System design recommendations
Refrigerant charge limit Danfoss SM / SY / SZ compressors can tolerate
liquid refrigerant up to a certain extend
without major problems. However, excessive
liquid refrigerant in the compressor is always
unfavorable for service life. Besides, the
installation cooling capacity may be reduced
because of the evaporation taking place in the
compressor and/or the suction line instead of the
evaporator. System design must be such that the
amount of liquid refrigerant in the compressor
is limited. In this respect, follow the guidelines
given in the section: “essential piping design
recommendations” in priority.
Use the tables below to quickly evaluate the
required compressor protection in relation with
the system charge and the application.
More detailed information can be found in the paragraphs hereafter. Please contact Danfoss
Technical Support for any deviation from these guidelines.
O-cycle migration O-cycle refrigerant migration is likely to occur
when the compressor is located at the coldest
part of the installation, when the system uses
a bleed-type expansion device, or if liquid is
allowed to migrate from the evaporator into
the compressor sump by gravity. If too much
liquid refrigerant accumulates in the sump it
will saturate the oil and lead to a ooded start:
when the compressor starts running again,
the refrigerant evaporates abruptly under the
sudden decrease of the bottom shell pressure,
causing the oil to foam. In extreme situations,
this might result in liquid slugging (liquid
entering the scroll elements), which must be
avoided as it causes irreversible damage to the
compressor.
Danfoss SM/SZ/SY scroll compressors can
tolerate occasional ooded starts as long as
the total system charge does not exceed the
maximum compressor refrigerant charge.
A suitable test to evaluate the risk of o-cycle
migration is the following:
• Stabilize the non running system at 41°F
ambient temperature,
• Raise the ambient temperature to 68°F and
keep it for 10 minutes,
• Start the compressor and monitor sump
temperature, sight glass indication and sound
level.
The presence of liquid in the crankcase can be
easily detected by checking the sump level
through the oil sight glass. Foam in the oil sump
indicates a ooded start.
A noisy start, oil loss from the sump and sump
cool down are indications for migration.
Depending on the amount of migration graduate
measures shall be taken:
• Sump heater
• Liquid line solenoid valve
• Pump down cycle
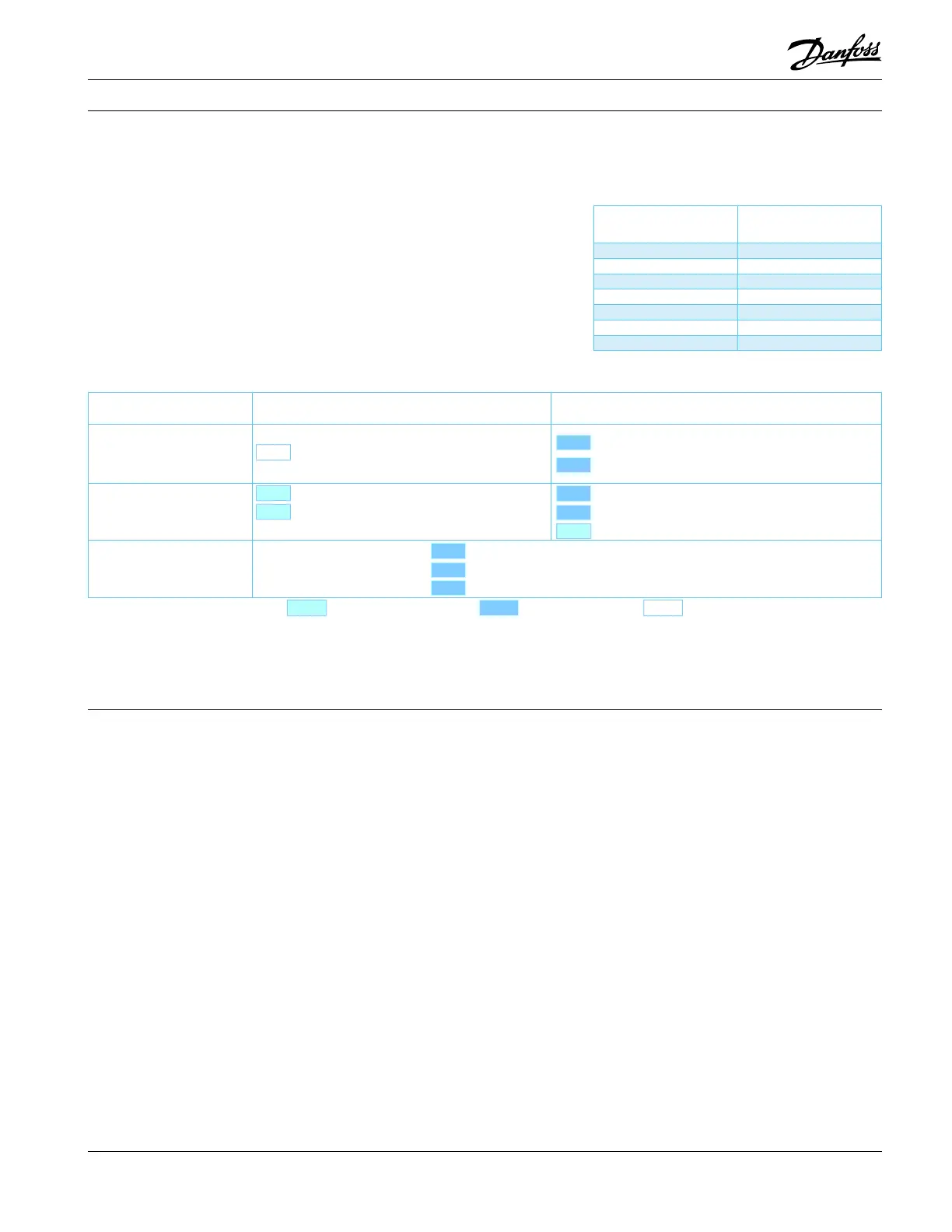
REQREC
BELOW charge limit ABOVE charge limit
Cooling only systems,
Packaged units
No test or additional safeties required
Refrigerant migration & oodback test
Sump heater
Cooling only systems
with remote condensor
and split system units
Refrigerant migration & oodback test
Crankcase heater, because full system
charge is not denable (risk of overcharging)
Refrigerant migration & oodback test
Sump heater
Liquid receiver (in association with LLSV & pump down)
Reversible heat pump system
Specic tests for repetitive oodback
Sump heater
Defrost test For more details refer to section "Reversible heat pump system.
Recommended Required No test or additional safeties required
Note: for special conditions such as low ambient temperature, low refrigerant load or brazed plate heat exchangers please refer
to corresponding section "Specic application recommendations".
REC
REC
REQ
REQ
REQ
REQ
REQ
REQ
REQ
REC
Compressor models
Refrigerant charge limit
(lbs)
S 084-090-100 19
S 110-120 22
S 112-124-147 17
S 148-161 28
S 175-185 30
S 240 35
S 300-380 44
33
FRCC.PC.003.A5.22
Application guidelines
 Loading...
Loading...











