12 PowerBox-Systems − World Leaders in RC Power Supply Systems
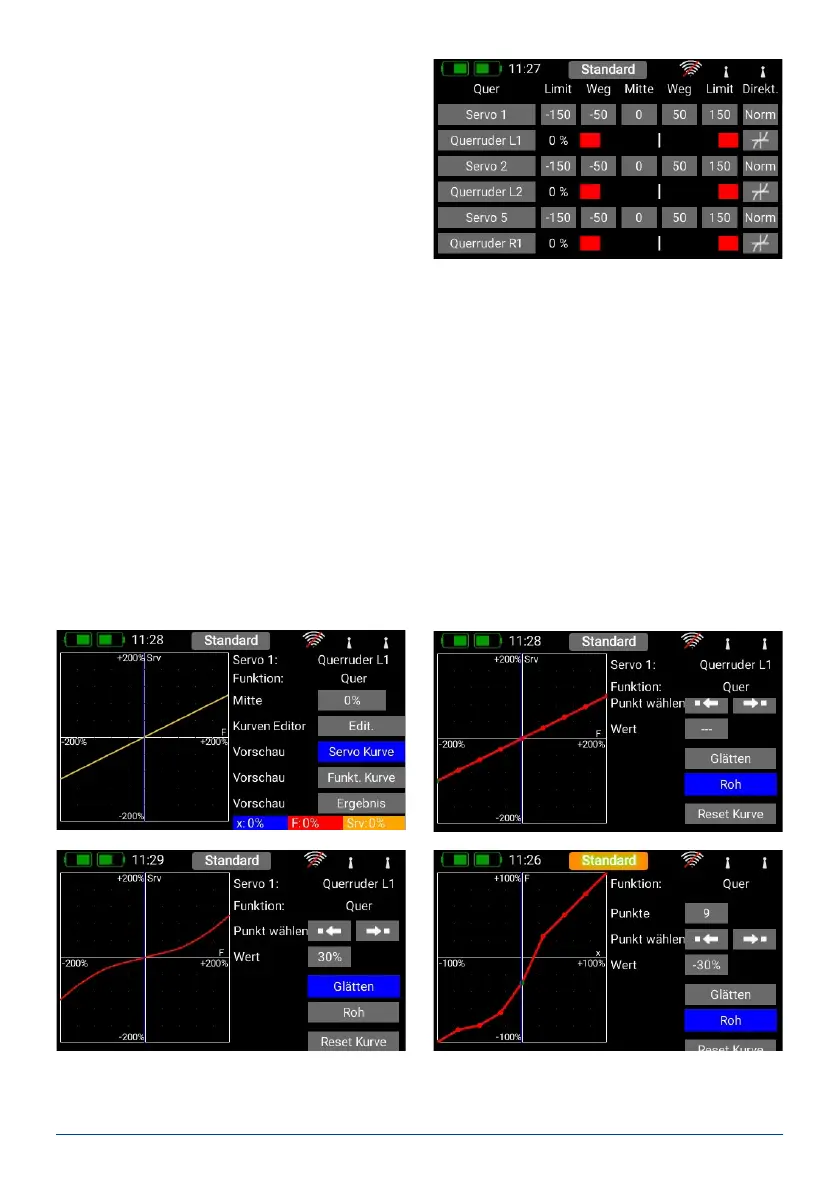
a) Servo number: indicates the receiver output at
which this servo signal is present.
b) Servoname: the servo name can be changed indivi-
dually. Hold your nger on it to open up the keypad.
c) Limit: works like a mechanical stop – the servo
does not move beyond the set point.
d) Travel: adjusts the servo travel.
e) Center: offsets the servo center position. Acts like a “mechanical” center offset – it also affects the end-points.
f) Direction: reverses the direction of rotation of the servo.
g) Curve editor: the travel of each servo can be adjusted using a 9-point curve to match the mechanical installa-
tion even more accurately. The most common use for this function is to match servos to each other where
they are mechanically linked (servo matching).
At top right you will see the name of the servo whose curve you wish to adjust, and the function which the
servo controls. If you alter the servo curve in the selected function, the change will have no effect on the travel
which you have set for the same servo in other functions.
- Center
The Center button is used to set a center offset which affects the whole of the servo’s travel. You will see the
effect of the change immediately in the graph on the left-hand side.
- Curve Editor
Press Edit. when you wish to adjust servo travel using a maximum of 17 points.
 Loading...
Loading...