CP80 and CP80 Plus Service Manual 2-19
Reading Data
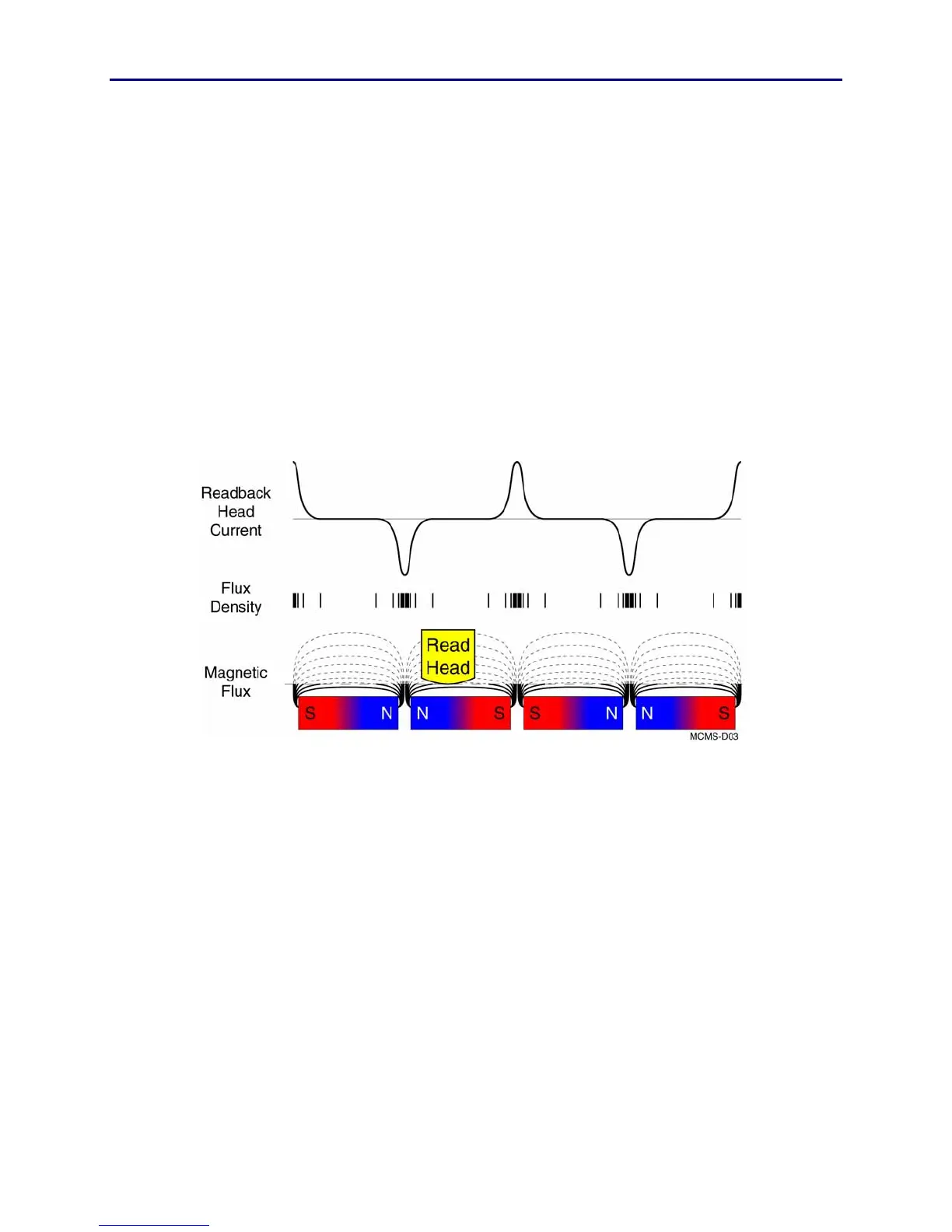
To read the magnetic information from a card, the magnetic field on the card is
used to generate a current in the magnetic head. This is possible because a
moving magnetic field induces a current (or voltage) in a conductor.
The magnitude of the current is dependant on the rate of change of the magnetic
field passing by the head. The greater the change, the larger the current. A simple
way of understanding this is that current will be induced when the read head
cuts through a line of flux. When the read head is traveling parallel to a flux line,
no current will be induced.
Because the flux density is greatest at the poles of a magnet, the current will also
be greatest as the magnetic pole passes below the head. This is illustrated in the
drawing below. If the magnetic stripe were comprised of a single north-to-south
magnet, no current would be induced in the magnetic head for the majority of
the length of the card.
When two north poles or two south poles are adjacent to one another, the
magnetic field is compressed and becomes even more dense. The higher the
density of the magnetic field, the larger the current induced in the magnetic
head.
For this reason, magnetic data is comprised of Transition Points where the
polarity of the magnetism reverses, which results in north-to-north or south-to-
south polarity.

 Loading...
Loading...