The Gas Correction Factor (GCF) Cha
ter Three: Overview
36
How To Calculate the GCF for Gas Mixtures
For gas mixtures, the calculated Gas Correction Factor is not simply the weighted average of
each component’s GCF. Instead, the GCF (relative to nitrogen) is calculated by the following
equation:
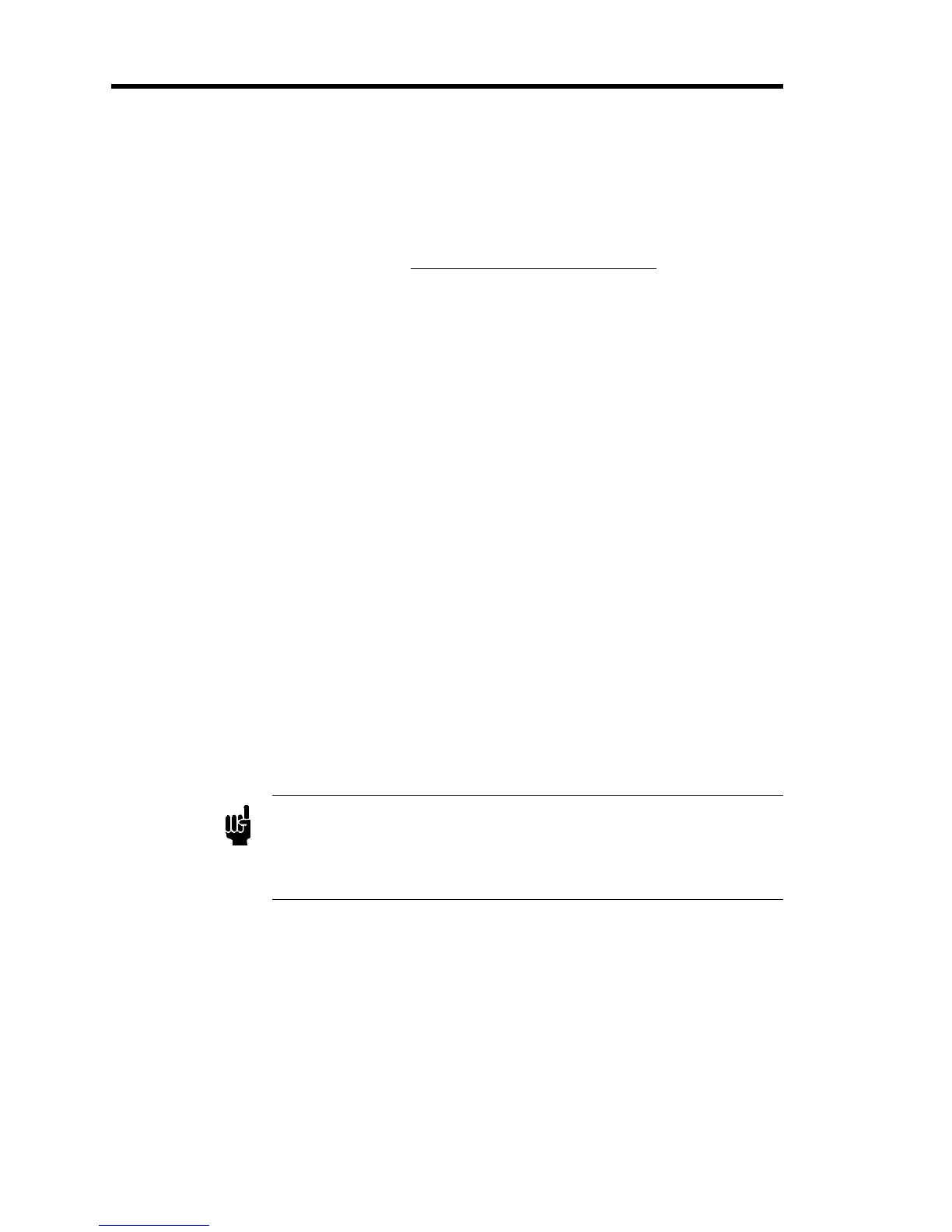
GCF
M
11 22 nn
11 1 22 2
nn n
=
(0.3106) (a s + a s + ...a s )
(a d cp +a d cp + ...a d cp )
where:
GCF
M
= Gas Correction Factor for a gas mixture
0.3106 = (Standard Density of nitrogen) (Specific Heat of nitrogen)
a
1
through a
n
= Fractional Flow of gases 1 through n
Note
: a
1
through a
n
must add up to 1.0
s
1
through s
n
= Molecular Structure correction factor for gases 1 through n
where S equals:
1.030 for Monatomic
ases
1.000 for Diatomic
ases
0.941 for Triatomic
ases
0.880 for Pol
atomic
ases
d
1
through
d
n
= Standard Density for gases 1 through n, in g/l
(at 0° C and 760 mmHg)
cp
1
through cp
n
= Specific Heat of gases 1 through n, cal/g° C
Note
The values for s, d, and cp
x
are available for most gases, refer to
Appendix C: Gas Correction Factors
, page 65.
The values for a
1
through a
n
(which must add up to 1.0) are application
dependent.
 Loading...
Loading...