7-6
Chapter 7. SPECIFICATIONS
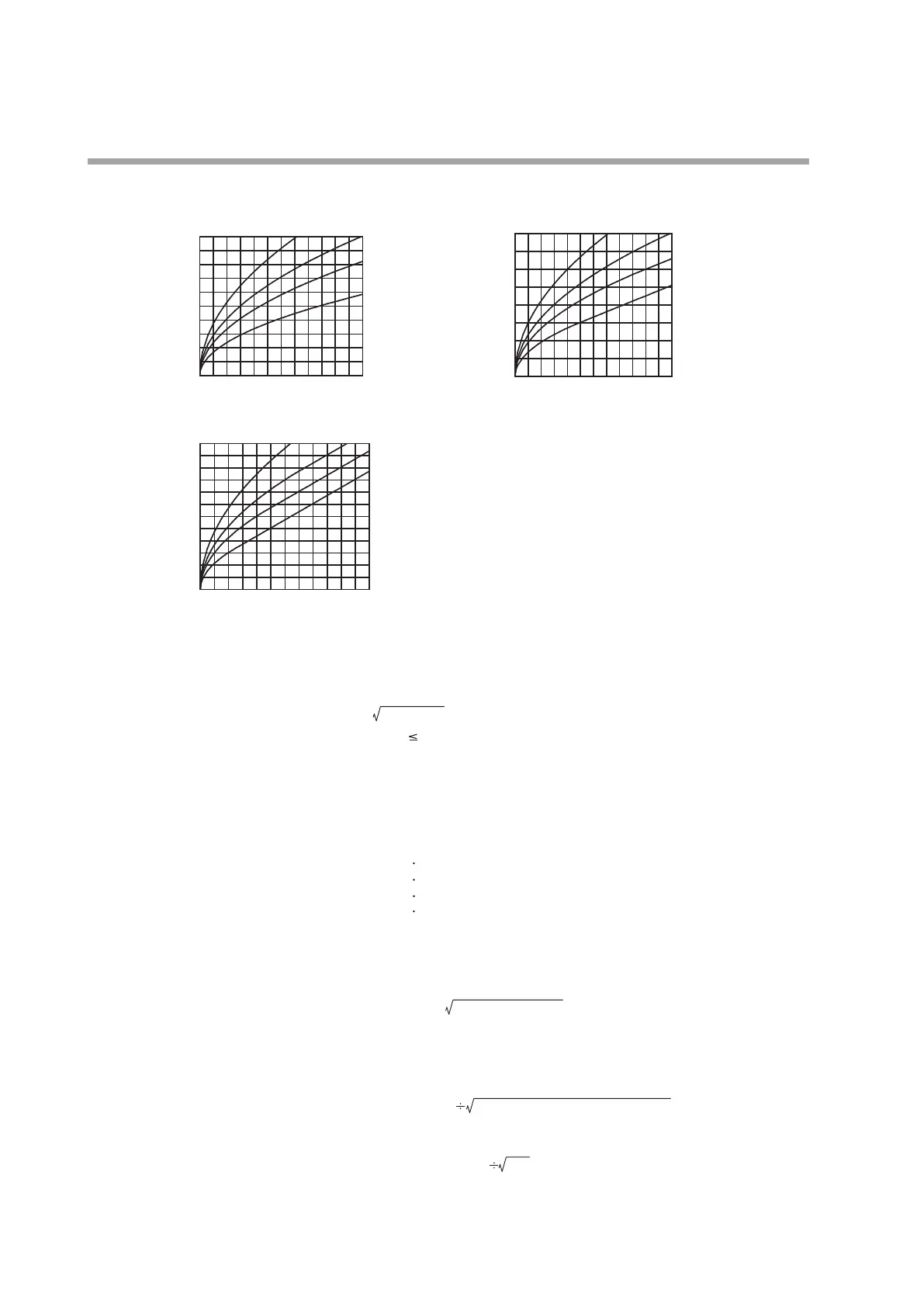
Relationship between flowrate and differential pressure with valve fully opened (in air)
Four parameter show outlet pressure.
MPC9500 MPC0002/0005
MPC0020
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
0 40 80 120 160 200 240
Flowrate [L/min(standard)]
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
Flowrate [L/min(standard)]
Dirential pressure [kPa]
Dirential pressure [kPa]
0
2
4
6
8
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Flowrate [L/min(standard)]
150 kPa(gauge)
150 kPa(gauge)
50 kPa(gauge)
150 kPa(gauge) 50 kPa(gauge)
0 kPa(gauge)
-50 kPa(gauge)
0 kPa(gauge)
-50 kPa(gauge)
50 kPa(gauge)
0 kPa(gauge)
-50 kPa(gauge)
Dirential pressure [kPa]
• If the outlet pressure is diffrent from the values graphed on the above,
calculate the flowrate using the appropriate formula below.
(1) When P2 / P1 > 0.53,
Q=C1 (P1-P2) X P2
(2) When P2 / P1 0.53,
Q=C2 X P1
P1: Inlet absolute pressure [kPa (abs)]
P2: Outlet absolute pressure [kPa (abs)]
(Absolute pressure =gauge pressure +atmospheric pressure)
Q: Flowrate [L/min (standard)]
C1 and C2: Constant values by model
MPC 9500 : C1=0.01054, C2=0.00526
MPC 0002 : C1=0.05971, C2=0.02981
MPC 0005 : C1=0.05971, C2=0.02981
MPC 0020 : C1=0.16740, C2=0.08357
Example : When using the MPC0020 with inlet pressure = 120 kPa (gauge) and outlet pressure
= 0 kPa (gauge),
P1 = 221.3 kPa (abs), P2 = 181.3 kPa (abs)
P2 / P1 = 0.819
Q = 0.1674 X (221.3 - 181.3) X 181.3
= 14.3 [L/min (Standard)]
• When used with the gases other than air, convert the flowrate using the
following formula :
Flowrate = Flowrate in air specic gravity of gas to be controlled
Example : When using the
MPC
0020 with
CO
2, inlet pressure = 100
kPa (gauge) and outlet pressure
= 0 kPa (gauge)
16.8 L /min (standard) 1.53 = 13.6 L /min (standard)
Specific gravity standard compatible gas (air is taken as 1.0)
Argon = 1.38
Carbon dioxide (CO
2
) = 1.53

 Loading...
Loading...