6 Parameter Settings and Functions
© Copyright Reserved Autonics Co., Ltd. 57
6.3.3 PID control
PID control is a combination of proportional (P), integral (I), and derivative (D) controls and offers
superb control over control subjects, even with a delay time.
Proportional control (P) implements smooth, hunting-free control; integral control (I)
automatically corrects offsets; and derivative control (D) speeds up the response to disturbance.
Through these actions, PID control realizes ideal temperature control.
How to apply PID control
Proportional (P) control: Set both integral and derivative times to 0 after PID control is
selected.
Proportional-Integral (PI) control: Set the derivative time to 0 after PID control is selected.
Proportional-Derivative (PD) control: Set the integral time to 0 after PID control is selected.
When using the multi-SV function, the same PID time constant will be applied to SV0 to
SV3.
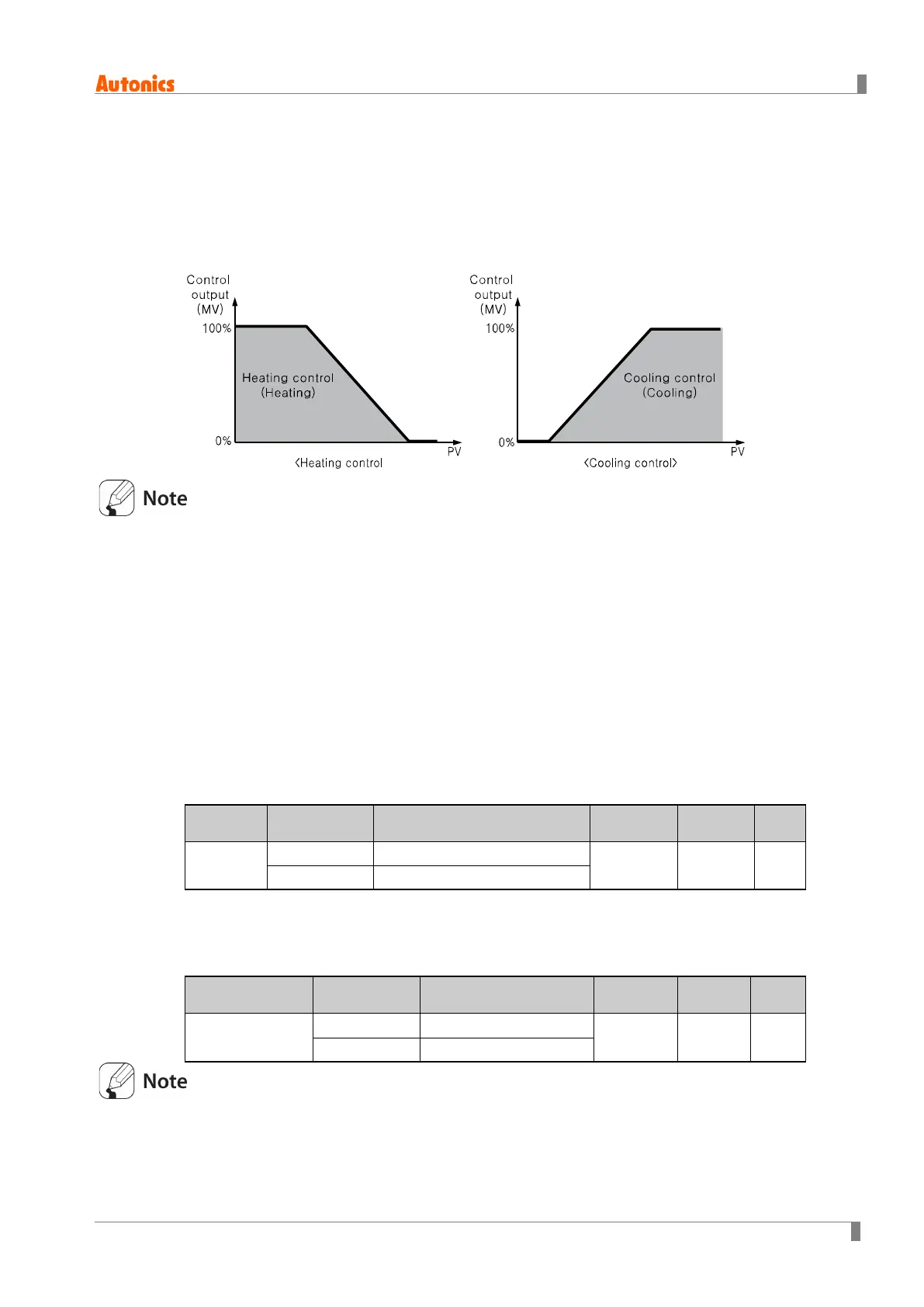
6.3.3.1 Proportional band
When PV (present value) is within the proportional band (P), the ON/OFF ratio needs to be
adjusted during the proportional period (T). The defined proportional control (time proportional
control) section is referred to as the proportional band.
Parameter
Unit
Control
Operation
Heating, PID Heating_Proportional Band
0.1 to
999.9
10.0
℃/℉
Cooling, PID Cooling_Proportional Band
6.3.3.2 Integral time
MVs from integral and proportional operation become the same when deviation is consistent.
The time taken for the two MVs to match is called the integral time.
Setting group
Parameter
Unit
Control
Operation
Heating, PID Heating_Integral Time
0 to 9999 0 Sec.
Cooling, PID Cooling_Integral Time
Integral control is not conducted if the integral time is set to 0.
Setting the integral time too short can intensify Correction Movements and cause hunting.
 Loading...
Loading...











