Carburetor Operation The Diaphragm Pump
(cont'd)
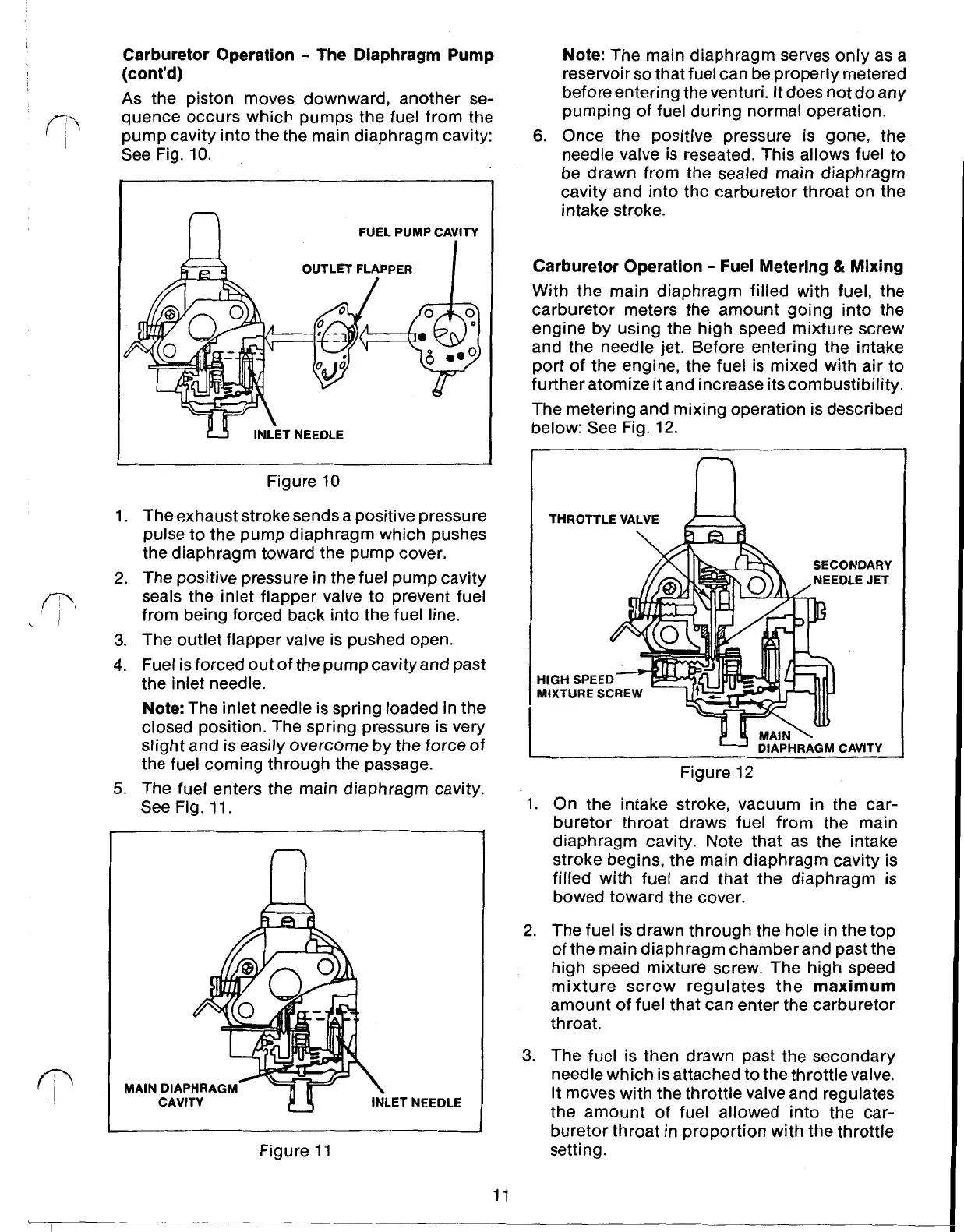
As
the piston moves downward, another se-
quence occurs which pumps the fuel from the
pump cavity into the the main diaphragm cavity:
See Fig. 10.
OUTLET FLAPPER
INL'ET
NEEDLE
Figure 10
1. The exhaust stroke sends a positive pressure
pulse to the pump diaphragm which pushes
the diaphragm toward the pump cover.
2. The positive pressure in the fuel pump cavity
from being forced back into the fuel line.
3.
The outlet flapper valve is pushed open.
4.
Fuel is forced out of the pump cavity and past
the inlet needle.
Note:
The inlet needle is spring loaded in the
closed position. The spring pressure is very
slight and is easily overcome by the force of
the fuel coming through the passage.
5.
The fuel enters the main diaphragm cavity.
seals the inlet flapper valve to prevent fuel
See Fig. 11.
MAIN DIAPHRAGM
CAVITY
.ET
NEEDLE
Figure 11
11
Note:
The main diaphragm serves only as a
reservoir
so
that fuel can be properly metered
before entering the venturi. It does not do any
pumping of fuel during normal operation.
6.
Once the positive pressure is gone, the
needle valve is re-seated. This allows fuel to
be drawn from the sealed main diaphragm
cavity and into the carburetor throat on the
intake stroke.
Carburetor Operation Fuel Metering
&
Mixing
With the main diaphragm filled with fuel, the
carburetor meters the amount going into the
engine by using the high speed mixture screw
and the needle jet. Before entering the intake
port of the engine, the fuel is mixed with air to
further atomize it and increase its combustibility.
The metering and mixing operation is described
below: See Fig. 12.
SECONDARY
NEEDLE JET
DIAPHRAGM CAVITY
Figure 12
1. On the intake stroke, vacuum in the car-
buretor throat draws fuel from the main
diaphragm cavity. Note that as the intake
stroke begins, the main diaphragm cavity is
filled with fuel and that the diaphragm is
bowed toward the cover.
2. The fuel is drawn through the hole in the top
of the main diaphragm chamber and past the
high speed mixture screw. The high speed
mixture screw regulates the
maximum
amount of fuel that can enter the carburetor
throat.
3.
The fuel
is
then drawn past the secondary
needle which is attached to the throttle valve.
It moves with the throttle valve and regulates
the amount of fuel allowed into the car-
buretor throat in proportion with the throttle
setting.

 Loading...
Loading...











