7.2 Electrical Inspection
Inspect the control board and temperature sensor every 6 months for loose electrical connections and
circuit corrosion.
The steps to inspect the boards are as follows:
• Firmly tighten all the electrical contacts.
• Clean the electrical and control components with a brush or by using compressed dry air.
7.3 Main Components Maintenance
7.3.1 Evaporator Fan
Since the fan operates 24/7 throughout the year, any unusual airflow obstruction must be cleared in time
to avoid damage to the cooling system and other system components caused by reduced air volume.
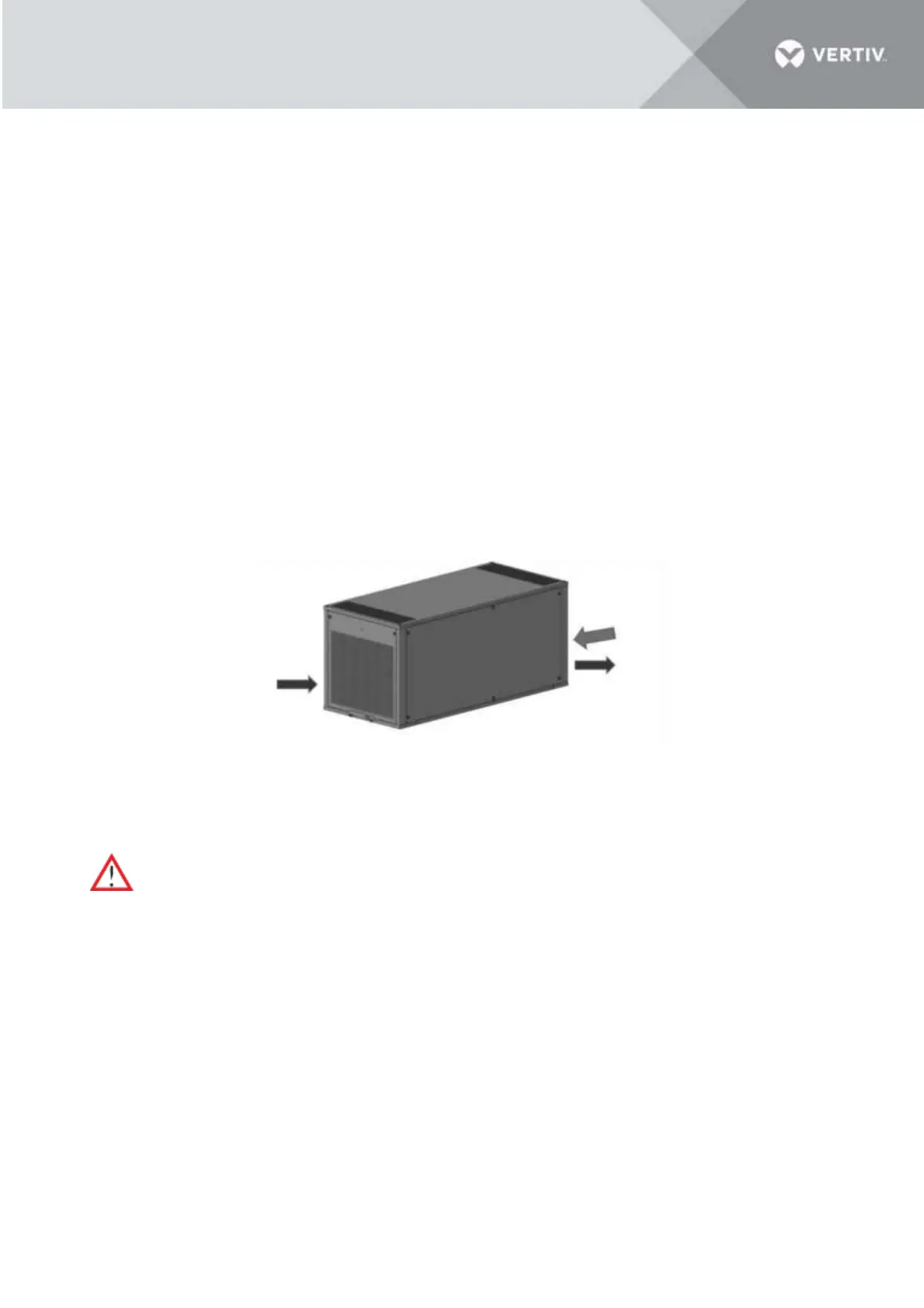
7.3.2 Air Cooled Condenser
There are times when the airflow through heat rejection unit is restricted. In such a scenario, use
compressed air to clean the dust and debris that inhibits airflow off the condenser. The compressed air
should be blown in the reverse airflow direction.
Figure 7-1 Condenser airflow direction
7.3.3 Compressor
CAUTION: Avoid touching or having skin contact with the residual gas and oils in the compressor.
Wear long rubber gloves to handle contaminated parts. The air conditioning system contains
refrigerant. The release of refrigerant is harmful to the environment.
The compressor faults can be categorized into two types:
• Motor faults (such as winding burnout, insulation failure, short circuit between coils, etc.)
• Mechanical faults (such as compressor failure, relief valve faults, etc.)
If the operating pressure is not established, it means that the compressor has failed. Confirm- that the
suction pressure and discharge pressure are balanced and verify that the motor does not rotate in reverse.
The controller is streamlined with capabilities like powerful alarm and protection functions to ensure safe
operation of the compressor. Periodic checks of high pressure and low pressure along with alarm
protection for such pressure-related issues should be carried out by maintenance personnel on a regular

 Loading...
Loading...