32
Preparing the tibial IM canal
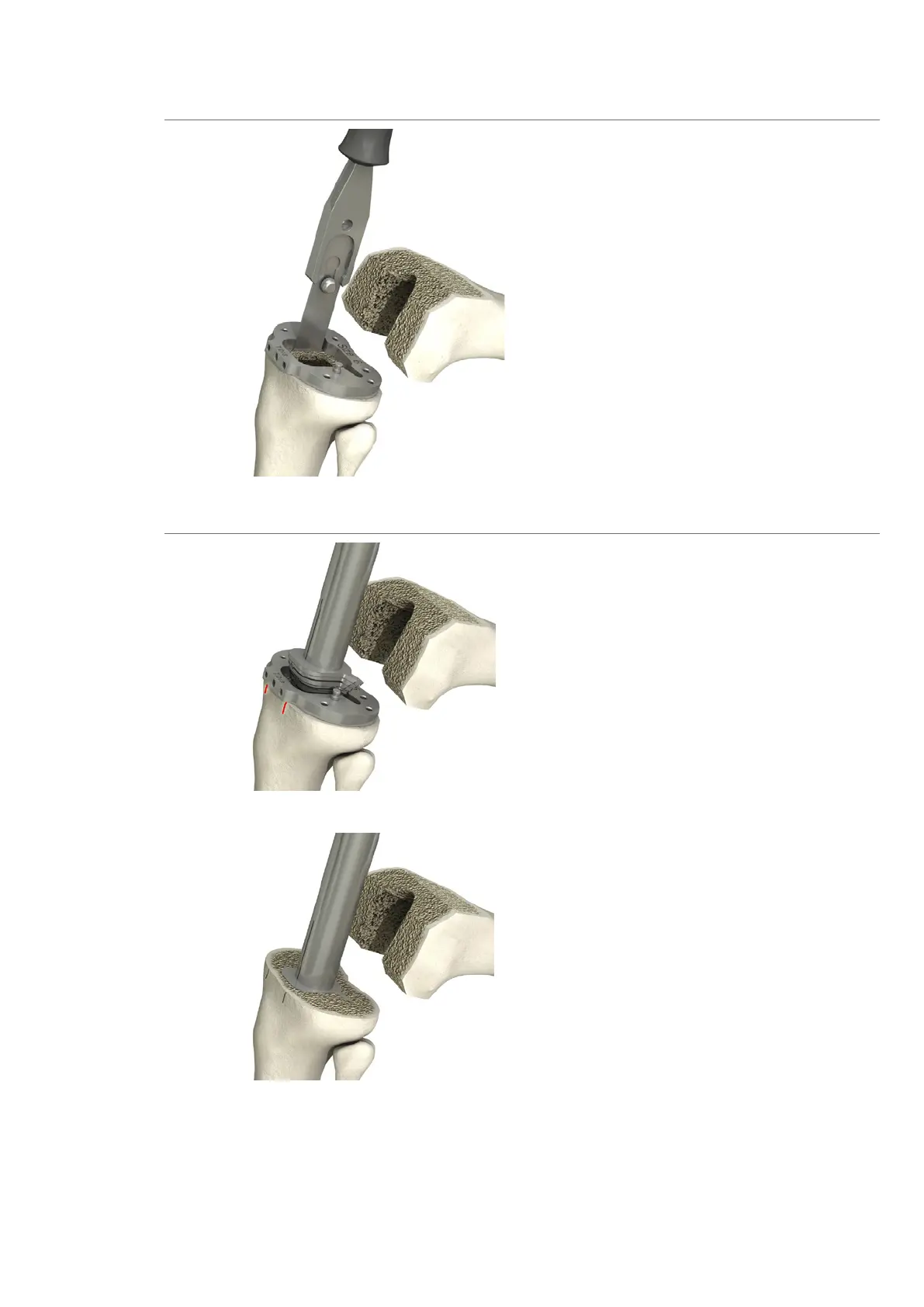
Prepare the proximal tibial anchorage using
the osteotome and rasp.
Using the thin, narrow 10 mm chisel; prepare
the tibial cavity initially along the internal
sizer contour, thereby avoiding bone frac-
tures especially if the bone quality is poor.
Important
If sclerotic bone is present, preparation of the
fins is especially important! These can also
be used as a reference for the tibial rotation
positioning.
The tibial sizer can be removed if necessary.
Using the tibial rasp, complete preparation
of the proximal tibial cavity. The rasp must be
knocked in far enough to ensure the top of
the rasp is flush with the (more proximal)
bone resection (or flush with the height of
the lower plane of the tibial sizer).
Important
To avoid bone fractures, knock the rasp in
carefully.
To protect the sharp threads of the rasp,
perform rasping without the tibial sizer if
necessary. In this case, use a thin chisel or
electrocautery to mark the tibial anchorage
fin positions on the bone in order to guide
the rasp.
If a 10 mm tibial augmentation block is used,
rasping down to the resection level is not
necessary. The rasp must be impacted until
the 10 mm line marked on it is flush with the
bone resection.
 Loading...
Loading...