Proteus 1000 Operation Manual 73
Programming Basics
Modulation Processors
Dynamic
Filters
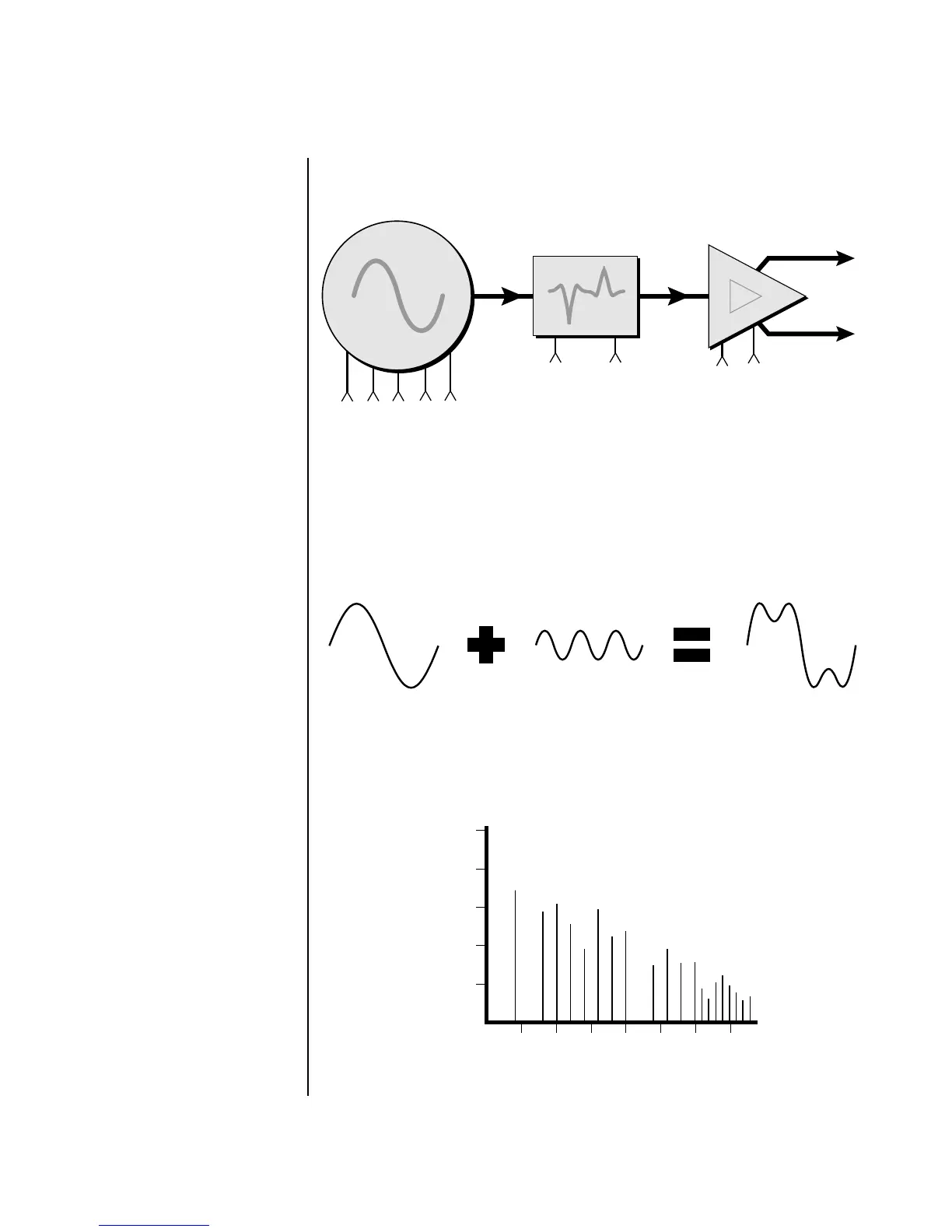
The block diagram of the Proteus 1000’s signal path is shown below.
To understand how a filter works, we need to understand what makes up a
sound wave. A sine wave is the simplest form of sound wave. Any
waveform, except a sine wave, can be analyzed as a mix of sine waves at
specific frequencies and amplitudes.
Any waveform can be analyzed as a mixture of sine waves.
One way to represent complex waveforms is to use a chart with frequency
on one axis and amplitude on the other. Each vertical line of the chart
represents one sine wave at a specific amplitude and frequency.
Instrument
Amp
L
Freq. VolQ
Retrigger
Pitch
Glide
Glide
Start Offset
Pan
Z-Plane
Filter
20
40
60
80
100
40 80 160 360 720 1440 2880
Frequency
...
Amplitude

 Loading...
Loading...