Note: stop running immediately, it may has mechanical damage.
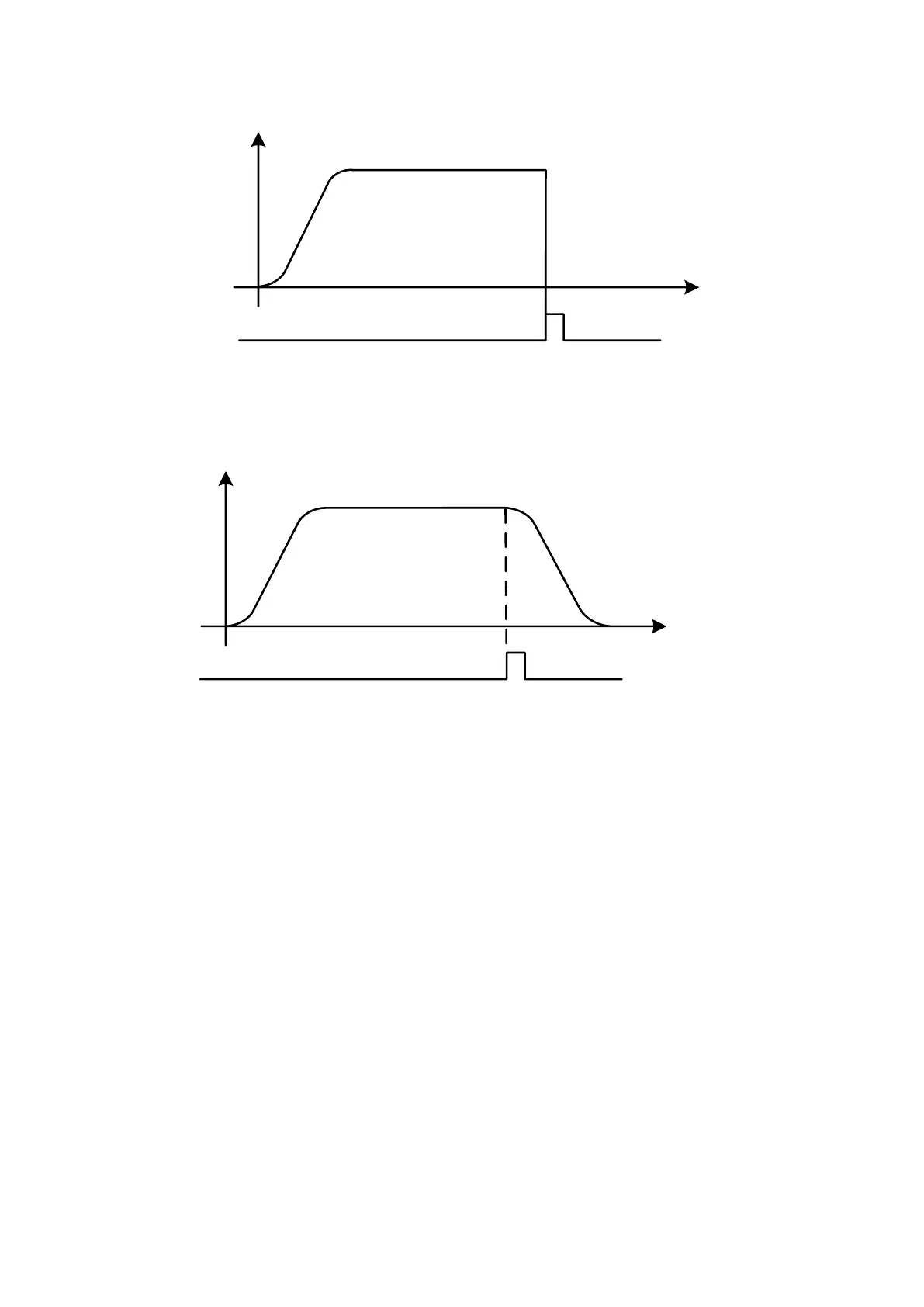
◆slow stop (K0):
When S0 is K0: decelerate as the time (SD2036+60*(N-1)), decelerate to stop.
◆fixed-length stop (positive value):
S0 is positive value: slow stop, deceleration distance S is set to positive value.
(1) If S is less than min deceleration distance Smin (calculate from deceleration time
SD2036+60*(N-1)), forward decelerate to stop, then reverse run the distance S.
(2) If S is larger than Smin, decelerate to stop. If the distance is too long, the motor will run
with constant speed then decelerate to stop.
(3) If S is larger than Smin and over the limit, the motor will take the limit position as the
target position.

 Loading...
Loading...