3 - 14 3 - 14
MELSEC-Q/QnA
3 CONFIGURATION OF INSTRUCTIONS
(2) Devices Capable of Indirect Designation
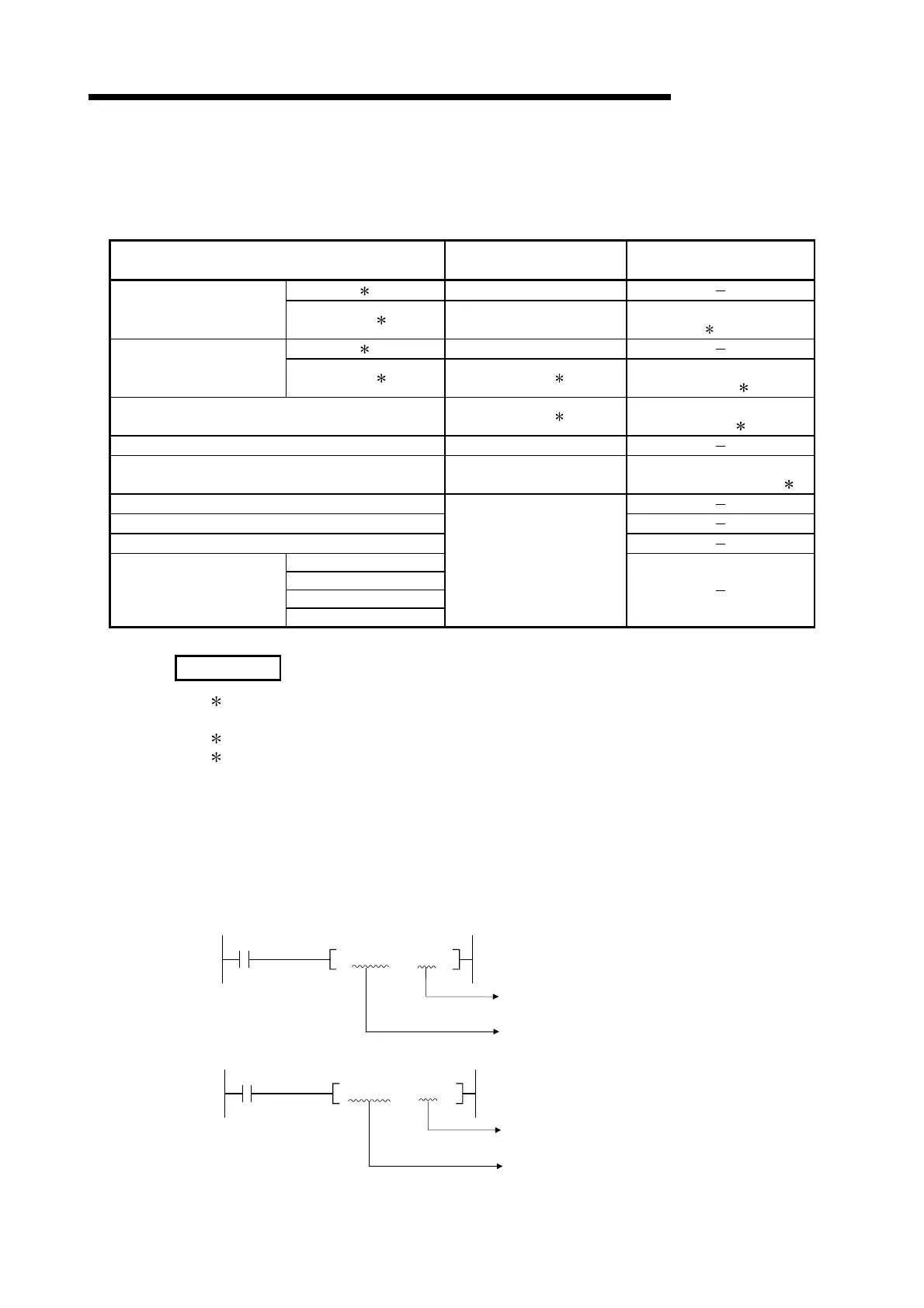
The CPU module devices that can be designated indirectly is shown in Table 3.3.
Table 3.3 List of Devices Capable of Indirect Designation
Device Type
Capable/Incapable of
Indirect Designation
Example of Indirect
Designation
Bit devices 1 Incapable
Internal user devices
Word devices
1 Capable
• @D100
• @D100Z2
2
Bit devices 1 Incapable
Link direct devices
Word devices
1 Capable 3
• @J1\W10
• @J1Z1\W10Z2
2
Special direct devices Capable 3
• @U10\G0
• @U10Z1\G0Z2
2
Index register Incapable
File register Capable
• @R0, @ZR20000
• @R0Z1, @ZR20000Z1
2
Nesting
Pointer
Constants
SFC block devices
Devices below SFC
Network No.
Other
I/O No.
Incapable
REMARKS
1) 1: Refer to the User's Manual (Functions Explanation, Programming Fundamentals) of the
used CPU module or QnACPU Programming Manual (Fundamentals) for device names.
2)
2: Indicates index modification by index register
3)
3: The device can be designated indirectly, however the address cannot be written in the
ADRSET instruction.
(3) Cautions
The address for indirect designation is designated using two words.
Therefore, to substitute indirect designation for index modification, the addition/subtraction of
32-bit data is required.
The following is the ladder used for the addition/subtraction of the address of the device stored
in D1 and D0 for indirect designation.
[To add "1" to the address of the device for indirect designation]
DINCP D0
32-bit instruction
Device used for indirect designation
[To subtract "1" from the address of the device for indirect designation]
DDECP D0
32-bit instruction
Device used for indirect designation
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com

 Loading...
Loading...











