AT90S2313
38
EEPROM Address Register - EEAR
•
Bit 7 - Res: Reserved bit
This bit is a reserved bit in the AT90S2313 and will always read as zero.
•
Bit 6..0 - EEAR6..0: EEPROM Address
The EEPROM Address Register - EEAR6..0 - specifies the EEPROM address in the 128 bytes EEPROM space. The
EEPROM data bytes are addressed linearly between 0 and 127.
EEPROM Data Register - EEDR
•
Bit 7..0 - EEDR7..0: EEPROM Data
For the EEPROM write operation, the EEDR register contains the data to be written to the EEPROM in the address given
by the EEAR register. For the EEPROM read operation, the EEDR contains the data read out from the EEPROM at the
address given by EEAR.
EEPROM Control Register - EECR
•
Bit 7..3 - Res: Reserved bits
These bits are reserved bits in the AT90S2313 and will always read as zero.
•
Bit 2 - EEMWE: EEPROM Master Write Enable
The EEMWE bit determines whether setting EEWE to one causes the EEPROM to be written. When EEMWE is set(one)
setting EEWE will write data to the EEPROM at the selected address If EEMWE is zero, setting EEWE will have no effect.
When EEMWE has been set (one) by software, hardware clears the bit to zero after four clock cycles. See the description
of the EEWE bit for a EEPROM write procedure.
•
Bit 1 - EEWE: EEPROM Write Enable
The EEPROM Write Enable Signal EEWE is the write strobe to the EEPROM. When address and data are correctly set up,
the EEWE bit must be set to write the value into the EEPROM. The EEMWE bit must be set when the logical one is written
to EEWE, otherwise no EEPROM write takes place. The following procedure should be followed when writing the
EEPROM (the order of steps 2 and 3 is unessential):
1. Wait until EEWE becomes zero.
2. Write new EEPROM address to EEAR (optional)
3. Write new EEPROM data to EEDR (optional)
4. Write a logical one to the EEMWE bit in EECR
5. Within four clock cycles after setting EEMWE, write a logical one to EEWE.
When the write access time (typically 2.5 ms at V
CC
= 5V or 4 ms at V
CC
= 2.7V) has elapsed, the EEWE bit is cleared
(zero) by hardware. The user software can poll this bit and wait for a zero before writing the next byte. When EEWE has
been set, the CPU is halted for two cycles before the next instruction is executed.
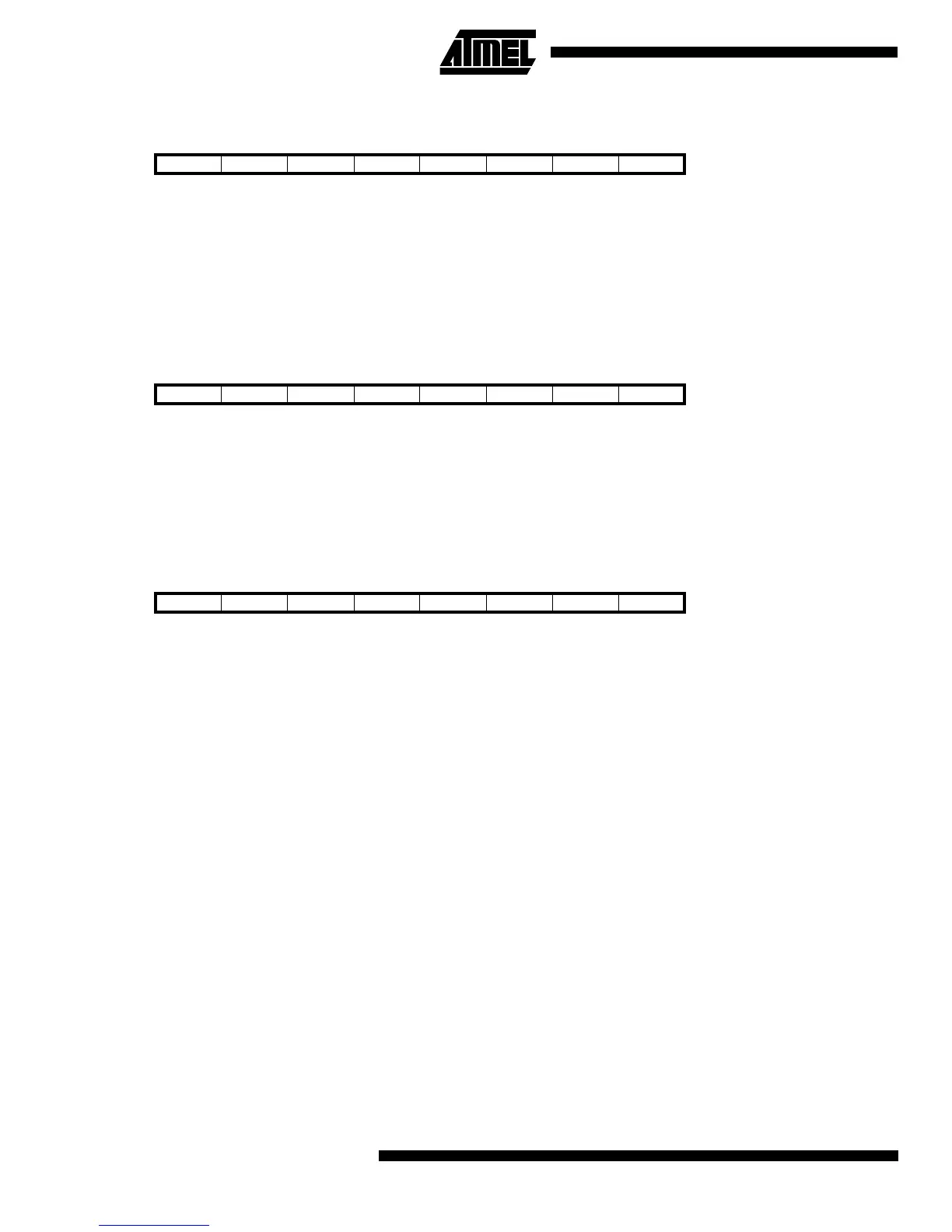
Bit 76543210
$1E ($3E) - EEAR6 EEAR5 EEAR4 EEAR3 EEAR2 EEAR1 EEAR0 EEAR
Read/Write R R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Initial value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 76543210
$1D ($3D) MSB LSB EEDR
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Initial value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 76543210
$1C ($3C) - - - - - EEMWE EEWE EERE EECR
Read/Write R R R R R R/W R/W R/W
Initial value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
 Loading...
Loading...