PM0214 Rev 10 25/262
PM0214 The Cortex-M4 processor
261
Base priority mask register
The BASEPRI register defines the minimum priority for exception processing. When
BASEPRI is set to a nonzero value, it prevents the activation of all exceptions with same or
lower priority level as the BASEPRI value. See the register summary in Table 3 on page 18
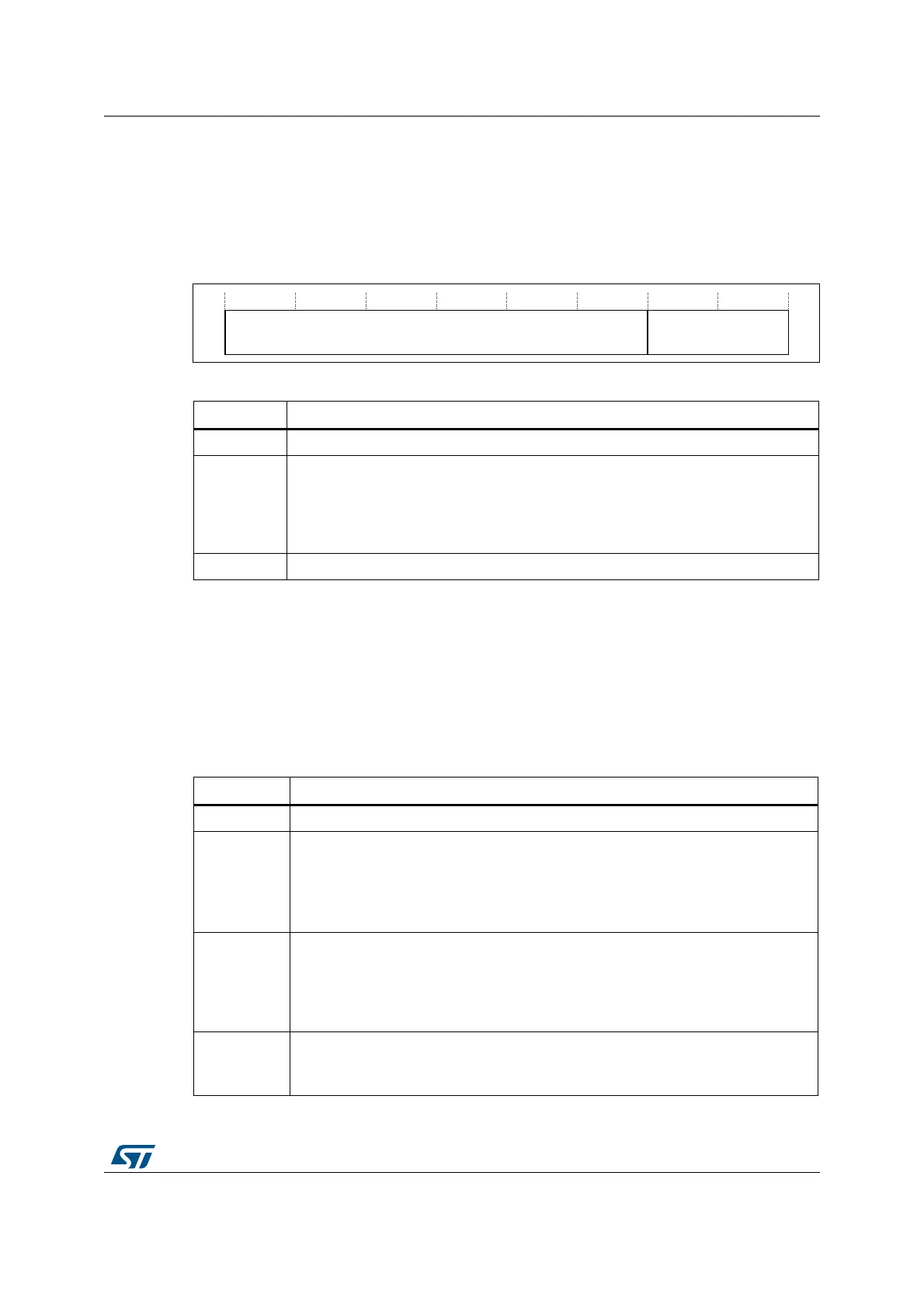
for its attributes. Figure 7 shows the bit assignment.
Figure 7. BASEPRI bit assignment
CONTROL register
The CONTROL register controls the stack used and the privilege level for software
execution when the processor is in Thread mode and indicates whether the FPU state is
active. See the register summary in Table 3 on page 18 for its attributes.
Table 10. BASEPRI register bit assignment
Bits Function
Bits 31:8 Reserved
Bits 7:4 BASEPRI[7:4] Priority mask bits
(1)
0x00: no effect
Nonzero: defines the base priority for exception processing.
The processor does not process any exception with a priority value greater than or
equal to BASEPRI.
1. This field is similar to the priority fields in the interrupt priority registers. See Interrupt priority register x
(NVIC_IPRx) on page 215 for more information. Remember that higher priority field values correspond to
lower exception priorities.
Bits 3:0 Reserved
Table 11. CONTROL register bit definitions
Bits Function
Bits 31:3 Reserved
Bit 2 FPCA: Indicates whether floating-point context currently active:
0: No floating-point context active
1: Floating-point context active.
The Cortex-M4 uses this bit to determine whether to preserve floating-point state
when processing an exception.
Bit 1 SPSEL: Active stack pointer selection. Selects the current stack:
0: MSP is the current stack pointer
1: PSP is the current stack pointer.
In Handler mode this bit reads as zero and ignores writes. The Cortex-M4 updates
this bit automatically on exception return.
Bit 0 nPRIV: Thread mode privilege level. Defines the Thread mode privilege level.
0: Privileged
1: Unprivileged.

 Loading...
Loading...