www.ti.com
Generic Access Profile (GAP)
29
SWRU271H–October 2010–Revised April 2019
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2010–2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
The Bluetooth Low Energy Protocol Stack
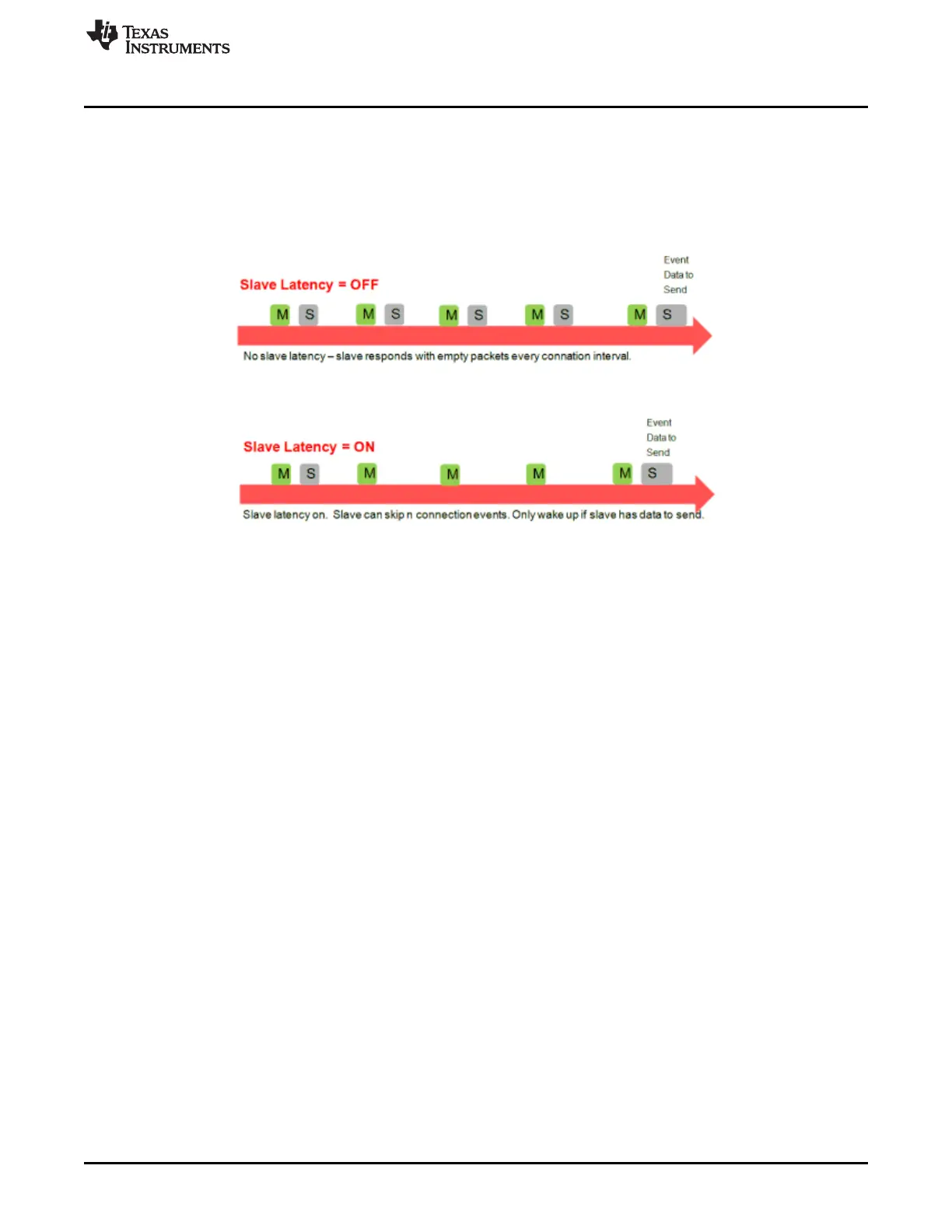
• Slave Latency – This parameter lets the slave (peripheral) device skip several connection events. If the
device has no data to send, it can skip connection events and deactivate its radio during the
connection event, which saves power. The slave latency value represents the maximum number of
events that can be skipped. This value ranges from a minimum value of 0 (no connection events)) to a
maximum of 499. The maximum value must create an effective connection interval less than 16
seconds. For an overview of this parameter, see Figure 5-3.
Figure 5-3. Slave Latency
• Supervision Time-out – This parameter is the maximum time period between two successful
connection events. If this time period passes without a successful connection event, the device
considers the connection lost and returns to an unconnected state. This parameter value is
represented in units of 10 ms. The supervision time-out value can range from a minimum of 10 (100
ms) to 3200 (32 seconds). The time-out must be larger than the effective connection interval. For more
details, see Section 5.2.1.2.
5.2.1.2 Effective Connection Interval
The effective connection interval is equal to the amount of time between two connection events, assuming
the slave skips the maximum number of possible events if slave latency is allowed. The effective
connection interval is equal to the actual connection interval if slave latency is set to zero.
Calculate this interval using the following formula:
Effective Connection Interval = (Connection Interval) × (1 + [Slave Latency])
Where:
• Connection Interval: 80 (100 ms)
• Slave Latency: 4
• Effective Connection Interval: (100 ms) × (1 + 4) = 500 ms
When no data is sent from the slave to the master, the slave will transmit during a connection event once
every 500 ms.

 Loading...
Loading...