TECHNICAL NOTE
MOTION APPLICATION ENGINEERING GROUP
Yaskawa Electric America - 2121 Norman Drive South – Waukegan IL 60085
(800) YASKAWA - Fax (847) 887-7280
11/23/2005 12 of 12 eng/05.055/MCD
To further understand and evaluate motion programming methods, consider the table below.
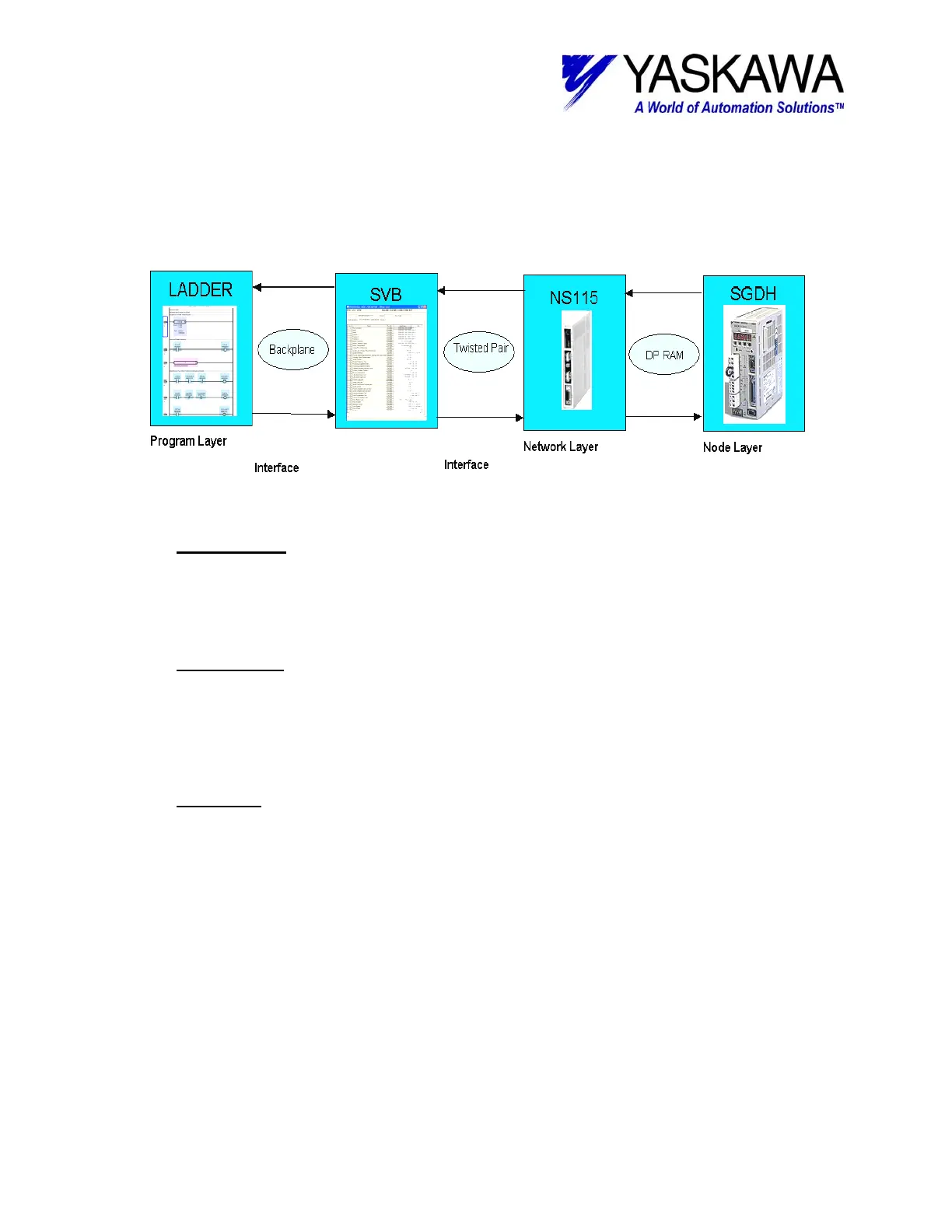
This diagram illustrates how logic in the controller is translated to motion via the SVB
components of a MP Controller system.
Overview of Motion from MP Controller Code to Amplifier
-The Program Layer can be broken down into High and Low scan priorities. Code efficiency
determines the ultimate scan rate. The interface between the Program Layer and Network Layer
is the SVB IF module. As the application program grows, performance of the segregated network
layer module is not affected. This is a key point for performance!
-The Network Layer
can be broken down into scalable scan rates and scalable data packet size.
Scan rates are determined by the quantity of axes and quantity of network interface cards.
Above eight axes, the system operates at a 2msec update rate, even for hundreds of axes. Data
sent down to the network card is further interpolated at the servo update rate. The interface
between Network Layer and Node layer is MechatrolinkII IF.
-The Node Layer
can be broken down into Servopack, I/O, and Inverter/ VFD nodes. For servo
motion control, the speed of the position loop update and local interpolation between commands
promote high performance, and ability to control any of the following: Rotary, Direct Drive, and
Linear Motors. The load, coupling, and transmission mechanics further determine overall
performance.
 Loading...
Loading...











