1-6 General Information
1.6.2 Explication Notes
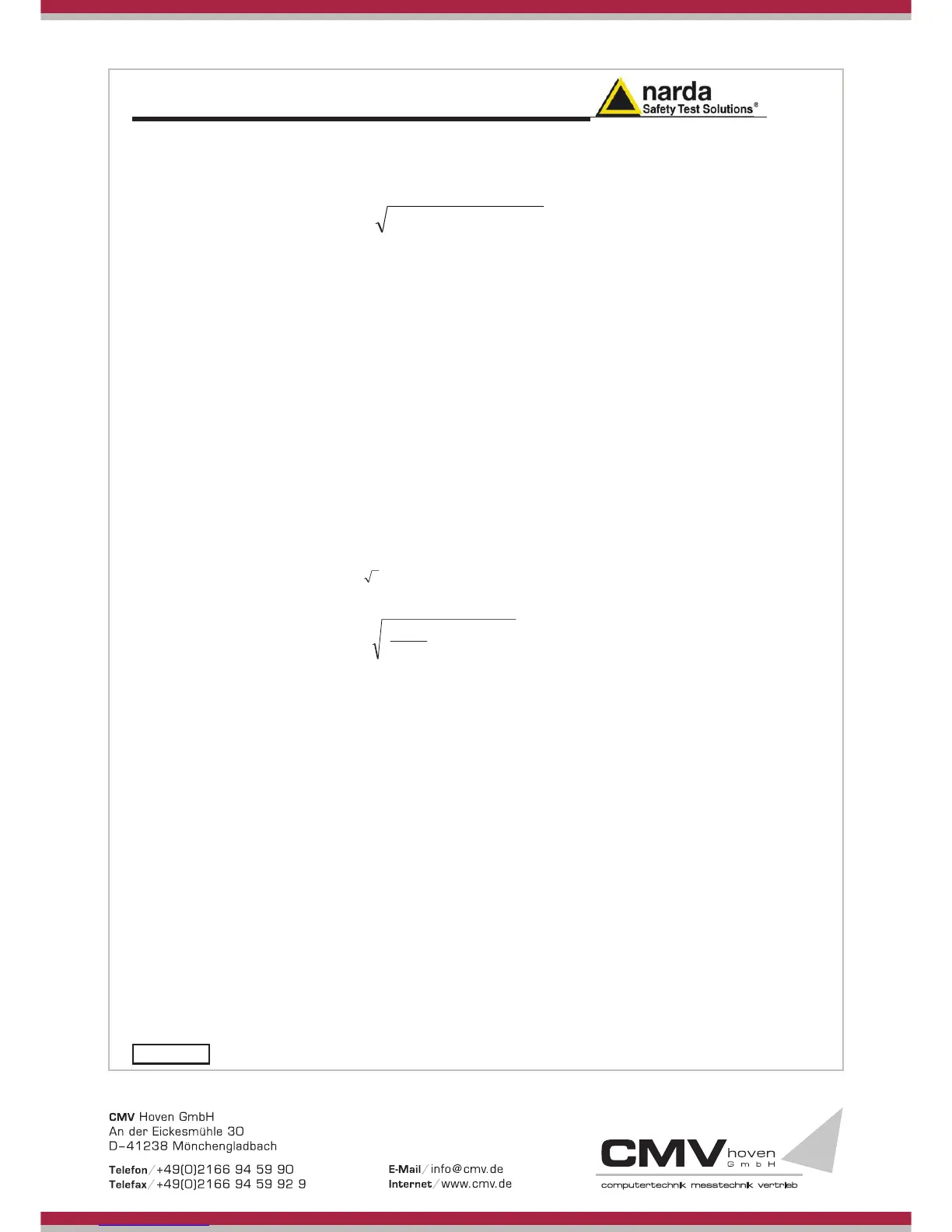
a) If we have the certificate with different values of the uncertainty of
calibration, in order to calculate the total expanded uncertainty U
T
, the
uncertainty of calibration has to be taken into account:
22
50 CalFEHPT
UUU
where
FEHP
U
50
is the standard uncertainty
(
FEHP
U
50
= U
FEHP50
/ 2 )
Cal
U is the standard uncertainty
(
Cal
U = U
Cal
/ 2 )
where U
Cal
is the expanded uncertainty reported on certificate
The quadratic sum is considered a precaution because the
uncertainty
Cal
U is added quadratically to an uncertainty that is
already a combined uncertainty.
b) When the environmental temperature is higher than 23 °C, the contribute
due to the temperature can be added quadratically to the uncertainty.
Example: for magnetic measurements, if the temperature is 43°C, we get a
variation of 20°C in comparison to 23°C, corresponding to a variation o
0.26 dB ( 0.013 dB / °C ) equivalent to 3,04% and therefore, assuming a
rectangular distribution of probability, the standard uncertainty is 1.75%
( = 0,03 /
3
).
Assuming an expanded uncertainty U
T
=2.3%,
042.00175.0
2
029.0
2
2
2
¸
¹
·
¨
©
§
x
TOT
U
is obtained.
The quadratic sum is considered a precaution because the uncertainty due
to temperature, is added quadratically to an uncertainty that is already a
combined uncertainty.
A similar calculation can be made in case the relative humidity overcomes
50%.
 Loading...
Loading...