7SR45 Description of Operation
© 2017 Siemens Protection Devices Limited Chapter 1 Page 33 of 34
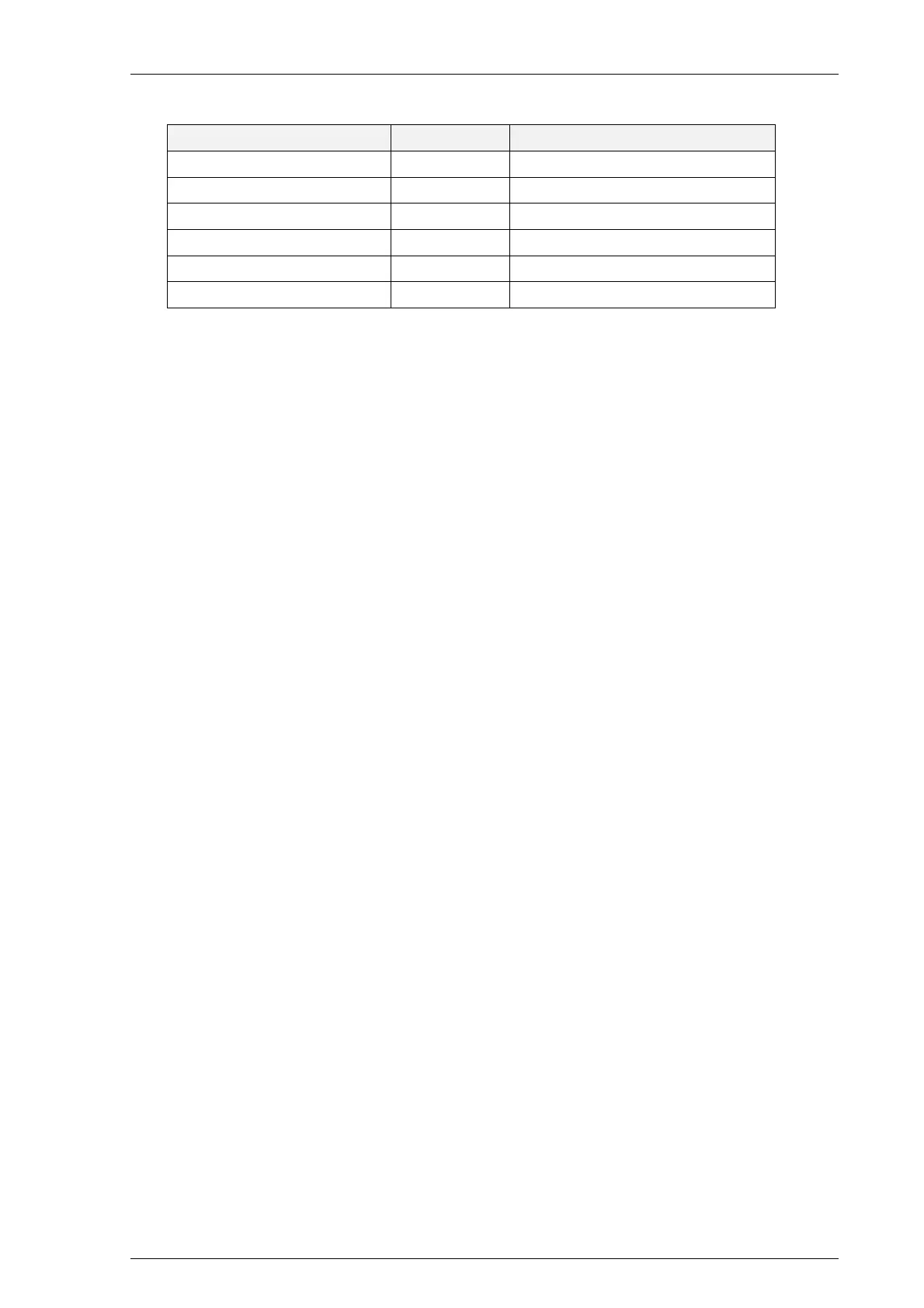
Table 3-13 Error Message
Errors Error Code Error Message
Setting Error 00000001 Load default settings!
Calibration Error 00000010 Load default calibration!
MLFB Error 00000100 MLFB Information Error!
Card Error 00001000 Analog & IO card Error!
Internal Supply Voltage Error 00010000
Unexpected Error 00100000
3.18 Data Storage
The relay stores the following two types of data:
• Fault Records
• Event records
The data records are stored in the non-volatile memory. The data storage menu contains the settings for clearing
the events and faults.
3.18.1 Fault Records (Trip Log)
The fault records are triggered when the protection function detects a fault condition and the trip alert message
appears on LCD to indicate a new fault has occurred. The relay can store up to 10 fault records and displayed
on the LCD fascia.
The fault records provide a summary of relay status when the trip occurs, i.e. element issued the trip, any
phase/earth picked up, fault magnitude, LED indications, general alarm, and date and time.
The trip alert message is displayed until the fault is acknowledged by the user.
When analyzed the event records and the fault records provide the full sequence of events that resulted to a trip.
The fault records are stored in a rolling buffer with the oldest faults overwritten. The fault storage can be cleared
with the DATA STORAGE/Fault Storage > Clear Faults setting in HMI.
3.18.2 Event Records (Event Log)
The event recorder feature allows the time tagging of any change of state (Event) in the relay. When an event
occurs, the actual event condition is logged as a record with a date and time stamp to a resolution of 1 ms. The
relay can store maximum of 100 event records. When the event buffer is full and any new record will overwrite the
old records.
Stored events can be erased by using the DATA STORAGE > Clear Events setting in HMI or from Reydisp.
The following events are logged:
• Change of state of binary outputs
• Change of state of binary inputs
• Change of settings
• Device start up and shut down
• Protection element operation
• Low battery
• General alarm
• IRF
All the events can be uploaded over the data communications channel(s) and displayed in the ‘Reydisp’ package
in chronological order and viewed in the sequence of events.

 Loading...
Loading...











