Chapter 1 Overview of CSS SSL
Overview of the SSL Module Functions in the CSS
1-10
Cisco Content Services Switch SSL Configuration Guide
OL-5655-01
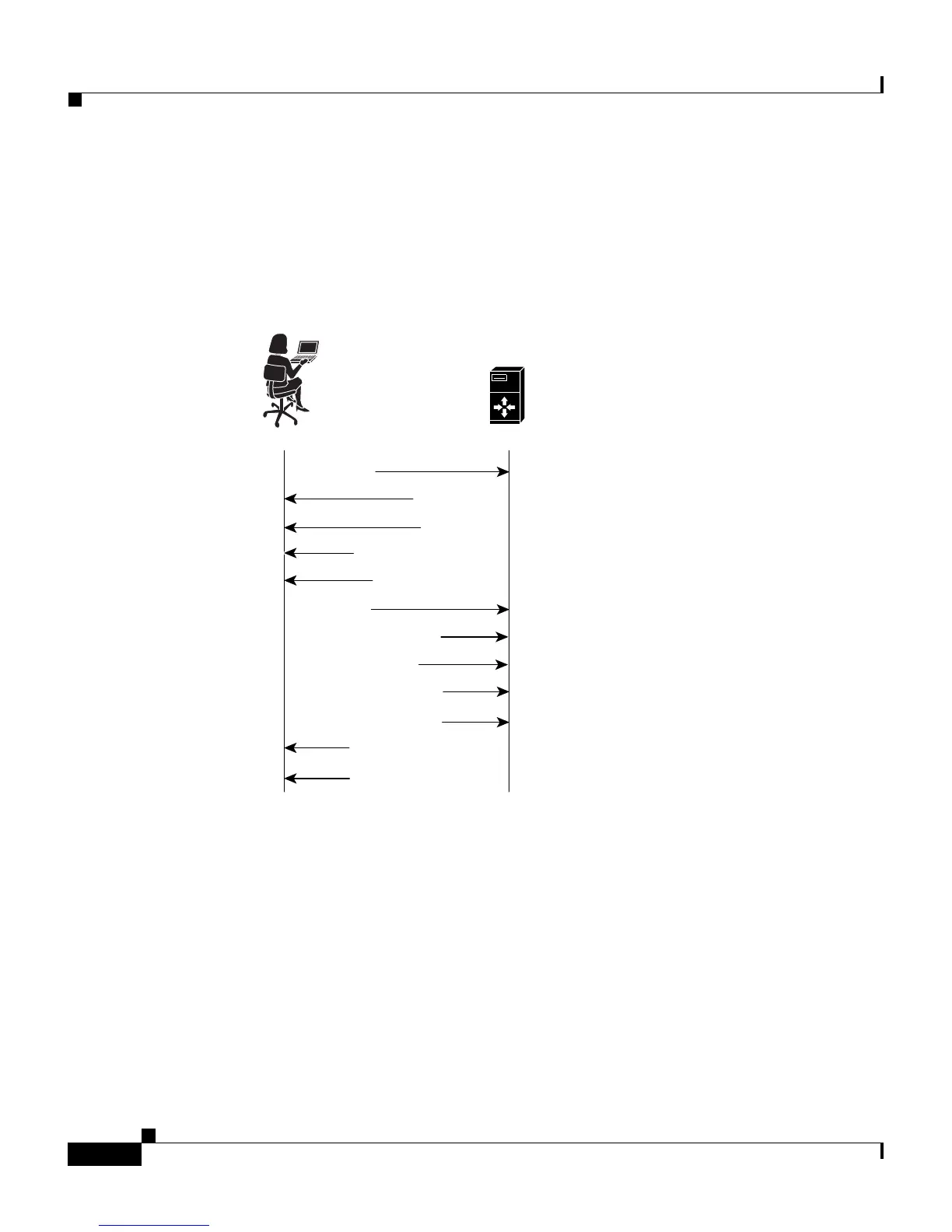
For a client to send a certificate, the server must include a certificate request
(CertificateRequest) message in the handshake as shown in Figure 1-2. The
request message includes which types of certificates the server accepts. However,
this message does not identify certificate authorities.
Figure 1-2 SSL Handshake With Client Authentication
After the server sends the ServerHelloDone message, the client responds with its
certificate (Certificate) and key exchange. Then the client sends a
CertificateVerify message that contains a digest of all the handshake messages
from the server and was signed using the client public key. The server decrypts
the message using the client public key ensuring that the client possesses the
correct private key.
The CertificateVerify message does not check the authenticity of the certificate.
However, it does check that the public portion of the client private key matches
what is embedded in the certificate. This ensures that the client possesses the
keypair that used to generate the certificate, and is not passing someone else’s
certificate. However, the CSS can check whether the issuer signature is authentic.
119228
SSL Client SSL Server
ClientHello
ServerHello
Certificate
ServerHelloDone
ClientKeyExchange
ChangeCipherSpec
Finished (encrypted)
ChangeCipherSpec
Finished (encrypted)
Certificate
CertificateVerify
CertificateRequest

 Loading...
Loading...