(Table 9, contd)
1103 Naturally Aspirated Engine without an oil cooler
Compartment or System
Liters
Quarts
External cooling system capacity (OEM
recommendation)
(1)
Total Cooling System
(2)
(1)
The external cooling system includes a radiator or an expansion
tank with the following components: heat exchanger, aftercooler
and piping. Refer to the OEM specifications. Enter the value for
the external system capacity in this row.
(2)
The Total Cooling System includes the capacity for the engine
cooling system plus the capacity for the external cooling system.
Enter the total in this row.
Table 10
1103 Naturally Aspirated Engines and Turbocharged
Engines with an oil cooler
Compartment or System
Liters
Quarts
Engine Only
4.43 4.02
External cooling system capacity (OEM
recommendation)
(1)
Total Cooling System
(2)
(1)
The external cooling system includes a radiator or an expansion
tank with the following components: heat exchanger, aftercooler
and piping. Refer to the OEM specifications. Enter the value for
the external system capacity in this row.
(2)
The Total Cooling System includes the capacity for the engine
cooling system plus the capacity for the external cooling system.
Enter the total in this row.
i05899606
Fluid Recommendations
General Coolant Information
NOTICE
Never add coolant to an overheated engine. Engine
damage could result. Allow the engine to cool first.
NOTICE
If the engine is to be stored in, or shipped to an area
with below freezing temperatures, the cooling system
must be either protected to the lowest outside temper-
ature or drained completely to prevent damage.
NOTICE
Frequently check the specific gravity of the coolant for
proper freeze protection or for anti-boil protection.
Clean the cooling system for the following reasons:
• Contamination of the cooling system
• Overheating of the engine
• Foaming of the coolant
NOTICE
Never operate an engine without water temperature
regulators in the cooling system. Water temperature
regulators help to maintain the engine coolant at the
proper operating temperature. Cooling system prob-
lems can develop without water temperature
regulators.
Many engine failures are related to the cooling
system. The following problems are related to cooling
system failures: Overheating, leakage of the water
pump and plugged radiators or heat exchangers.
These failures can be avoided with correct cooling
system maintenance. Cooling system maintenance is
as important as maintenance of the fuel system and
the lubrication system. Quality of the coolant is as
important as the quality of the fuel and the lubricating
oil.
Coolant is normally composed of three elements:
Water, additives and glycol.
Water
Water is used in the cooling system in order to
transfer heat.
Distilled water or deionized water is
recommended for use in engine cooling systems.
DO NOT use the following types of water in cooling
systems: Hard water, softened water that has been
conditioned with salt and sea water.
If distilled water or deionized water is not available,
use water with the properties that are listed in Table
11 .
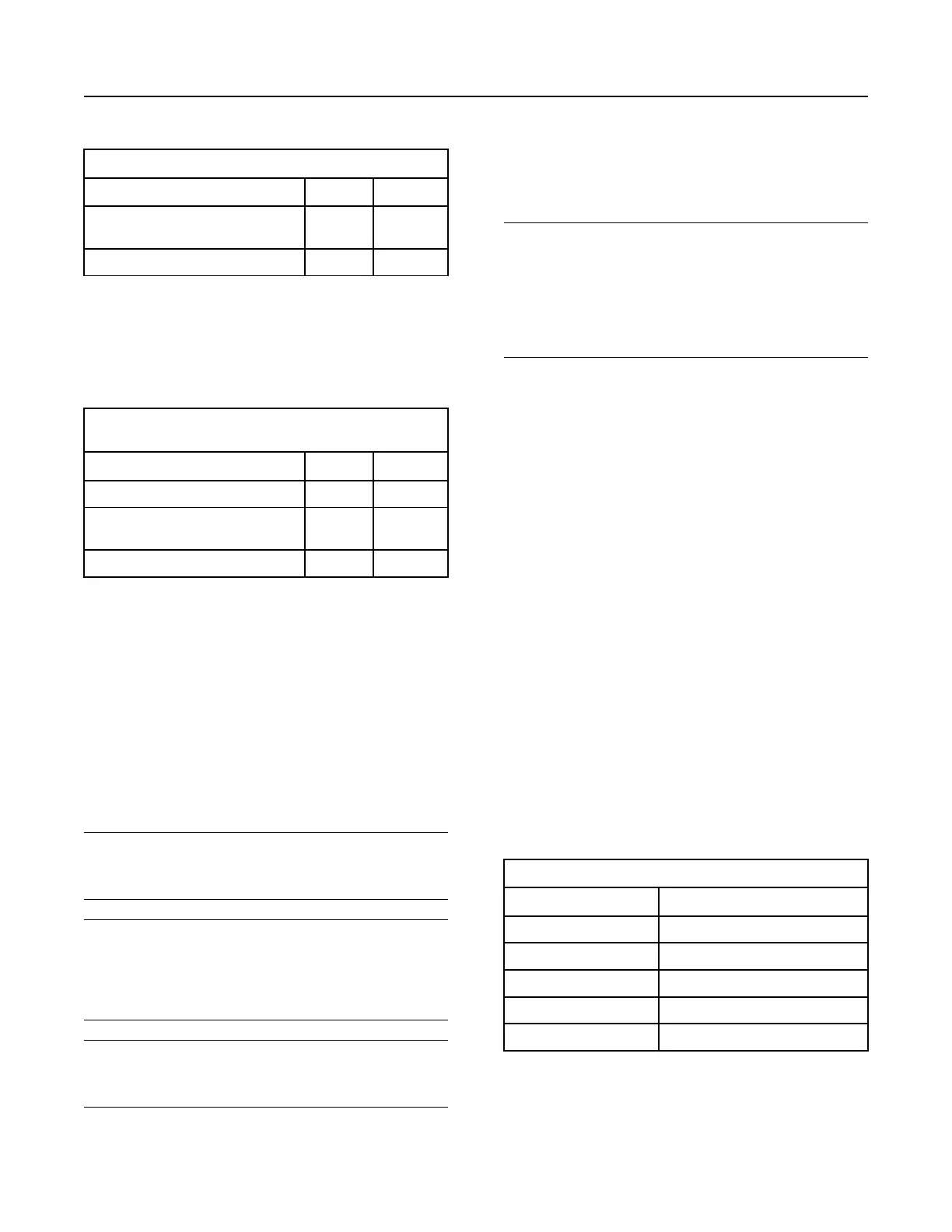
Table 11
Acceptable Water
Property
Maximum Limit
Chloride (Cl) 40 mg/L
Sulfate (SO
4
) 100 mg/L
Total Hardness
170 mg/L
Total Solids
340 mg/L
Acidity pH of 5.5 to 9.0
For a water analysis, consult one of the following
sources:
36 SEBU7833
Refill Capacities
Fluid Recommendations
 Loading...
Loading...