28 Math Functions
with
optional
tolerance
Classic Mode or Entry
In Classic mode or in classic edit lines, the nDeriv( command will paste from the
keypad or MATH menu.
Syntax: nDeriv(expression,variable,point[,tolerance]) where tolerance is optional and
the default H is 1EM5.
Example
% A
or
d
MATH
7:nDeriv(
% A
z F T 5 z
% ` z
% ` M 1 )
<
About the Numerical Derivative at a Point
The numerical derivative at a point command, nDeriv( or d/dx, uses the symmetric
difference quotient method. This method approximates the numerical derivative at a
given point as the slope of the secant line about the point.
( )
f x′ =
f x ε f x ε
ε
(
+
)
−
(
−
)
2
As H becomes smaller, the approximation usually becomes more accurate to
approximate the slope of the tangent line at the given point x.
• Because of the method used to calculate the numerical derivative at a point, the
calculator can return a false derivative value at a non-differentiable point.
• Always have some knowledge of the function behaviour near the point by using a
table of values near the point (or a graph of the function).
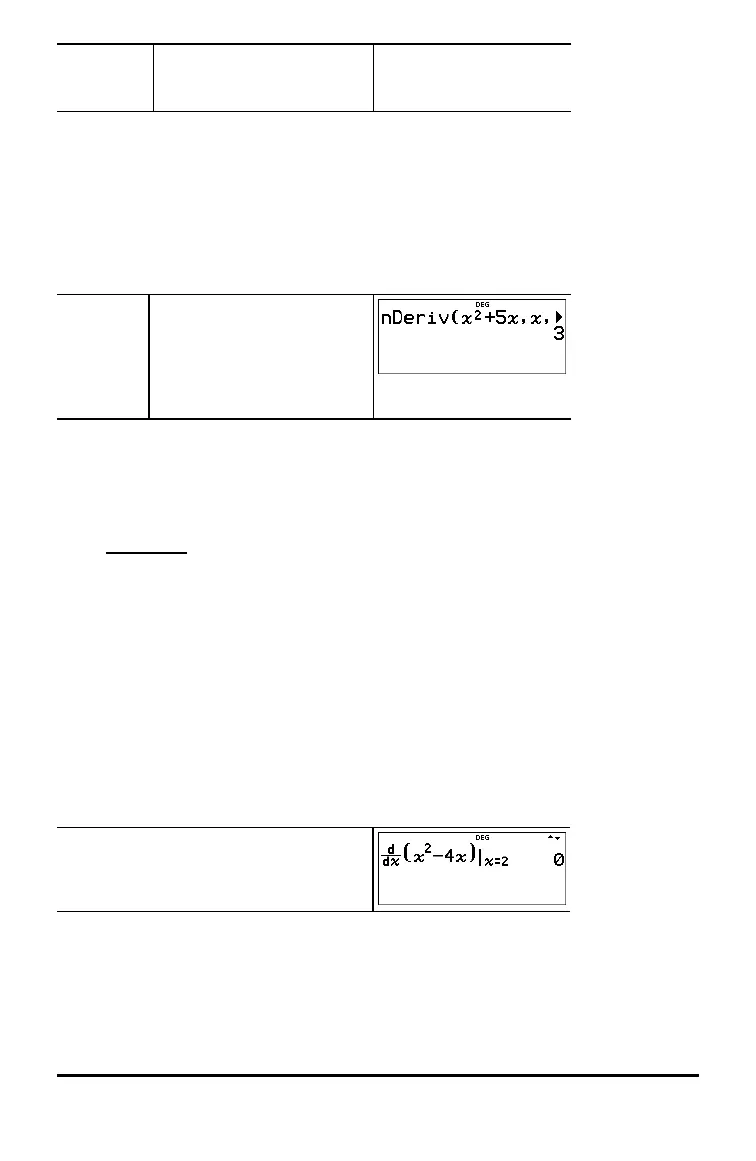
³ Problem
Find the slope of the tangent line to the function f(x) = x
2
- 4x at x = 2. What do you
notice?
% A
z F U 4 z " "
2 <
Numerical Integral
The TI-30X Pro MathPrint™ calculates the (approximate) numerical integral of an
expression with respect to a variable x, given a lower limit, an upper limit and a
tolerance for the numerical method.
 Loading...
Loading...











