ACCURACY
3-5
L + Q ACCURACY
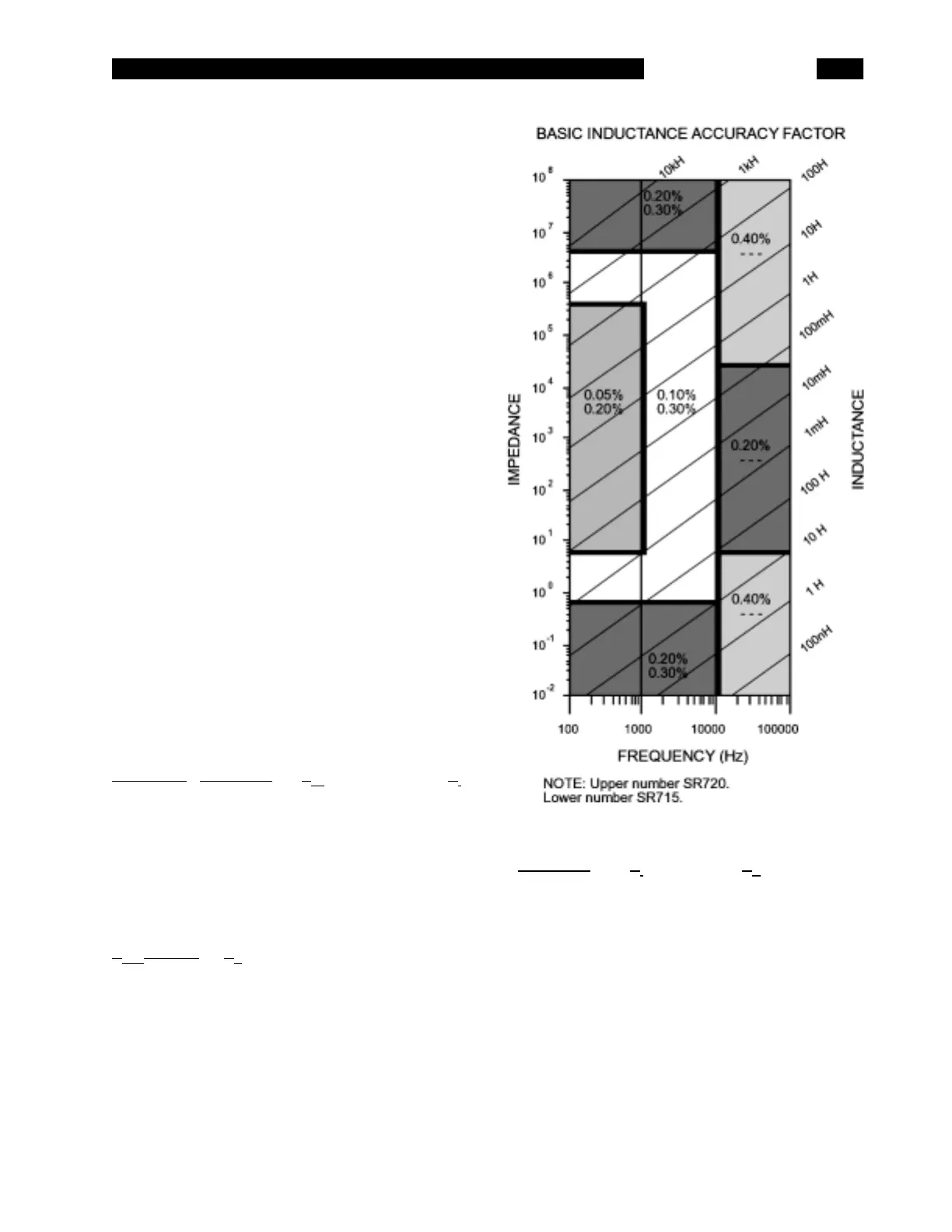
Accuracy of L = ± [A x K
i
x K
v
+ (K
h
+ K
l
) x 100] %
A = Basic Inductance Accuracy Factor
from graph.
For Q < 10, multiply the basic
accuracy factor by (1 + 1/Q).
If the unit is in the constant voltage
(CV) mode, double the basic
accuracy factor.
K
i
= Integration Time Factor (see K
i
Table below)
K
v
= Voltage Error Factor (see K
v
table
below).
K
h
, K
l
= Extreme Range Error Term (see
K
h
, K
l
table below).
Accuracy of Q = ± [(Al / 100) x (1 + Q2)]
A
l
= the accuracy of the Inductance
measurement (above)
Note that the accuracy of Q is specified as a
magnitude, NOT as a percent.
K
i
Table
Meas Rate Frequency
Z
m
K
i
slow, med all 1
fast 100 Hz-1 kHz 6.25 Ω<Z
m
<400 kΩ 3
fast all other 2
Z
m
= 2πfL = impedance of device
K
v
Table
V
out
(V rms) K
v
1.0 - 0.55 1 / V
out
0.5 - 0.3 0.5 / V
out
0.25 - 0.15 0.25 / V
out
0.10 0.11/V
out
Note that K
v
equals one for the primary drive
voltages (1.0, 0.5 and 0.25 Vrms).
K
h
& K
l
Table
Frequency K
l
K
h
100,120 Hz (1 µH / L
m
)(L
m
/ 2.6 MH)
1 kHz (0.1 µH / L
m
)(L
m
/ 260 kH)
10 kHz (0.02 µH / L
m
)(L
m
/ 10 kH)
100 kHz (0.02 µH / L
m
)(L
m
/ 100 H)
L
m
= the inductance of the device being
measured.
Note that K
l
is negligible for inductances above
15.9/f H and K
h
is negligible for inductances below
159./f kH, where f is the output frequency.
 Loading...
Loading...