AH Motion Controller – Operation Manual
7-14
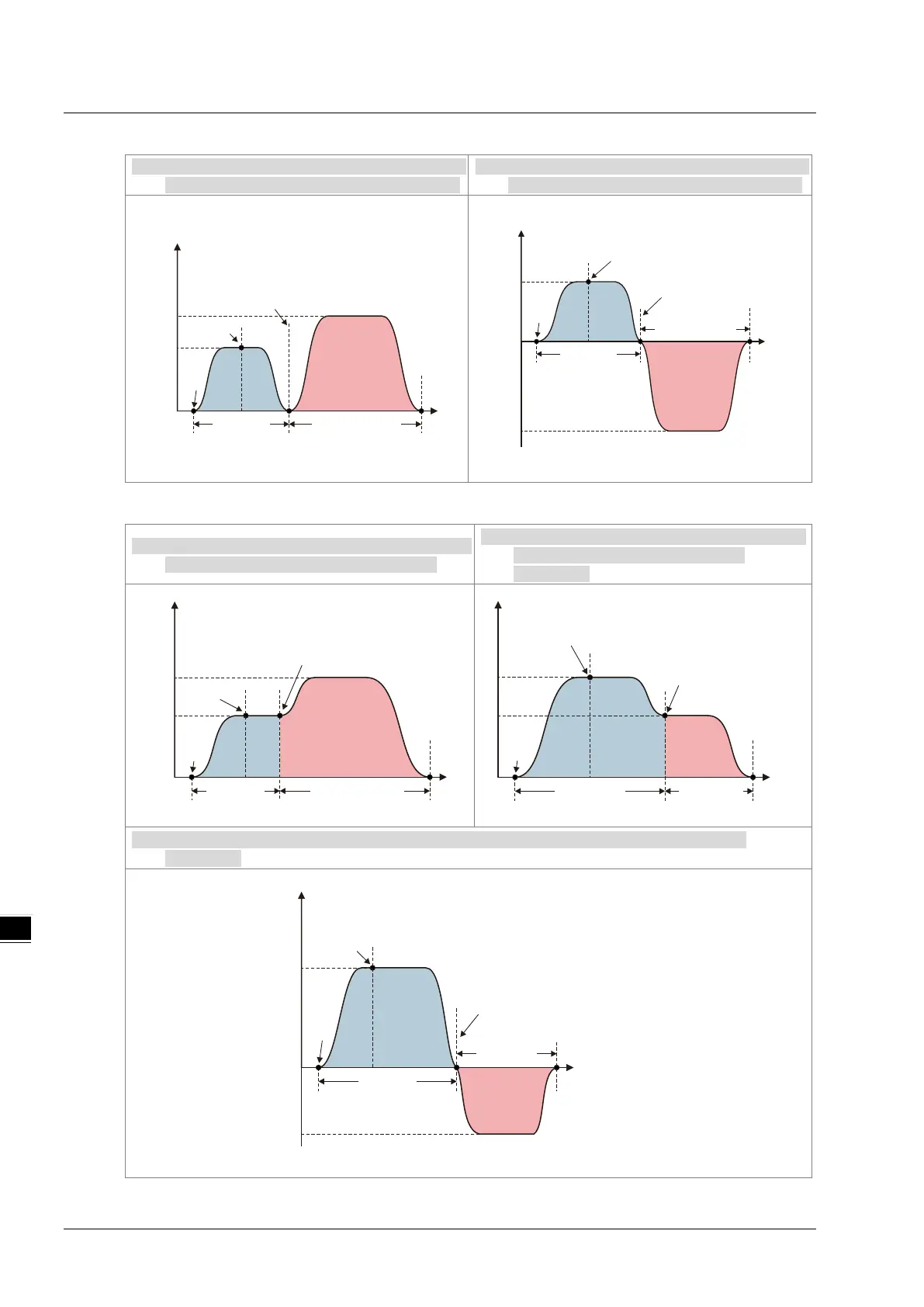
Buffermode = mcBuffered: see the two examples below.
1.
When the direction of the buffered instruction
is the same as that of the current instruction
2. When the direction of the b
uffered instruction
is opposite to that of the current instruction.
t
Cur rent
instruction
is started
When current i nstruction execution
is completed, the buffered instruction
starts to controlthe axis.
Buffered instruction
V
Current
instruction
The buffered
instruction
is started
V
2
V
1
S1
S2
t
When cur rent instruction execution is
is compl eted, t he buffered instruction
starts to control the axis.
Buffer ed instruction
V
Current
instruction
is started
Current
instruction
The buffer ed
instruction
is started
V
1
V
2
S1
S2
Buffermode = mcBlendingLow: see the three examples below.
1. When the velocity of the current instruction is
less than that of the buffered instruction.
2. When the velocity of the current instruction
is greater than that of the buffered
t
Buffered instruction
V
Current
instruction
is started
Cur rent
instruction
The buffered
instruction
is started
The buffered instruction starts to control
the axis when current instruction execution
is completed and the axis velocity is the lower
of the two instruction velocities.
V
2
V
1
S1
S2
t
Bufferedinstruction
V
Curr ent
instruction
is started
Curr ent
instruction
The buffered
instruction
is started
The buffered i nstruction starts to control the axi s
when cur rent instruction execution is completed
and the axis velocity is the lower of the
two instruction velocities.
V
1
V
2
S1
S2
3. When the velocity direction of the current instruction is opposite to that of the buffered
t
Buffered instruction
V
Current
instruction
is started
Current
instruction
The buffer ed
instruction
is started
The motion directions of current instruction
and buffered instruction are opposite.
The buffered instruction starts to control the
axis w hen current instruction
decelerates till the velocity is 0.
V
1
V
2
S1
S2

 Loading...
Loading...











