How To Determine the Flow Controller Range A
endix D: MFC Sizin
Guidelines
70
How To Determine the Flow Controller Range
The Type 1179 controller is available in ranges of 10, 20, 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000, 2000, 5000,
10,000, 20,000, and 30,000 sccm (N
2
equivalent). To select the appropriate range, you must
determine the flow rate of nitrogen that is equivalent to the flow rate of the desired gas.
Calculate the ratio of the GCF of nitrogen (1.00) to the GCF of the desired gas (refer to
Appendix C: Gas Correction Factors,
page 65) as shown in the following example.
Example:
You need a flow rate of 250 sccm of argon (Ar). What range flow controller should you use?
1. Find the Gas Correction Factor of Ar (refer to
Appendix C: Gas Correction Factors,
page 65).
The GCF for Ar is 1.41.
2. Insert the GCF of Ar in the following formula:
()
GCF of N
2
()
GCF of Ar
=
()
x
()
Desired flow rate of Ar
where
x
is the equivalent flow rate of nitrogen (sccm).
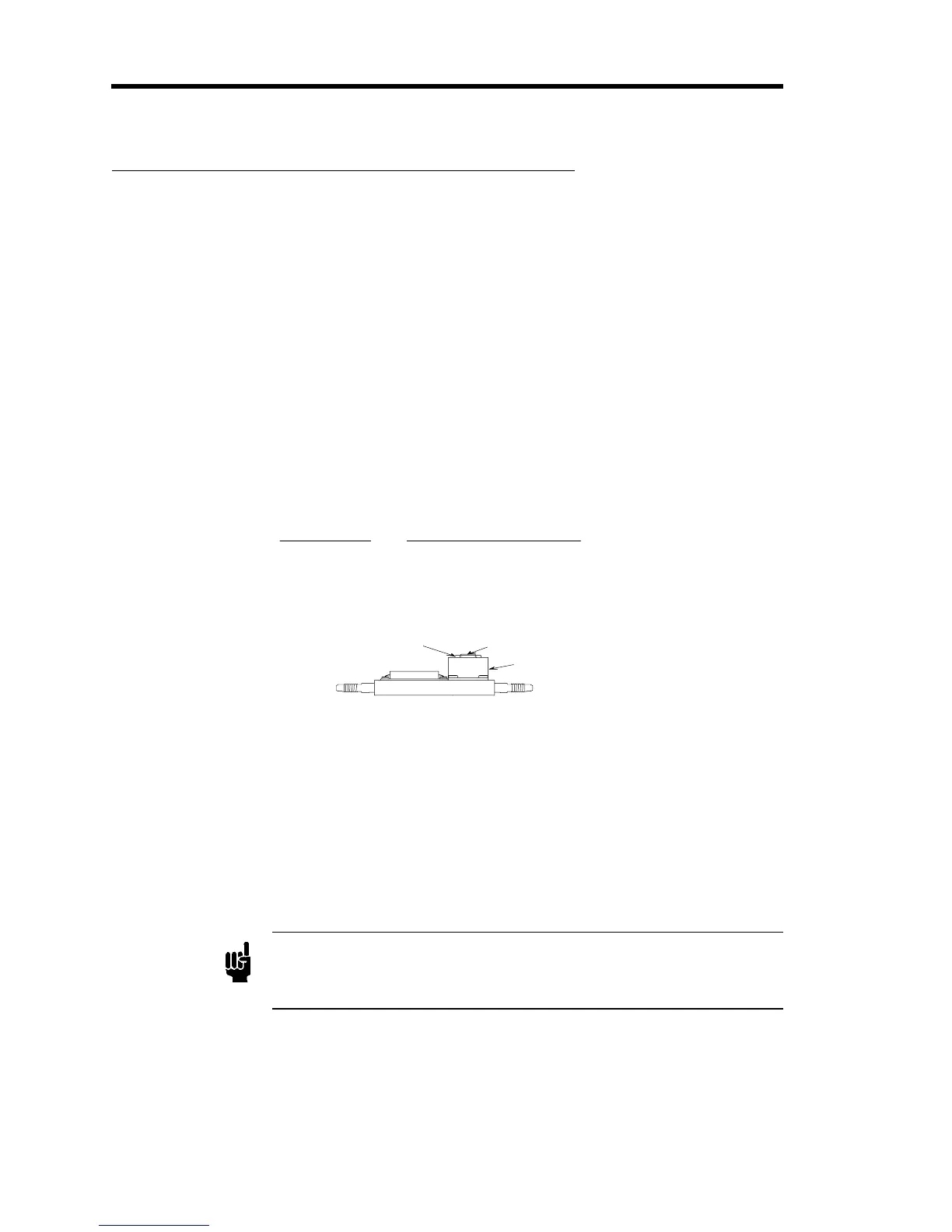
Jam N ut
C ente rshaft
V a lv e C o il
Enclosure
x
= 177 sccm N
2
A flow rate of 250 sccm of Ar will produce a flow rate equivalent to 177 sccm of N
2
. This falls
within the range of a 200 sccm flow controller.
When calculating equivalent N
2
flows using gas correction factors, be sure to use a flow
controller with a sufficient flow rate range. For example, if the calculated equivalent N
2
flow in
the example shown above is 205 sccm, use a 500 sccm flow controller. The 500 sccm instrument
can then be calibrated such that 205 sccm N
2
= full scale.
Note
When using a gas with a density
higher
than nitrogen, be sure that the
control valve Full Scale range can accommodate the desired flow rate.
Please call the MKS Applications group if you have any questions.
 Loading...
Loading...