Chapter 2 Configuring the Programmer
TransCore Proprietary
2–17
Generic/Non-AAR Tag Programming
This section applies to programming of non-AAR-compliant tags, with the permissions tag settings factory-
programmed to support this programming mode.
In this programming mode, the programmer does not enforce all of the restrictions described in “AAR Tag
Programming” on page 2–16. This mode permits nearly unrestricted programming of all user data bits in
the ATA/AAR frame data space in the rail tag, excluding the security characters. This mode’s programming
functions are summarized here:
• No rail tag owner look up or matching; all associated data in the permissions tag are ignored
• No security character lookup or matching in this mode, only non-secure characters may be
programmed (refer to “Table 10 6-Bit ASCII Codes” on page C–34); ignore all associated data in
the permissions tag
AP4119 Programmer CN and Permissions Tag ID Programming
During each tag programming operation, for both ATA and non-ATA data and addresses, the rail tag should
be programmed with adequate information to allow tracing of the most recent tag programming operation
to a specific programmer and/or permissions tag. Page 3 (hex address 0x18) of the rail tag is allocated for
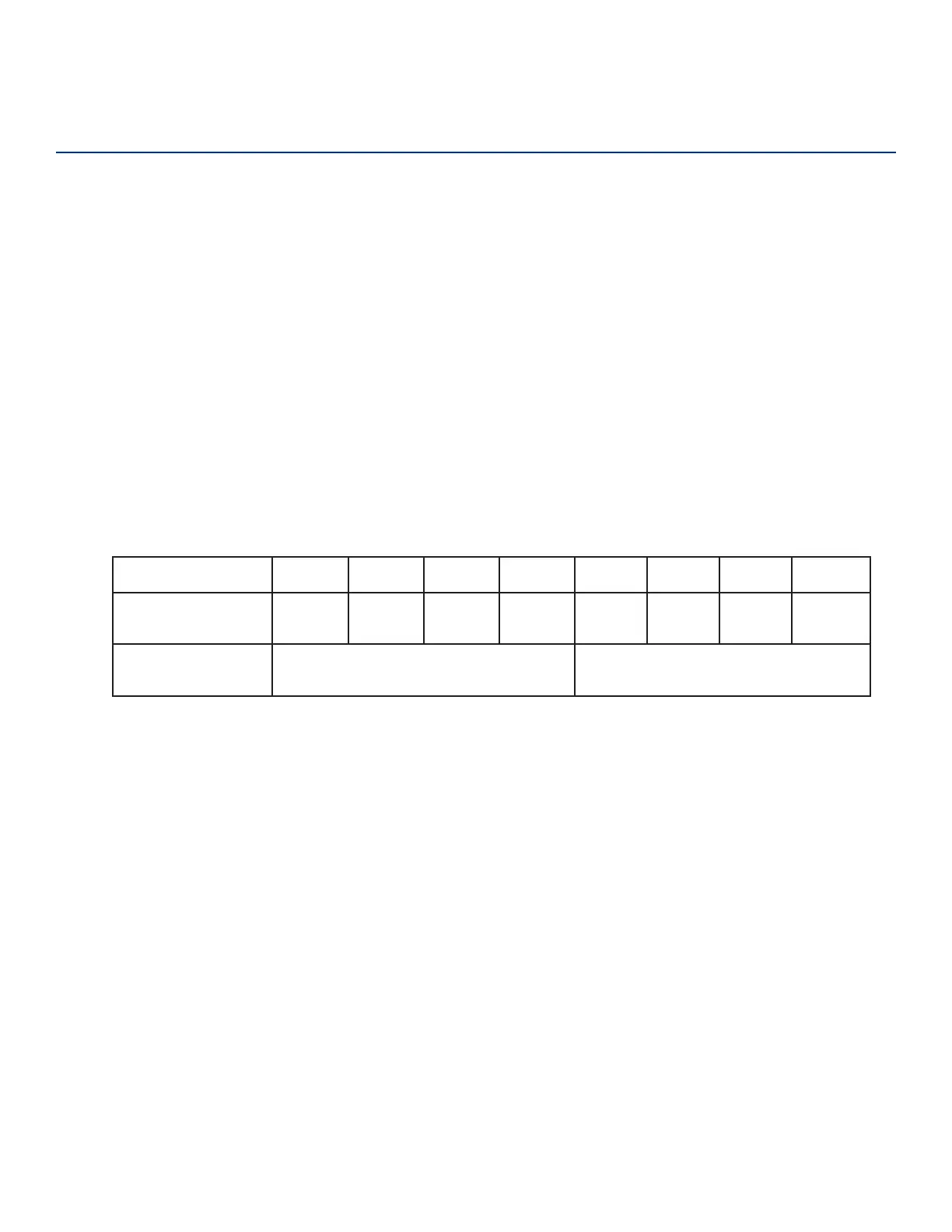
storing this information. Table 4 lists the Page 3 layout in the rail tag.
Table 4 Rail tag Page 3 layout
BYTE 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
7
Rail Tag Data
Address
0x18 0x19 0x1A 0x1B 0x1C 0x1D 0x1E
0x1F
Rail Tag Data
Values
Least-significant 4 bytes of the
PERMISSIONS TAG’s unique ID
Programmer CN (32 bits, 4 bytes)
(DWORD)
Safeguarding the Permissions Information
Once the AP4119 tag programmer is configured, keep the permissions tag and/or license certificate
available for future reference.

 Loading...
Loading...