Astraada DRV-24 frequency inverters Installation guidelines
20
Figure 3-13 PNP modes
3.3 Layout protection
3.3.1 Protecting the inverter and input power cable in short-circuit situations
Protect the inverter and input power cable in short circuit situations and against thermal overload.
Arrange the protection according to the following guidelines.
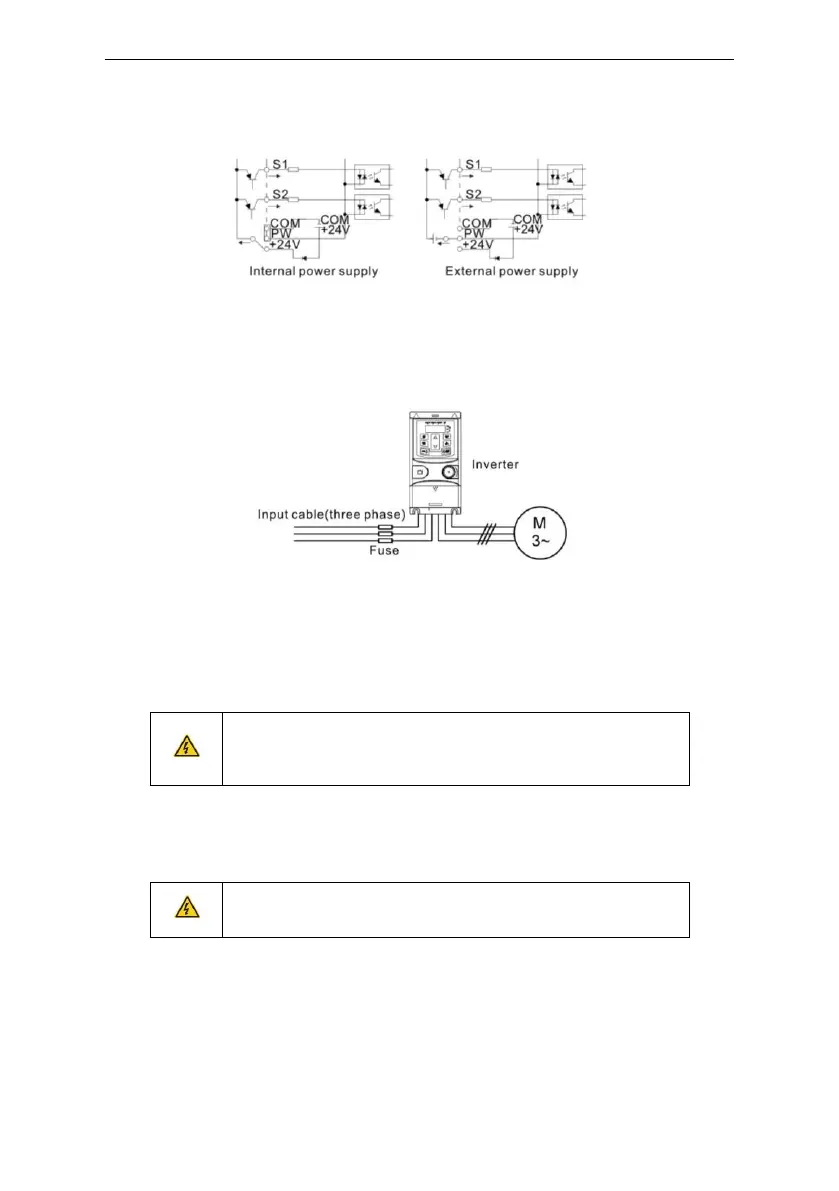
Figure 3-14 Fuse configuration
Note: Select the fuse as the manual indicated. The fuse will protect the input power cable from
damage in short-circuit situations. It will protect the surrounding devices when the internal of the
inverter is short circuited.
3.3.2 Protecting the motor and motor cables
The inverter protects the motor and motor cable in a short-circuit situation when the motor cable is
dimensioned according to the rated current of the inverter. No additional protection devices are
needed.
If the inverter is connected to multiple motors, a separate thermal
overload switch or a circuit breaker must be used for protecting each
cable and motor. These devices may require a separate fuse to cut off
the short-circuit current.
3.3.3 Implementing a bypass connection
It is necessary to set power frequency and variable frequency conversion circuits for the assurance
of continuous normal work of the inverter if faults occur in some significant situations.
In some special situations, for example, if it is only used in soft start, the inverter can be conversed
into power frequency running after starting and some corresponding bypass should be added.
Never connect the supply power to the inverter output terminals U,
V and W. Power line voltage applied to the output can result in
permanent damage to the inverter.
If frequent shifting is required, employ mechanically connected switches or contactors to ensure
that the motor terminals are not connected to the AC power line and inverter output terminals
simultaneously.
 Loading...
Loading...