2.20 Circuit Breaker Failure Protection
367
7SD5 Manual
C53000-G1176-C169-1
(No. 3504) (Refer also to Section 2.4). An easier procedure is to combine the
command output with the intertrip input via the user definable logic functions (CFC).
Stub Fault
Protection
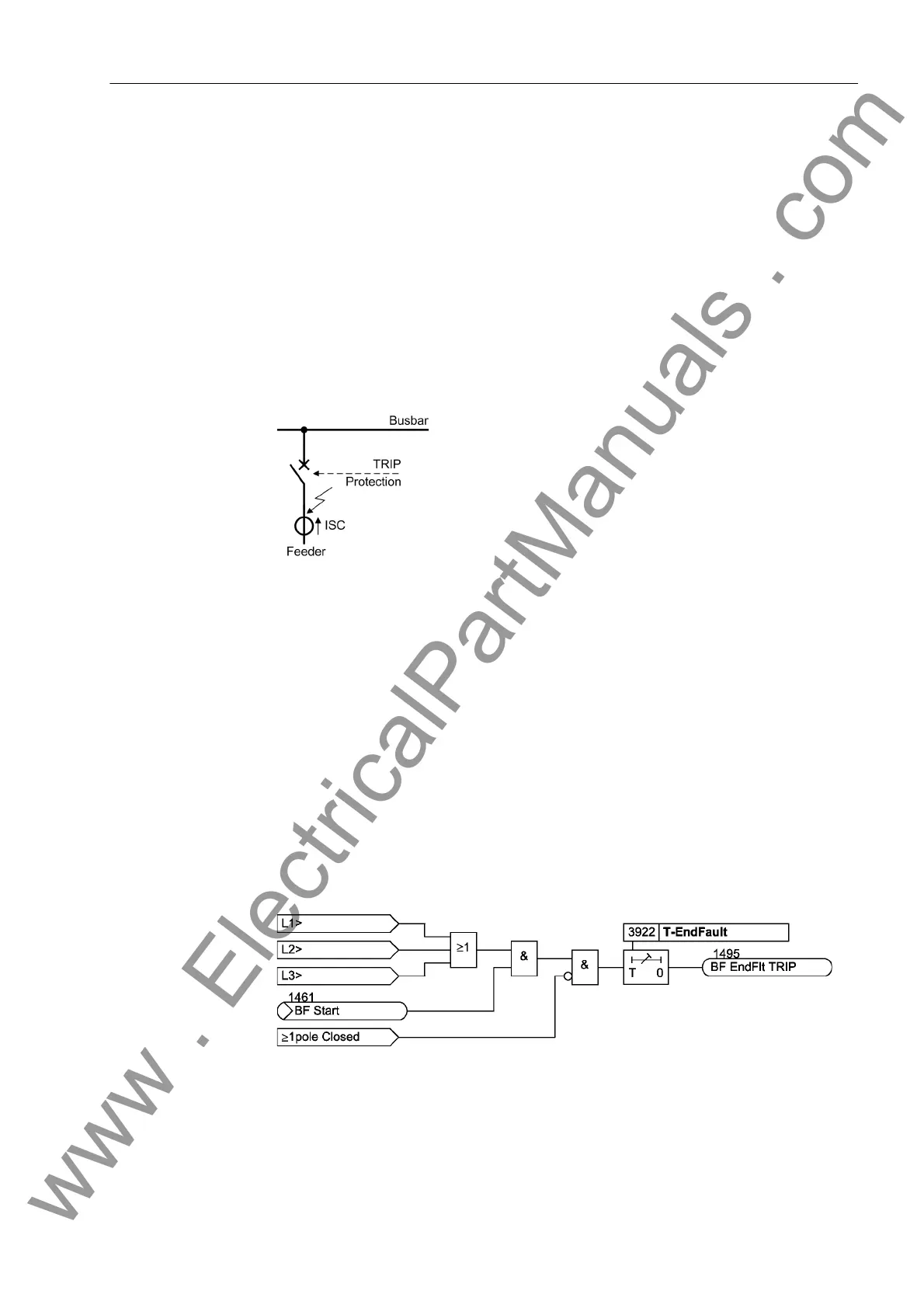
An end fault is defined here as a short–circuit which has occurred at the end of a line
or protected object, between the circuit breaker and the current transformer set.
This situation is shown in Figure 2-156. The fault is located — as seen from the current
transformers (= measurement location) — on the bus-bar side, thus, it will not be re-
garded by the feeder protection relay as a feeder fault. It can only be detected by either
a reverse stage of the feeder protection or by a busbar protection. Nevertheless, a trip
command given to the feeder circuit breaker cannot clear the fault since the opposite
end continues to feed the fault. Thus, the fault current does not stop flowing even
though the feeder circuit breaker has properly responded to the trip command.
Figure 2-156 End fault between circuit breaker and current transformers
The end fault protection has the task to recognize this situation and to transmit a trip
signal to the remote end(s) of the protected object to clear the fault. For this purpose,
the output command „BF EndFlt TRIP“ (No. 1495) is available to trigger the inter-
trip input of the differential protection — if applicable, together with other commands
that need to be transferred. This can be achieved by external connection or via CFC.
The end fault is recognized when the current continues flowing although the circuit
breaker auxiliary contacts indicate that the breaker is open. An additional criterion is
the presence of any breaker failure protection initiate signal. Figure 2-157 illustrates
the functional principle. If the breaker failure protection is initiated and current flow is
detected (current criteria „L*>“ according to Figure 2-145), but no circuit breaker pole
is closed (auxiliary contact criterion „any pole closed“), then the timer T-EndFault is
started. At the end of this time an intertrip signal is transmitted to the opposite end(s)
of the protected object.
Figure 2-157 Operation scheme of end fault protection
Pole Discrepancy
Supervision
The pole discrepancy supervision has the task to detect discrepancies in the position
of the three circuit breaker poles. Under steady-state operating conditions, either all
three poles of the breaker must be closed, or all three poles must be open. Discrep-
www . ElectricalPartManuals . com

 Loading...
Loading...











