10
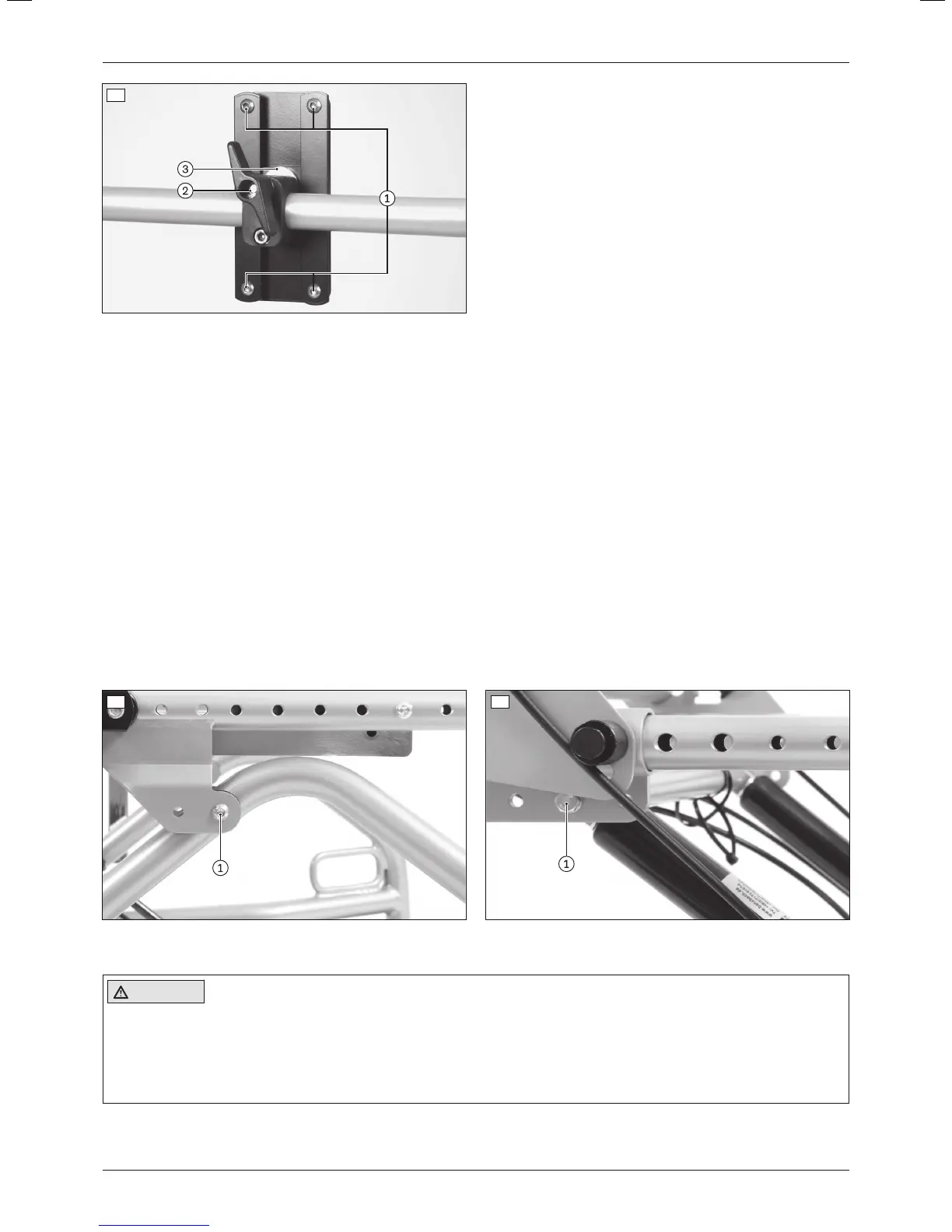
6.5 Adjusting the position of the seat bars
The seat bars can be moved to an anterior or posterior position, e.g.to shift the centre of gravity or to provide more
space for the legrests:
1) Loosen and remove the screw connection on the pivot point of the seat tilt (see fig.11, item1).
CAUTION! Risk of pinching between freely movable frame components. Actively secure the seat frame
against falling.
2) Move the seat bars to the desired position.
3) Reinsert the screw connections at the pivot point for the seat tilt on both sides and firmly tighten them to a
torque of 10Nm (see fig.11, item1).
4) Loosen and remove the screw connection between the perforated plate and gas compression spring on both
sides (see fig.12, item1).
CAUTION! Risk of pinching between freely movable gas compression springs. Actively secure the gas
compression springs against falling.
5) Move the gas compression springs along the perforated plate according to the position of the seat bars.
INFORMATION: Slide the position of the seat bars and the position of the gas compression springs
equally. This maintains the angle setting of the seat frame. If the raster provided by the perforated
plate is insufficient, carry out the adjustment according to the seat depth (see Page12).
6) Reinsert all screw connections and firmly tighten them to a torque of 10Nm (see fig.12, item1).
11 12
6.6 Checking/adjusting the seating centre of gravity
CAUTION
Improper adjustment of the seating centre of gravity
Tipping, falling from the seating shell / seating system due to incorrect adjustment
► Avoid extreme settings that could lead to tipping when adjusting the seat angle.
► For transfemoral amputees, shift the seating centre of gravity forward. This improves the stability of the mobil
ity base for seating shells.
Checking the seating centre of gravity is required in order to ensure that the seat angle can be adjusted easily
when the user is seated.
15Discovery
Settings

 Loading...
Loading...











