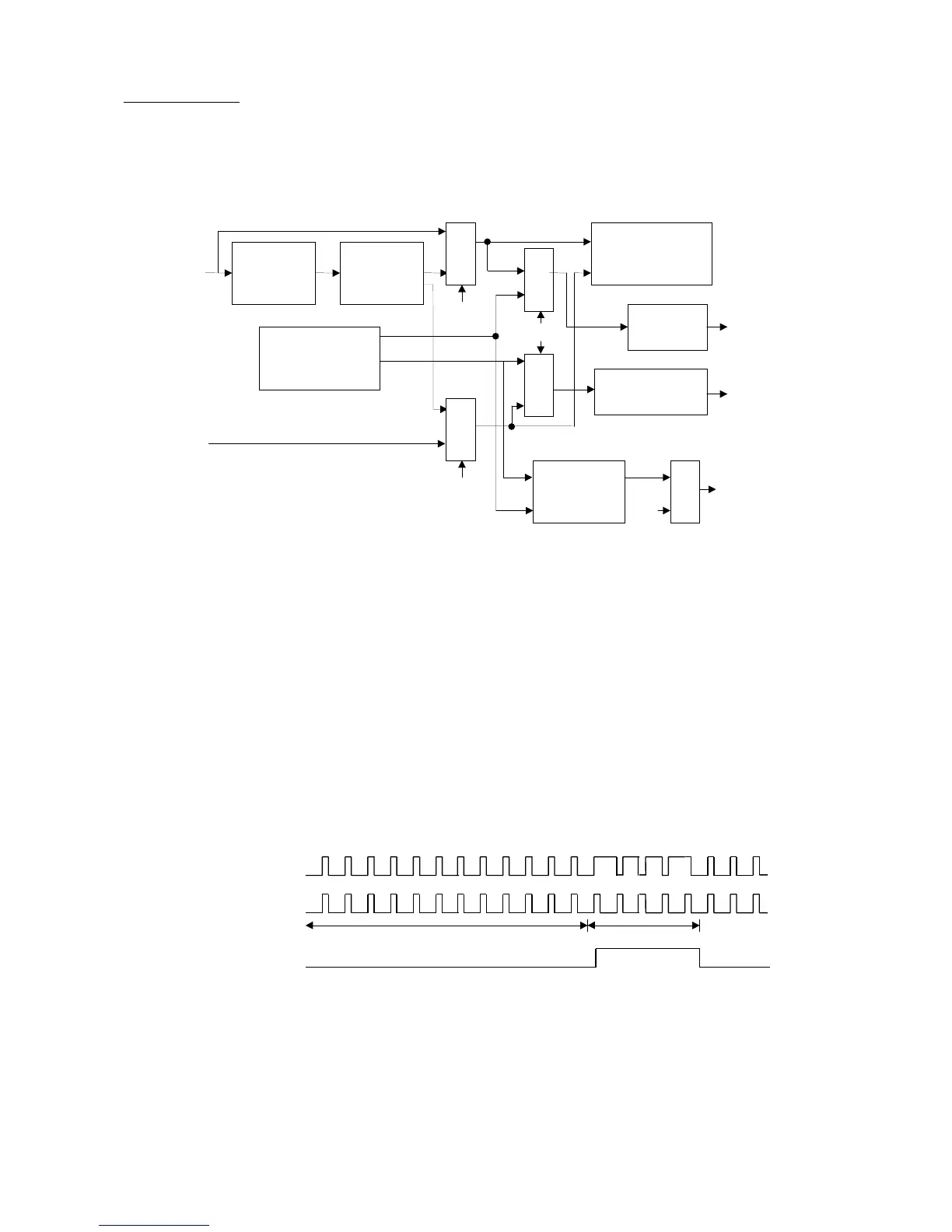
SYNC Processor
The SYNC processor can : (1) separate the composite sync signal; (2) calculate HSYNC and VSYNC
frequencies; (3) detect polarities of HSYNC and VSYNC input; (4) control the output polarities of HSO and
VSO pin; (5) generate free-running horizontal and vertical sync signals for burn-in test; (6) generate self-test
pattern signal.
HSYNC
VSYNC
H Polarity
detect
Sync
Separator
Mux
Mux
H/V Freq. Counter
H/V SYNC
Generator
Mux
Mux
H Polarity
Control
V Polarity
detect & control
SELF
TEST Pattern
Generator
Mux
PB3
HSO
VSO
PB3/PAT
H+V
H+V
V
H
Composite Sync Signal Separation
The composite sync signal comes from HSYNC pin and is separated by the sync separator.
The operations of sync separator are:
- detect the polarity and covert composite sync signal to positive polarity.
- extract Vsync
Pulse width less than 8us will be filtered, but the Vsync will be widened about 8us.
- count the pulses during the separated Vsync is low and save the counter value (N
H
).
- bypass the composite sync pulses before the counter equals to N
H.
- start inserting Hsync pulses after the counter equals to N
H
until the separated Vsync is low.
- the period of inserted Hsync is decided by the last two bypassed Hsync.
- the pulse width of the inserted Hsync is 2us.
bypass
insert HSYNC
Positive H+V
Separated Hsync
Separated Vsync
To decide whether the HSYNC input is a composite sync signal or not, program should check the fre-
quency of VSYNC first (reset H+V bit to “0”). If the VSYNC frequency is lower than 15.25Hz (OVF2=1), set
H+V bit to “1” and check VSYNC frequency again. If VSYNC still has no frequency, that is power saving
condition, program should reset H+V bit. If it has a valid frequency, the HSYNC input is composite signal.
49
 Loading...
Loading...