IM 12D07J01-10E-E
31
5.1. Calibration of the sensor
The conductivity sensors are factory calibrated
traceable to NIST standards. The cell constant
values are indicated on the sensor or on the
integral cable of the sensor. The cell constant
value can be entered directly in the Yokogawa
analyser. The procedure is explained in the
Instruction Manual of the analyser. If the sensor
has been subject to abrasion (erosion or coating)
in the process, re-calibration of the sensor may
be necessary. Refer to the Instruction Manual of
the analyser for a detailed description.
Note: During calibration the temperature
compensation is still active. This means
that the display reading refer to the
default reference temperature (25 °C).
Calibration is normally carried out by measuring
a solution with a known conductivity value at
a known temperature. These solutions are
commercially available. You can make your own
solution by dissolving an amount of salt in water.
Table 6 and 7 show some typical conductivity
values for Sodium Chloride (NaCl) and Potassium
Chloride (KCl) solutions which can be made,
preferably in a laboratory. The tables are derived
from the standards laid down in ‘International
Recommendation No. 56 of the Organisation
Internationale de Métrologie Legale’.
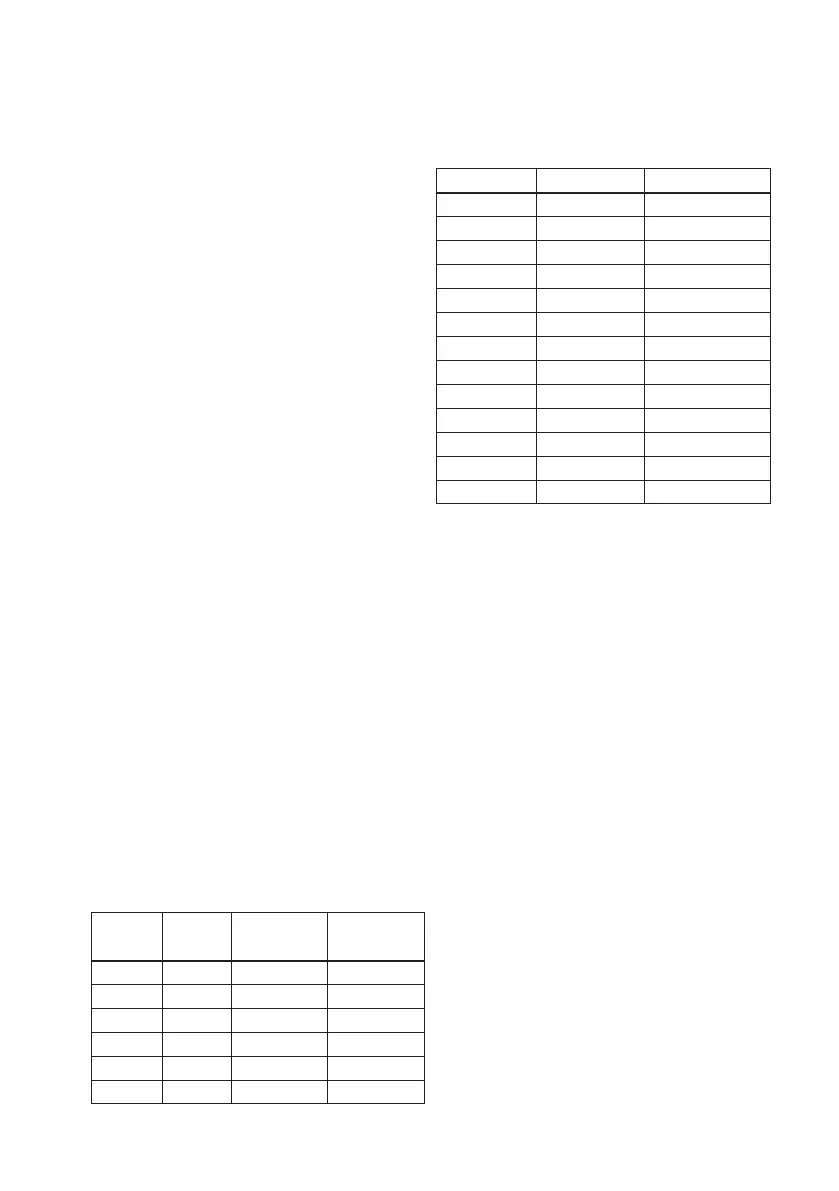
Table 6. KCl values at 25 °C (OIML)
Weigth % molal (m) mg of KCl / Conductivity
kg of solution
0.3 0.001 74.66 0.1469 mS/cm
0.5 0.002 149.32 0.2916 mS/cm
1 0.005 373.29 0.7182 mS/cm
3 0.01 745.263 1.4083 mS/cm
5 0.1 7419.13 12.852 mS/cm
10 1.0 71135.2 111.31 mS/cm
Table 7. NaCl values at 25 °C (IEC 746-1)
Weigth % mg/kg Conductivity
0.001 10 21.4 μS/cm
0.003 30 64.0 μS/cm
0.005 50 106 μS/cm
0.01 100 210 μS/cm
0.03 300 617 μS/cm
0.05 500 1.03 mS/cm
0.1 1000 1.99 mS/cm
0.3 3000 5.69 mS/cm
0.5 5000 9.48 mS/cm
1 10000 17.6 mS/cm
3 30000 48.6 mS/cm
5 50000 81.0 mS/cm
10 100000 40 mS/cm
5.2. Periodic maintenance of the sensor
In general conductivity sensors do not need
much periodic maintenance. In case the sensor
has become fouled, an insulating layer may be
formed on the surface of the electrodes, and
consequently giving a measuring error. Cleaning
the sensor will solve this problem. Effective
cleaning methods are given below:
1. Normal applications: hot water with some
commercially available washing-up liquid.
2. Lime, hydroxides or similar applications:
5 % solution of hydrochloride acid.
3. Organic (e.g. oils, fats) applications: alcohol
or iso-propanol.
4. Algae, bacteria or fungus: solution of
commercially available bleach (hypochlorite).
Note: Read the instructions on the package of
the cleaning agents for safe use.
5. GENERAL CALIBRATION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURE

 Loading...
Loading...