3 - 9 3 - 9
MELSEC-Q/QnA
3 CONFIGURATION OF INSTRUCTIONS
3.2.5 Using character string data
Character string data is character data used by basic instructions and application instructions.
It encompasses all data from the designated character to the NULL code (00
H
).
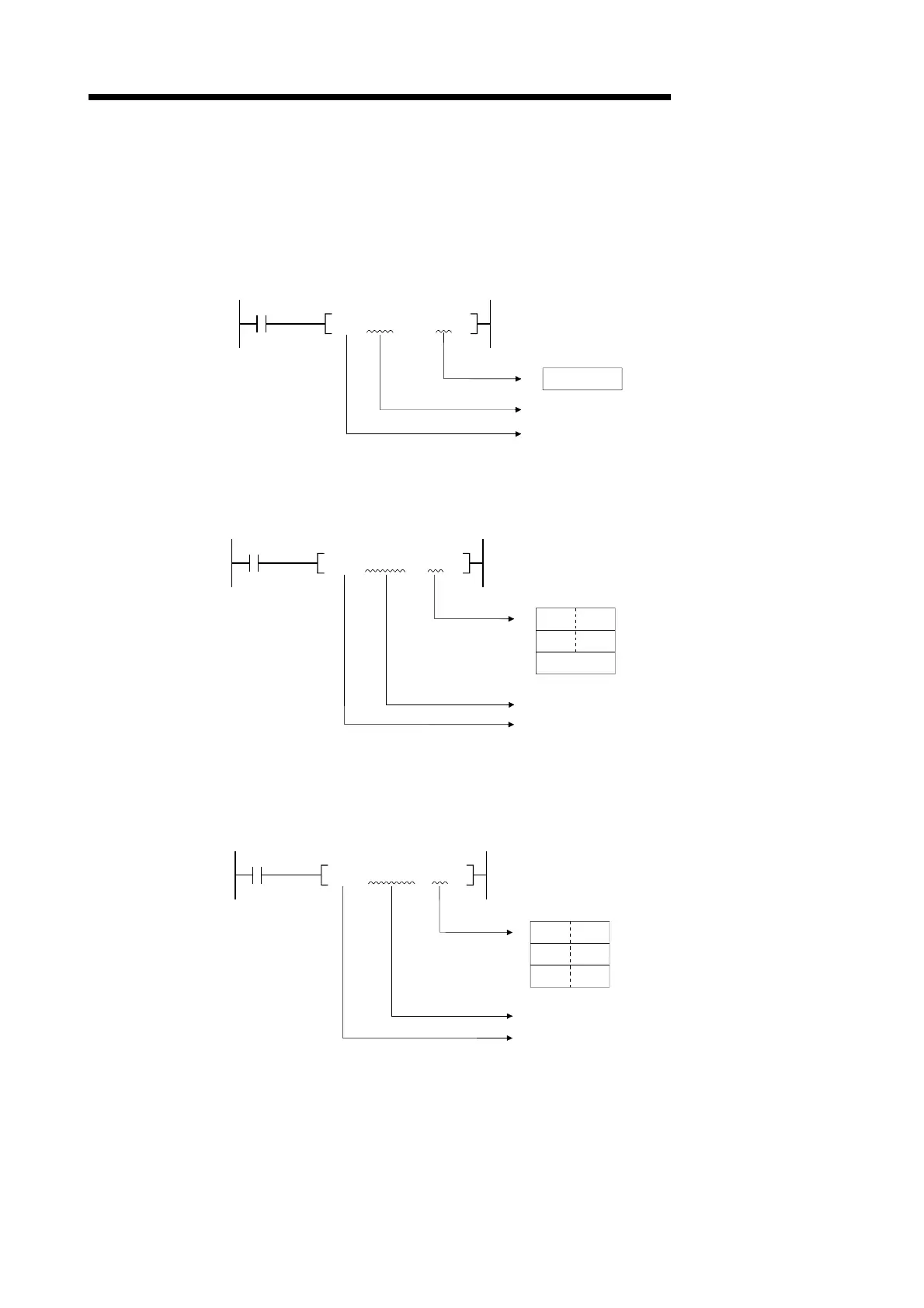
(1) When designated character is the NULL code.
One word is used to store the NULL code.
NULL code (00
H
) designation
M0
$MOV D0
Character string data transfer
D0 NULL
" "
(2) When character string is even
Uses (number of characters/2 + 1) words, and stores character string and NULL code.
For example, if "ABCD" is transferred to D0, the character string ABCD is stored at D0 and D1,
and the NULL code is stored at D2.
Designation of an even number
character string
M0
$MOV "ABCD"
D0
D0
Character string data transfer
42
H
44
H
41
H
43
H
NULL
D1
D2
(3) When number of characters is odd
Uses (number of characters/2) words (rounds up decimal fractions) and stores the character
string and NULL code.
For example, if "ABCDE" is transferred to D0, the character string (ABCDE) and the NULL
code are stored from D0 to D2.
Designation of an odd number
character string
M0
$MOV
"ABCDE"
D0
D0
Character string data transfer
42
H
44
H
41
H
43
H
NULL
D1
D2
45
H
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com

 Loading...
Loading...











