45
INSTALLATIONCONFIGURATIONOPERATION
FURTHER
INFORMATION
INDEX
APPENDIX A - Tips for success when networking ALIF units
ALIF units use multiple strategies to minimize the amount of data that they send
across networks. However, data overheads can be quite high, particularly when very
high resolution video is being transferred, so it is important to take steps to maximize
network efciency and help minimize data output. The tips given in this section have been
proven to produce very benecial results.
Summary of steps
• Choose the right kind of switch.
• Create an efcient network layout.
• Congure the switches and devices correctly.
Choosing the right switch
Layer 2 switches are what bind all of the hosts together in the subnet. However, they are
all not created equally, so choose carefully. In particular look for the following:
• Gigabit (1000Mbps) or faster Ethernet ports,
• Support for IGMP v2 (or v3) snooping,
• Support for Jumbo frames up to 9216-byte size,
• High bandwidth connections between switches, preferably Fibre Channel.
• Look for switches that perform their most onerous tasks (e.g. IGMP snooping) using
multiple dedicated processors (ASICS).
• Ensure the maximum number of concurrent ‘snoopable groups’ the switch can
handle meets or exceeds the number of ALIF transmitters that will be used to create
multicast groups.
• Check the throughput of the switch: Full duplex, 1Gbps up- and down- stream speeds
per port.
• Use the same switch make and model throughout a single subnet.
• You also need a Layer 3 switch. Ensure that it can operate efciently as an IGMP
Querier.
Layer 2 (and 3) switches known to work
• Cisco 2960
• Cisco 3750
• Cisco 4500
• Cisco 6500
• Extreme Networks X480
• HP Procurve 2810
• HP Procurve 2910
• H3C 5120
Creating an efcient network layout
Network layout is vital. The use of IGMP snooping also introduces certain constraints, so
take heed:
• Keep it at. Use a basic line-cascade structure rather than a pyramid or tree
arrangement (see note below).
• Keep the distances between the switches as short as possible.
• Ensure sufcient bandwidth between switches to eliminate bottlenecks.
• Where the A.I.M. server is used to administer multiple ALIF transceivers, ensure the
A.I.M. server and all ALIF units reside in the same subnet.
• Do not use VGA to DVI converters, instead replace VGA video cards in older systems
with suitable DVI replacements. Converters cause ALIF TX units to massively increase
data output.
• Stackable switches will allow you to create more ports at each cascade level.
• Wherever possible, create a private network.
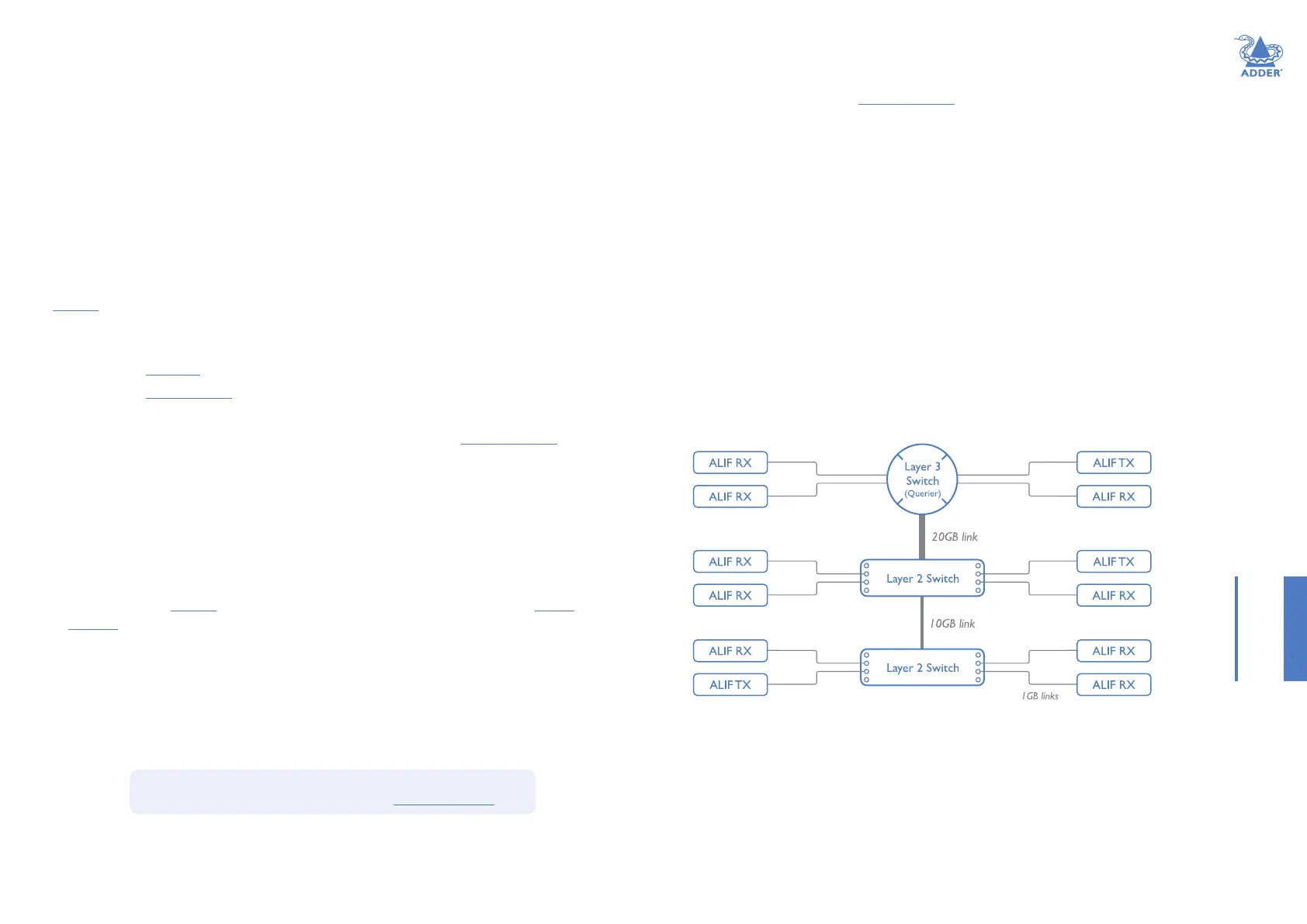
The recommended layout
The layout shown below has been found to provide the most efcient network layout for
rapid throughput when using IGMP snooping:
Note: From rmware version 3.0, tree and hierarchical structures of network switches are
also supported. The Transmitter now joins its own multicast group so there is always a route
from the querier to the transmitter which was previously missing in rmware versions 2.9 and
below.
• Use no more than two cascade levels.
• Ensure high bandwidth between the two L2 switches and very high bandwidth
between the top L2 and the L3. Typically 10GB and 20GB, respectively for 48 port L2
switches.
continued
For the latest list of switches known to work with ALIF and
setup instructions for them, please go to www.adder.com
• HuaWei Quidway
s5328c-EI
(Layer 3 switch)

 Loading...
Loading...