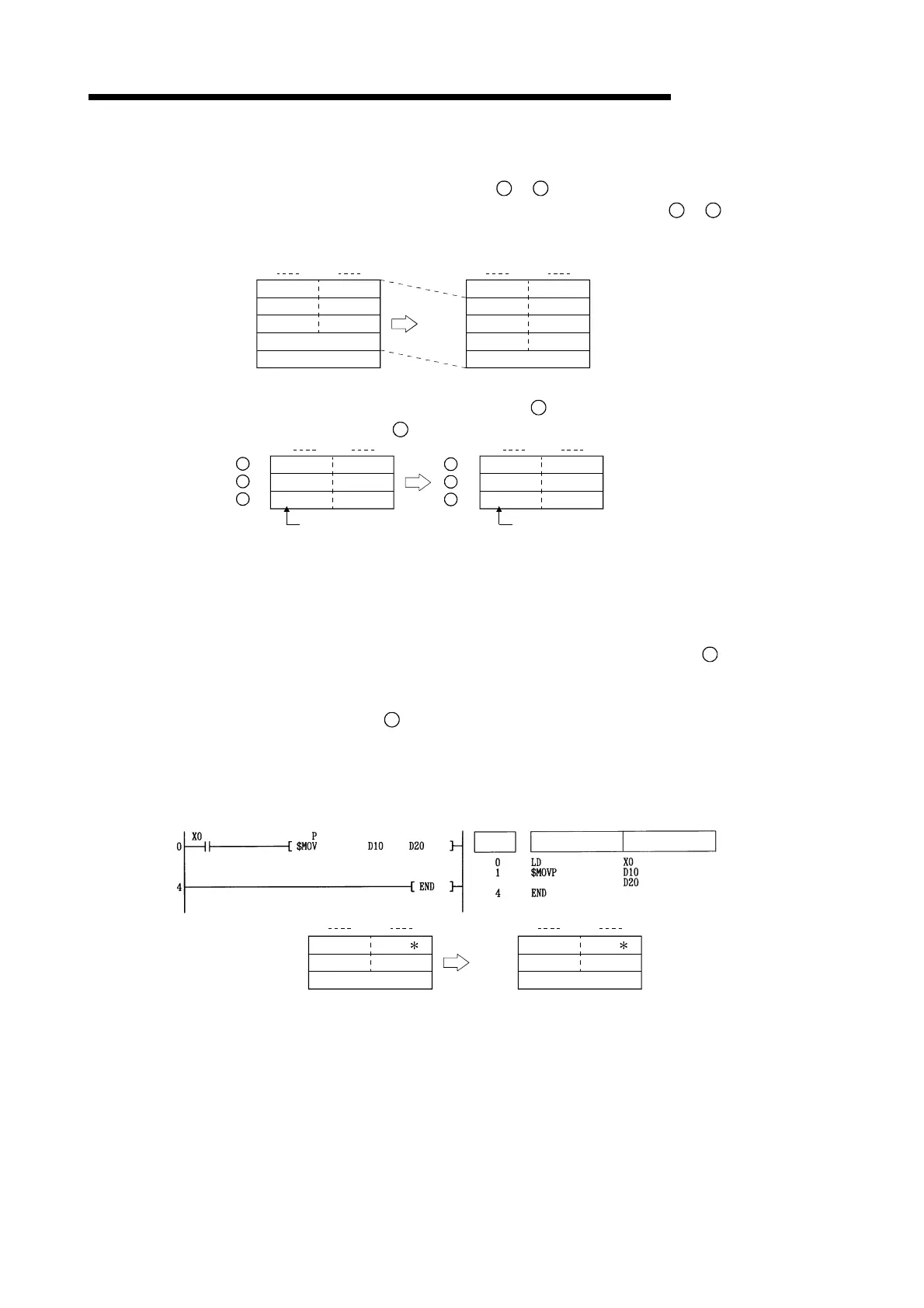
(2) Processing will be performed without error even in cases where the range for the devices
storing the character data to be transferred (
S
to
S
+n) overlaps with the range of the devices
which will store the character string data after it has been transferred (
D
to
D
+n).
The following occurs when the character string data that had been stored from D10 to D13 is
transferred to D11 to D14:
32
H
(2)
b15 b8
31
H
(1)
b7 b0
D11
31
H
(1)
33
H
(3)
32
H
(2)
00
H
34
H
(4)
D12
D13
D14
D10
35
H
(5)36
H
(6)
... Remains as the
character string
it was prior to
transfer
32
H
(2)
b15 b8
31
H
(1)
b7 b0
D11
33
H
(3)
35
H
(5)
34
H
(4)
00
H
36
H
(6)
D12
D13
D14
D10
(3) If the "00
H
" code is being stored at lower bytes of
S
+n, "00
H
" will be stored at both the higher
bytes and the lower bytes of
D
+n.
The "00
H
" code is automatically
stored at the Upper byte.
b15 b8b7 b0
+1
+2
b15 b8b7 b0
+1
+2
42
H
(B) 41
H
(A)
43
H
(C)
00
H
44
H
(D)
45
H
(E)
42
H
(B) 41
H
(A)
43
H
(C)
00
H
44
H
(D)
00
H
Upper byte is not
transferred
S
D
S
S
D
D
[Operation Errors]
(1) In the following cases an operation error occurs, the error flag (SM0) turns ON, and an error
code is stored at SD0.
• There is no "00
H
" code stored between the device number designated by
S
and the relevant
device. (Error code: 4101)
• It is not possible to store the entire designated character string in the number of points from
the device designated by
D
to the final device number cited. (Error code: 4101)
[Program Example]
(1) The character string data stored in D10 to D12 is transfered to D20 to D22 when X0 goes ON.
[Ladder Mode] [List Mode]
Device
Instruction
Steps
b15 b8b7 b0
D21
D22
D20
b15 b8 b7 b0
D11
D12
D10
4D
H
(M) 2A
H
( )
45
H
(E)45
H
(E)
00
H
4D
H
(M) 2A
H
( )
45
H
(E)45
H
(E)
00
H
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com

 Loading...
Loading...











