Safety Programming Guideline
Entry ID: 109750255, V1.0, 10/2017
3.9.4 Transferring HMI signals to the safety program
Human-machine interfaces (HMIs) are convenient, essential components in a
machine operator's daily work. In order to use this convenience for operator control
and monitoring of processes and plants even in safety-related applications,
additional measures are required.
Writing tags from the HMI to the safety program is a problem for the following
reasons:
Signals from the HMI panel are not safety-related and not monitored. An error
can result in forbidden changes of safety-related values, which increases the
risk.
Communication between the HMI and the CPU is acyclic. As a result, the
HMI's write access may take place while processing the safety program.
The first program run then still uses the original value. The encoded user
program uses the value that has been updated in the meantime. This causes
data corruption in the safety program and therefore a stop of the CPU (see
Chapter 5).
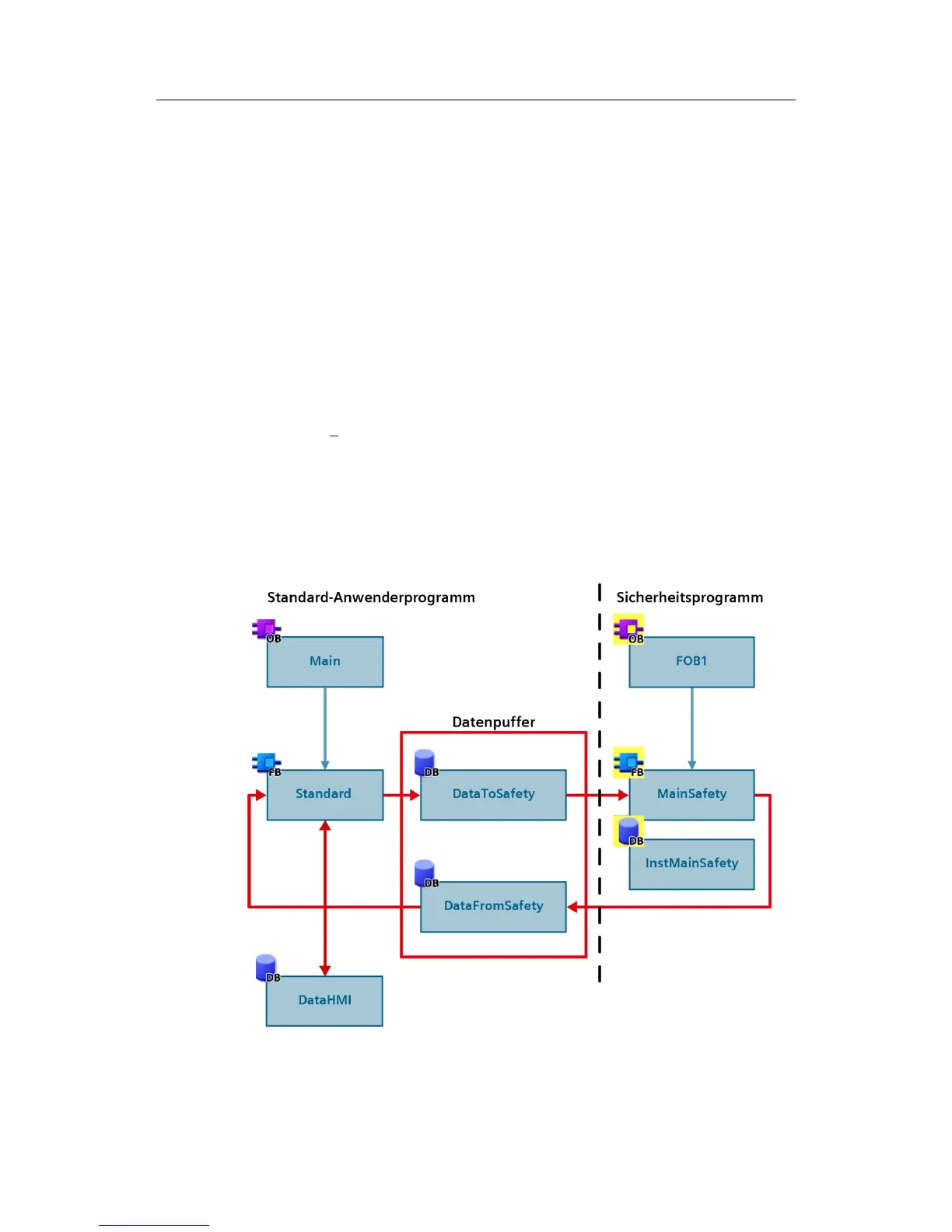
Recommendation
Use another data block for communication with the HMI and copy the safety-
related data in the standard user program to the data buffer.
Figure 3-12: Data exchange between HMI and safety program

 Loading...
Loading...