Proteus 1000 Operation Manual 61
Programming Basics
Low Frequency Oscillators (LFOs)
Low
Frequency
Oscillators
(LFOs)
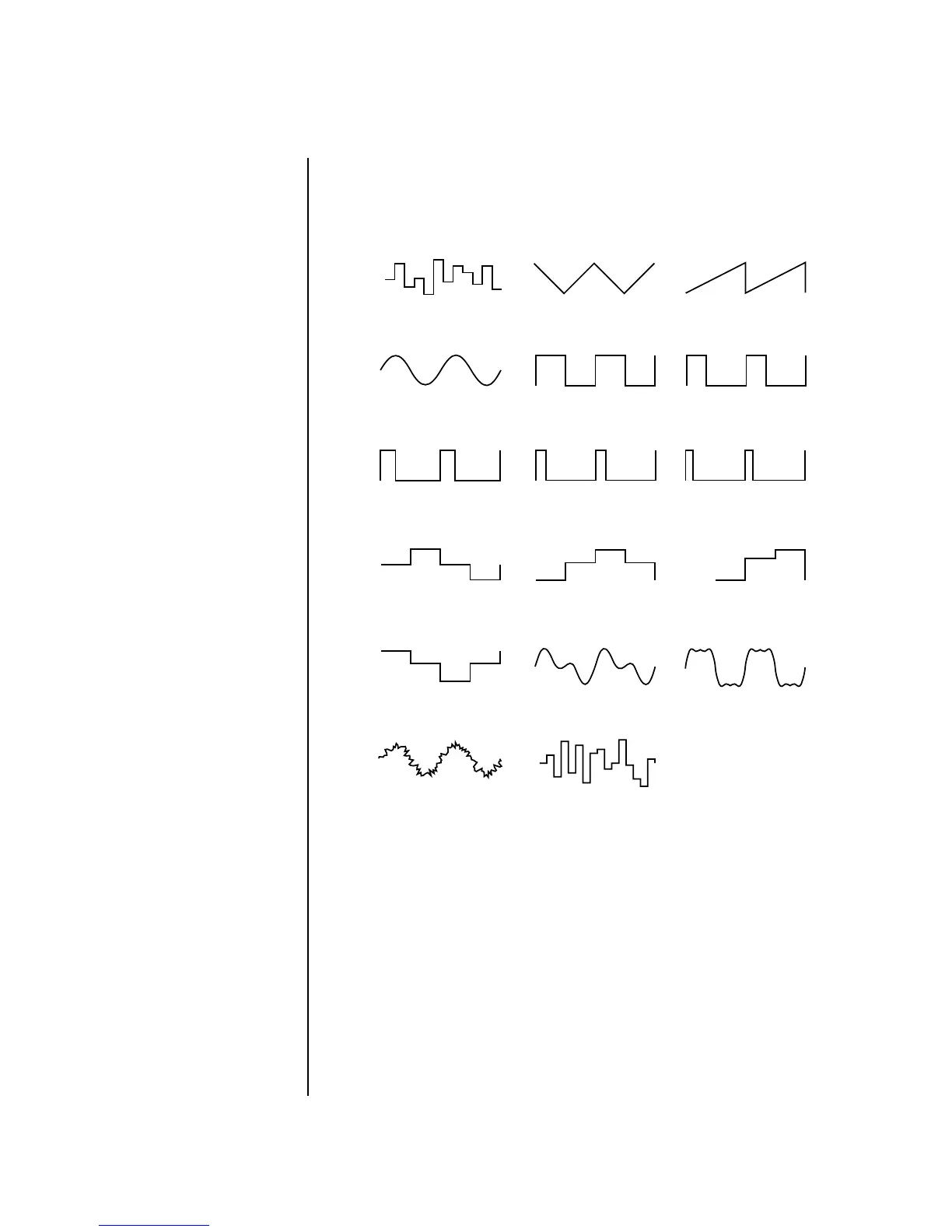
A Low Frequency Oscillator or LFO is simply a wave which repeats at a slow
rate. The Proteus 1000 has two multi-wave LFOs for each channel. The LFO
waveforms are shown in the following illustration.
By examining the diagram of the LFO waveforms, you can see how an LFO
affects a modulation destination. The shape of the waveform determines
the result. Suppose we are modulating the pitch of an instrument. The sine
wave looks smooth, and changes the pitch smoothly. The square wave
changes abruptly and abruptly changes from one pitch to another. The
sawtooth wave increases smoothly, then changes back abruptly. The
sound’s pitch follows the same course. Controlling the pitch of an
instrument is an easy way to hear the effects of the LFO waves.
Try combining the
Pattern LFOs, or controlling the
amount of one with another, or
combining them with the clock
divisors.
Like the Auxiliary Envelope, LFOs can be routed to control any real-time
function such as Pitch, Filter, Panning, or Volume. A common use for the
LFO is to control the pitch of the sound (LFO -> Pitch). This effect is called
vibrato and is an important performance effect. Many presets use this
routing with the modulation wheel controlling “how much” LFO
modulation is applied. Another common effect, Tremolo, is created by
controlling the volume of a sound with the LFO (LFO -> Volume).
Triangle
Square
Sine 1,2 Sine 1,3,5
Sine
Sawtooth
25% Pulse
33% Pulse
12% Pulse16% Pulse
Random
Pat: Fifth+Octave
C
C
G
Pat: Octaves
+ Octave
- Octave
C
F
G
Pat: Sus4 trip
C
G
A#
Pat: Neener
Hemi-quaver
Sine + Noise
LFO Tricks & Tips:
• The Random LFO wave is
truly random and is different
for each voice and layer.
• The Pattern (Pat) waveforms
will sound the same on
different layers and voices.
• Sine + Noise is very useful for
simulating trumpet and flute
vibrato.
★
When routing Hemi-quaver
to Pitch:
+38 = major scale
-38 = phrygian scale
+76 = whole tone scale
(+38) + (+76) = diminished
(two cords)
odd amount = S+H sound
Note: References to musical
intervals in the pattern LFO
shapes are with the LFO
routed to pitch and a
PatchCord amount of +38
.

 Loading...
Loading...