6 - 116 6 - 116
MELSEC-Q/QnA
6 BASIC INSTRUCTIONS
The count processing performed on the present value is as shown below:
-32768 -32767 -2 -1 0 1 2 3276732766
When counting up
When countin
down
(4) Count processing conducted according to the UDCNT2 instruction begins when the count
command goes from OFF to ON, and is suspended when it goes from ON to OFF.
When the count command goes from OFF to ON once again, the count is restarted from the
value in effect when it was suspended.
(5) The RST instruction clears the present value of the counter designated at
D
and turns the
contact OFF.
POINTS
(1) The UDCNT2 instruction registers the argument device data to the work area of the CPU
module and the actual counting operation is processed as a system interrupt.
(The device data registered to the work area of the CPU module are cleared when the
command input is turned OFF or when the CPU module is STOPped and then RUN.)
Therefore, to count pulses, it is necessary to provide their ON and OFF time as long as the
interrupt time of the CPU module or longer.
The interrupt time of individual CPU module is shown below:
CPU module T
e Name Interru
t Time
Hi
h Performance model QCPU, Process CPU 1ms
QnACPU 5ms
(2) The set value cannot be changed while a count operation performed according to the
UDCNT2 instruction is being executed (while the command input is ON).To change the set
value, first turn the command input off.
(3) Counters designated by the UDCNT2 instruction cannot be used by any other instruction.
If they are used by other instructions, they will not be capable of returning an accurate
count.
(4) The UDCNT2 instruction can be used as many as 5 times within all the programs being
executed.
The sixth and the subsequent UDCNT2 instructions are not processed.
[Operation Errors]
(1) There are no operation errors associated with the UDCNT2 instruction.
[Program Example]
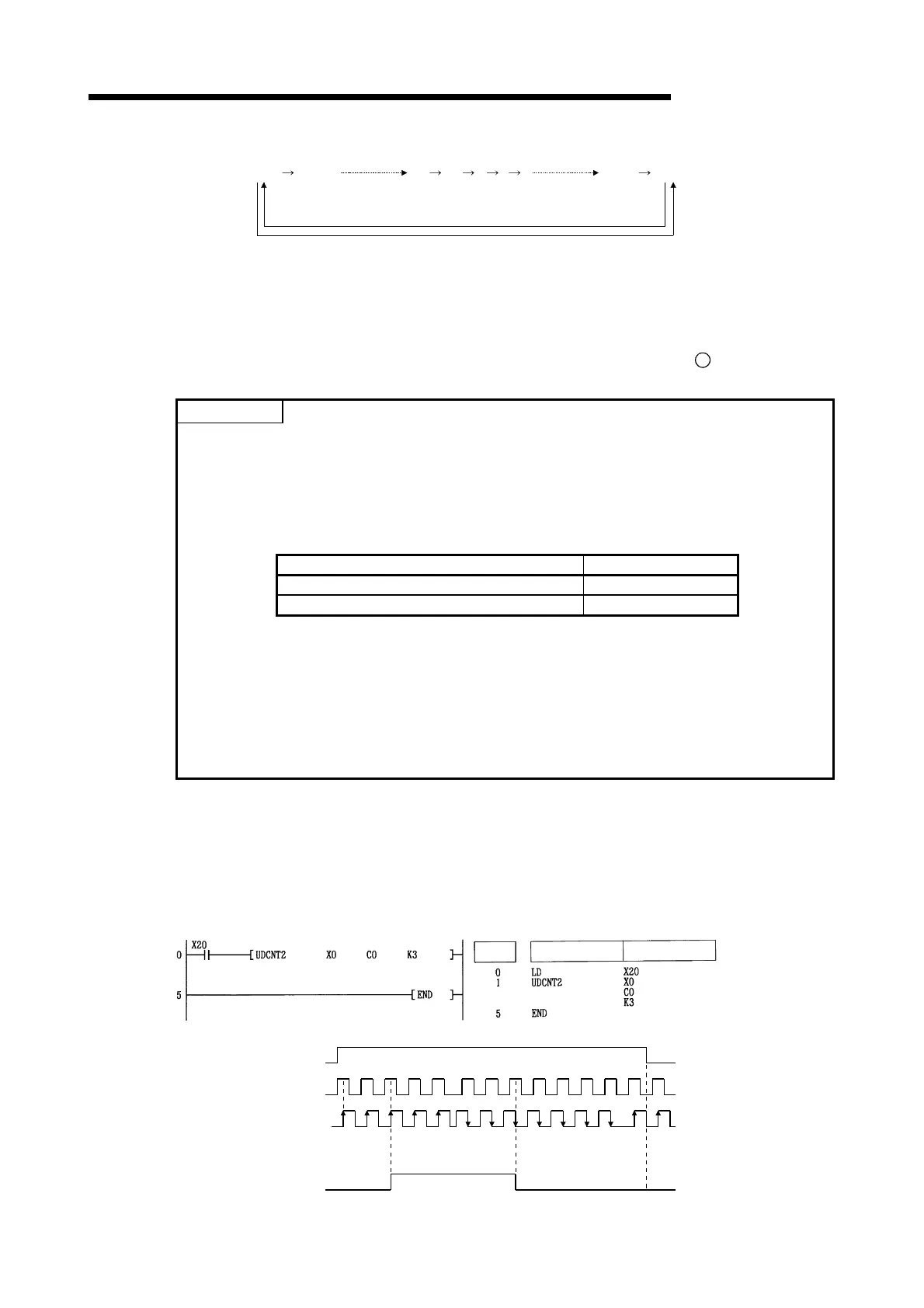
(1) The following program performs a count operation as instructed by C0 (count up or down) on
the status of X0 and X1 after X20 has gone ON.
[Ladder Mode] [List Mode]
Steps
Instruction
Device
[Operation]
X0
X20
X1
Present
value of COM
C0 contact
1
0 2345 43210
-1 -2 -1 -1
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com

 Loading...
Loading...











