Multi-Axis Coordinated Motion Instructions
472 Rockwell Automation Publication MOTION-RM002H-EN-P-February 2018
How Stop Types Affect Transforms an Axis Motion Example
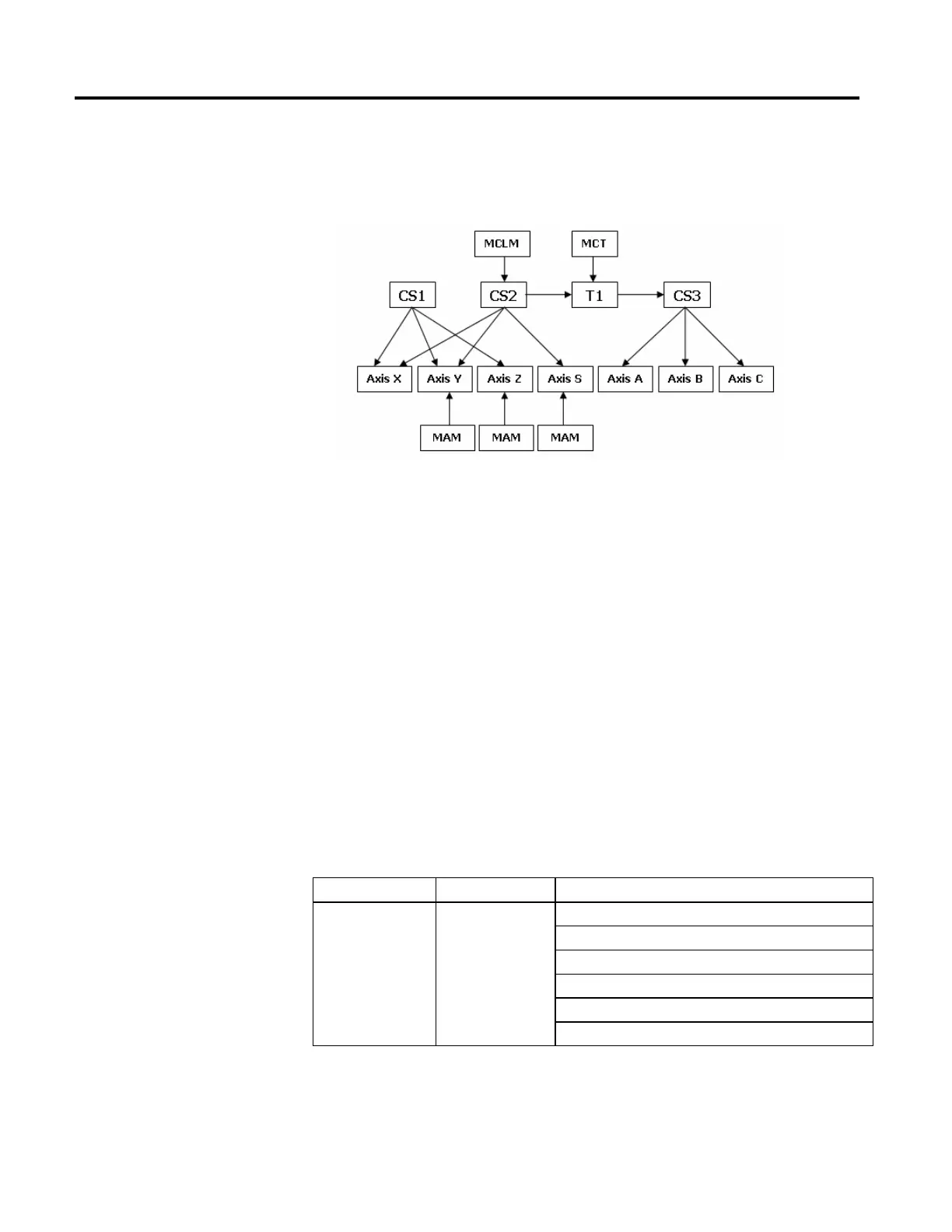
Suppose you have this situation.
Where:
• Coordinate system 1 (CS1) contains the X, Y, and Z axes.
• Coordinate system 2 (CS2) contains the Y, Z, and S axes.
• Coordinate system 3 (CS3) contains the A, B, and C axes.
• Transform (T1) links source coordinate CS2 to target CS3.
• CS2 (XYS) axes are mapped to CS3 (ABC) axes.
• MAM instructions executed on the Y, Z, and S axes.
• MCLM instruction executed on CS2.
• MCT instruction executed with CS2 as the source and CS3 as the target.
• No coordinate instructions were executed on CS2 or CS3.
This table shows the results of executing various MCS and MAS instructions with
different stop types.
Instruction Stop Type Result
MCS on CS1 All The MCLM instruction on CS2 will stop.
The MAM on Y will stop.
The MAM on Z will stop.
The MAM on S will continue.
T1 is canceled.
Axes ABC will stop due to canceling the transform.

 Loading...
Loading...