18
OPERATIONS
Before operating the table saw make sure
you have performed the important
adjustments and all the guards are in place.
Rip Cutting
Cutting solid wood with the grain or with
plywood cutting down the length of the
work-piece is called rip cutting.
Adjust the fence on the rails, according to
the width of the cut on the work-piece and
turn the hand-wheel to set the blade
approximately ¼” above the work-piece.
Use safety devices such as feather boards
to prevent kick back
Now, turn the table saw ON and use a push
stick to push the work-piece against the
blade.
Crosscutting
Cutting solid wood across the grain and in
plywood or metal cutting across the width of
the work-piece is called crosscutting.
Mark the work-piece where you want to
start the cut from and make sure the mitre
gauge is at a 90° position on the mitre slot.
Place the work-piece on the table so that
the marked point is aligned with the blade
and hold the work-piece against the mitre
gauge and turn the hand-wheel to set the
blade approximately ” above the work-
piece. Turn the table saw ON and feed the
work-piece against the blade.
Miter Cuts
Miter cut is an angled crosscut. It is done in
the same manner as crosscuts but using
mitre gauge.
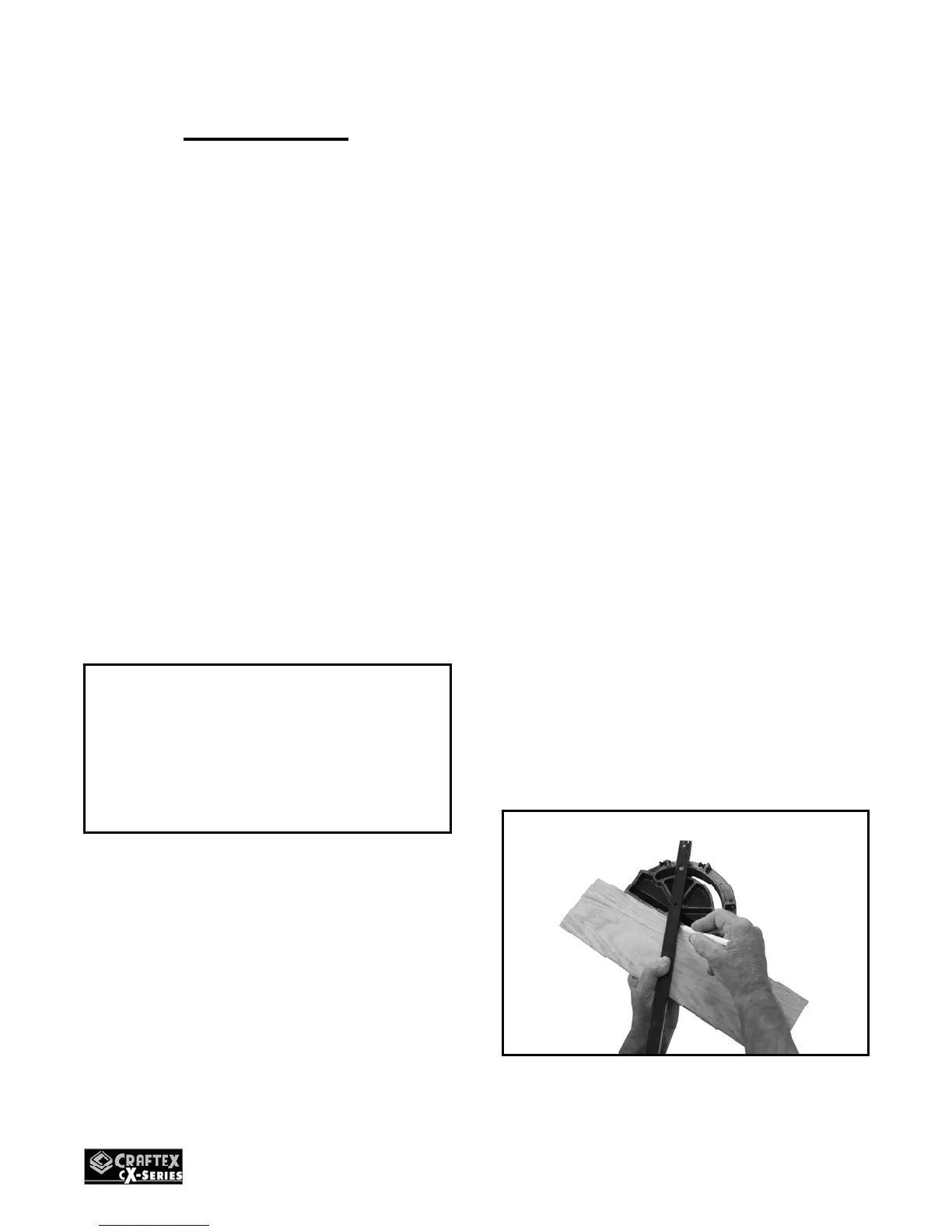
Make sure all the guards are in place and
place the miter gauge face against the edge
of the work piece and place the bar of the
miter gauge on the work piece. Use the bar
and mark the angle of your cut with a
pencil.
Figure-198 Marking the angle of the cut
WARNING
Do not use your fingers to feed a narrow
work-piece into the blade. If you slip,
your fingers might go against the blade.
Always use a push stick.
 Loading...
Loading...